Design and Development of Elder Aid Assist (EASA) for Elderly Support and Automation
IoT-Based Autonomous Robot Car for Remote Patient Monitoring and Facility Management in Hospitals
Prototype for Surface Waste Collection System in Water Bodies
Design of Smart Ventilator System for Emergency Conditions
Design and Evaluation of a USB Isolator for Embedded Product
Diagnosis of Air-Gap Eccentricity Fault for Inverter Driven Induction Motor Drives in the Transient Condition
Modelling and Simulation Study of a Helicopter with an External Slung Load System
Comparative Study of Single Phase Power Inverters Based on Efficiency and Harmonic Analysis
LabVIEW Based Design and Analysis of Fuzzy Logic, Sliding Mode and PID Controllers for Level Control in Split Range Plant
Trichotomous Exploratory Data Analysis [Tri–EDA]: A Post Hoc Visual Statistical Cumulative Data Analysis Instrument Designed to Present the Outcomes of Trichotomous Investigative Models
This paper presents a review and analysis of the popular controller design techniques applied to develop control law for helicopters. The control problem has been tackled using different approaches ranging from Proportional Integral Derivative (PID) control, to H∞ robust control. The review of the popular controller design methods evidenced that the helicopter control is still a very active research area and is mainly motivated by the factor that the current control methods cannot provide full satisfaction to the desired design requirements on flight handling quality, stability, and robustness, etc.
This paper presents an innovative digital instrument, that uses the novel “Trichotomous Exploratory Data Analysis” [or “Tri–EDA”] as an alternative or supportive research model for traditional confirmatory and probability-based Bayesian statistical analyses. This research adds to the publication entitled, “Introducing Tri–Factor Analysis: A Model and Statistical Test of Performance, Efficacy, and Content for Electronics and Digital Learning Ecosystems” published in i-manager’s Journal on Electronics Engineering. This narrative provides an epistemological rational for the use of “Exploratory Data Analysis” statistical analytical models for the in–depth analysis of the transformative process of qualitative data into quantitative outcomes through the Tri–Squared Test first introduced in i-manager’s Journal on Mathematics, and further detailed in i-manager’s Journal on Educational Technology, Journal on School Educational Technology, and in Journal on Educational Psychology. Tri–Exploratory Data Analysis (Tri–EDA) is a series of graphical and visual statistical models that are a part of the Tri–Squared Calculator © created, designed, and developed by the author to report Tri–Squared Test outcomes and check the validity and reliability of Tri–Squared Test results. This is a novel approach to advanced statistical Tri–Squared reporting, adds considerable merit and value to the mixed methods approach of the trichotomous research design (that intrinsically involves the holistic combination and comparison of qualitative and quantitative data outcomes).
Design of Proportional Integral Derivative (PID) controllers for Unstable Second Order systems Plus Time Delay (USOPTD) with/without a zero using equating coefficient method is proposed in this paper. The method is based on equating the corresponding coefficients of s , s2 , s3 of the numerator of the closed loop transfer function for servo problem to α1 ,α2 , α3 times that of the denominator. The time delay term in the denominator of the closed loop transfer function is written as, 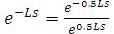 and it is expanded using Taylor series expansion upto four terms both in the numerator and denominator.This makes the numerator and denominator as polynomial of s. The time delay term in the numerator shifts the response on time axis and is not considered in the design problem. By equating the corresponding coefficients of s, s2 and s3 in the numerator with α1 , α2 , and α3 times that of the denominator; three linear equations are formulated and solved for the PID controller parameters. In the proposed work, the coefficients α1 , α2 , and α3 are obtained by minimizing Integral Time weighted Absolute Error (ITAE) for servo problem using fminunc of Matlab. Simulation results on various transfer function models and on the nonlinear model equations of jacketed CSTR (Continuous Stirred Tank Reactor) carrying out first order exothermic reaction are given to demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method. The smooth functioning of the controller is expressed interms of total variation. The controller performance is expressed in terms of ITAE. Nominal control performance of the proposed method is better than the existing methods.
and it is expanded using Taylor series expansion upto four terms both in the numerator and denominator.This makes the numerator and denominator as polynomial of s. The time delay term in the numerator shifts the response on time axis and is not considered in the design problem. By equating the corresponding coefficients of s, s2 and s3 in the numerator with α1 , α2 , and α3 times that of the denominator; three linear equations are formulated and solved for the PID controller parameters. In the proposed work, the coefficients α1 , α2 , and α3 are obtained by minimizing Integral Time weighted Absolute Error (ITAE) for servo problem using fminunc of Matlab. Simulation results on various transfer function models and on the nonlinear model equations of jacketed CSTR (Continuous Stirred Tank Reactor) carrying out first order exothermic reaction are given to demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method. The smooth functioning of the controller is expressed interms of total variation. The controller performance is expressed in terms of ITAE. Nominal control performance of the proposed method is better than the existing methods.
For most of the Industrial and pharmaceutical applications precise level control of tanks are necessary. When precise control of level is achieved much good quality of product can be yielded. To achieve better results it is needed, to implement a robust controller than conventional PID controller. In this paper a Split-Range Setup is prototyped and is used to control level in a tank. With this split-range setup the following controllers such as PID Controller, Fuzzy Logic Controller and Sliding Mode Controller (SMC) were designed and implemented. The whole control is programmed and implemented in LabVIEW (Laboratory Virtual Instrument Workbench) software. This software is based on graphical programming technique. By application of these controllers the best suited one is suggested considering the characteristics such as time taken to reach the setpoint, Settling time, peak overshoot etc.
This paper brings a whole new spectrum of light on Total Safety Management (TMS) philosophy and the evolution of TSM concept from a system perspective in an electronic components manufacturing industry. The traditional method of safety management employed in the industry was not productive in the context of organizational performance. In order to boost up the organizational performance, the establishment of TSM culture is viewed and focused. The functional content of the TSM model with its theoretical framework was discussed and the basic elemental features of TSM are highlighted in this paper. The components of TSM and the implementation steps are practically carried out, executed and fulfilled in the industry. Since the probability of occurrence of a fatal accidents are relatively less in this type of industries, TSM leadership communication and TSM training itself can influence the system to ensure the safety standards and keep down the incident rates thereby achieving the required safety performance. Finally, an impact study and evolution of TSM in the industry are discussed and recommendations/suggestions were given to the management safety professionals. The accident numbers are declining under the action of TSM in the industry.