 |
i-manager's Journal on School Educational Technology |
View PDF |
|||
| Volume :11 | No :3 | Issue :-2016 | Pages :10-17 | ||
Perceptual Learning styles are different ways in which people process the information in the course of learning, intimately involved in producing more effective response stimuli. The objective of the study was to find out the correlation between the variables of Perceptual learning style in total and with its dimensions to Academic achievement. Population of the study includes all students studying in High Schools of Kanyakumari District. Samples of the study were 328 students who were studying in various High Schools located in Kanyakumari District. The tool adopted here was ‘The Learning Styles Scale’ developed by the Investigator herself. Statistical techniques involved here were ‘t-test’ and ‘Pearson's Product Moment coefficient of correlation’. The findings of the study revealed that, perceptual styles of learning were greater for Female and Tamil medium students than that of their counterparts. Also from correlation, it was revealed that, the perceptual learning styles have a high correlation with the academic achievement of students. So, educators need to recognize different modes of learning and had to adopt different approaches to teaching, that enable students to adopt different learning styles to learn effectively. This means that, teaching needs to be designed to include different learning opportunities and appropriate assessments to ensure that, the learning is accessible to the largest number of students. The teachers must be persons who are capable for applying a mix of teaching approaches to the classroom and in planning the learning opportunities for students which should benefit the maximum numbers of students, thereby develop our Mother India.
Perceptual learning is the means by which learners extract information from their surroundings through the use of their five senses. Individuals have different 'pathways' that are specific to them. When information enters that 'pathway' the information is retained in short term memory. Repeated exposure and use promote retention in long term memory. Learning styles is a term used to explain different ways in which people process the information in the course of learning. “Learning style is the way, a person processes, internalizes and studies new and challenging material. Students' performance may be related to learning preferences or styles as learners” (Begam Binti Abdul Kadir, 2013). All persons differ each other in learning styles and techniques. Learning style refers to an individual's characteristic way to respond to certain forces in the instructional environment. Learning style according to Reid (1995) refers to an “individual's natural, habitual and preferred way of absorbing, processing and retaining new information and skills”. It is the uniqueness of how each learner receives and processes new information through their senses. Learning style is also defined as those Educational conditions under which a student is more likely to learn. Keefe (1979) defines learning styles as “the composite of characteristic cognitive, affective and physiological factors that serve as relatively stable indicators of how a learner perceives, interacts with and responds to the learning environment.” Other phrases like perceptual styles, learning modalities, and learning preferences are used interchangeable with learning style. Thus, learning styles are not really concerned with what learners learn; but, rather how they prefer to learn.
Perceptual learning is the effects of past experience on sensory perceptions. Perceptual learning styles are the means by which, learners extract information from their surroundings through the use of their five senses. An organism's readiness to learn is of primary importance to its survival, and this readiness depends largely on its perceptual skills. Perceptual skills are intimately involved in producing more effective response stimuli. The three main assumptions of perceptual learning styles are (1) The concept of separate, clearly defined modifies, (2) The ideal of matching instruction, and (3) The use of instruments to identify individual differences should be understood in more complex ways than is often presented in writings on the topic.
Learning styles are pragmatic manifestations of intelligences operating in natural contexts (Armstrong, S. & Mahmud, A. 2008). Students have preferences to learning and they perceive information differently. Some students get information more from external (sensory) input, and others depend more on internal (sights, sounds, physical sensations and intuitive) input. They have different insights and hunches, and view possibilities differently. Their external information is most effectively perceived in different ways as well, for example, visually (pictures, diagrams, graphs, demonstrations) as opposed to auditory (words and sounds). Students also prefer to process information differently. It may be actively (through engagement in physical activity or discussion) or reflectively (through introspection). In the end, it comes down to how well a person progresses toward understanding: sequentially (in continual steps) or globally (in large jumps). It is important for a student to recognize their own learning preferences to achieve in their subjects. This supports in the study of She (2005) that, the students learn better and enjoy their learning activities more, when the teaching style closely matches their learning styles. These learning styles should have to be co-ordinated with the information collected through their visual, auditory and kinesthetic through which they send, receive and store information (James and Gardner,1995). According to the learning style of a student, if resources were prepared by the teachers, it had an influence in the student's achievements, attitudes, empathy and transfer of knowledge (Farks, 2003). This idea was supported by Zapalska and Dabb (2002) by stating that, the information absorption and retention capacity of a student depends on the learning material provided by the teachers which results in better academic achievement of the student.
Learning style is an individual's natural or habitual pattern of acquiring and processing information in learning situation. Students enter in classrooms with a wide range of background knowledge, experiences, cognitive abilities and dispositions. These dispositions create varied orientation and learning experiences to students (Saxeena, 2012). The way in which the student approaches the learning tasks and the behaviour in learning situations determine their learning style. It is pointed out that, the learning style of an individual has relation to factors such as prior learning experiences, openness to interpersonal and intra-personal information, physical facilities, and learning environment. All the students do not process incoming information in the same way. Students have varying learning styles and, no single teaching styles and no single teaching style can fulfill all students' needs. A students learning styles has to do with the way he or she process information in order to learn it and then apply it. As it also contributes towards academic achievement, it was decided to study about the different learning styles of High Schools students. By understanding different learning styles, teacher may gain insight into ways of making academic information more accessible to our diverse needs of learners. While going through various Journals, Books etc., it came to the knowledge that, there are few studies related to perceptual learning styles and academic achievement directly on High School students. Hema Latha (2013) conducted a study on “Learning Styles and their Influence on Academic Achievement”. In the study conducted by Mehrdad & Ahghar (2012) “learning Styles and Learning Strategies of Left Handed EFL Students” aimed at investigating whether differences in the brain dominance is reflected in the learning style and therefore, learning strategy differences between left hand and right hand EFL students were studied and found there is no influence in this brain dominance. Also, Shikha and Parveen (2014) conducted a study on “Gender Variations on Learning Styles of Secondary School Students”. From the study of Lethaby, Carol Harries, Patricia (2016), it was found that accommodating sensory learning styles improves learning and have influenced their teaching. Shrivastava (2002) in his study of “learning Styles of Secondary School Students with Scientific Attitude and Their Achievement in Science” found that, most popular leaning styles of the students have accommodative learning style and second popular is the convergent learning styles. Cano & Garton (1994) in his study “The Relationship Between Agriculture Pre-service Teachers Learning Styles and Performance in a Method of Teaching Agriculture Course” suggested that, learning styles can enhance academic performance in several respects. So, the investigator selected the problem to study the perceptual learning styles and it's relation to academic achievement of high school students to contribute in the field of education.
The Problem entitled as “the Role of Perceptual Learning Styles on Academic Achievement Among High School Students”
Learning styles are the “composite of characteristic cognitive, affective and physiological factors that serve as relatively stable indicators of how a learner perceives, interacts with and responds to the learning environment.” stated by Keefe (1979).
Learning style is “ the way in which each learner begins to concentrate on process internalize, remember and retain new and difficult academic information” given by Dunn & Dunn (1993).
Academic achievement is defined as “a measure of knowledge gained in formal education usually indicated by test score”.
In the present study, the investigator took the score of students in midterm marks from the examination conducted by the State Government.
The students who are studying in classes VIII are recognized as High School Students whose age ranges between 12-13 years.
1) To find out whether there is any difference in the Perceptual learning style of high school students with respect to gender in the dimensions such as Visual learning style, Auditory learning style, Kinesthetic learning style and in total.
2) To find out whether there is any difference in the Academic achievement of high school students with respect to gender.
3) To find out whether there is any difference in the Perceptual learning style of high school students with respect to the medium of instruction in the dimensions such as Visual learning style, Auditory learning style, Kinesthetic learning style and in total.
4) To find out whether there is any difference in the Academic achievement of high school students with respect to the medium of instruction.
5) To find out the correlation between the variables of Perceptual learning style in total and with its dimensions to academic achievement.
H1 : There is no significant difference in the mean scores of Perceptual learning style of high school students with respect to gender in the dimensions such as Visual learning style, Auditory learning style, Kinesthetic learning style and in total.
H2 : There is no significant difference in the mean scores of Academic achievement of high school students with respect to gender.
H3 : There is no significant difference in the mean scores of Perceptual learning style of high school students with respect to the medium of instruction in the dimensions such as Visual learning style, Auditory learning style, Kinesthetic learning style and in total.
H4 : There is no significant difference in the mean scores of Academic achievement of high school students with respect to the medium of instruction.
H5 : There is no significant correlation between the variables in total, and with its dimensions to academic achievement.
Survey method was adopted in the study. A survey method means a pre-determined set of questions are given to a sample to collect information about how people think and act. Here, survey method is conducted by using Learning Style Scale which consists of pre-determined set of questions that is given to a representative sample.
Population means the entire group of people or objects to which the researcher wishes to generalize the study findings.
The population here consists of the High School students of various High Schools located in Kanyakumari District.
A sample is one that is representative of the larger population of interest. A researcher can describe the attitudes of the population from which, the sample was drawn.
The investigator here selected 328 students who are studying in various high schools located in Tirunelveli district by random sampling method.
Tools are the sources for collecting information from the samples. Learning Styles Scale was developed by the investigator herself.
The data were analyzed using the following statistical techniques.
(i) t-test (t)
(ii) Pearson's Product Moment Coefficient of Correlation (r)
Hypothesis- 1: There is no significant difference in the mean scores of Perceptual learning style of high school students with respect to gender in the dimensions such as Visual learning style, Auditory learning style, Kinesthetic learning style and in total.
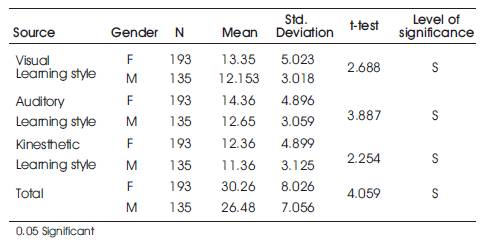
Table 1. Data and Results of t-test: Comparison of Male and Female Students in their Dimensions of Perceptual Learning Style and in Total
From Table 1, it was found that, the calculated t- values were greater than that of table value 1.97 at 0.05 level of significance. Therefore, on the basis of result, hypothesis -1 “There is no significant difference in the mean scores of Perceptual learning style of high school students with respect to gender in the dimensions such as Visual learning style, Auditory learning style, Kinesthetic learning style and in total” was rejected. From the mean value, it was found that, female students showed more perceptual learning styles than that of male students with respect to dimensions such as visual learning style, auditory learning style, kinesthetic learning style and in total.
Hypothesis- 2: There is no significant difference in the mean scores of Academic achievement of high school students with respect to gender.
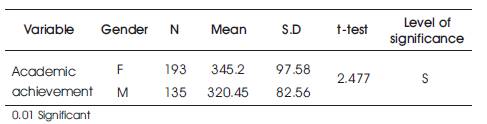
Table 2. Data and Results of t-test: Comparison of Male and Female Students in their Academic Achievement
From Table 2, it was shown that, the calculated t value was greater than the table value 1.97 at 0.01 level of significance. Therefore, on the basis of the result, Hypothesis- 2 “There is no significant difference in the mean scores of Academic achievement of high school students with respect to gender” was rejected. From the mean value, it was found that, female students showed more academic achievement than that of male students.
Hypothesis- 3: There is no significant difference in the mean scores of Perceptual learning style of high school students with respect to medium of instruction in the dimensions such as Visual learning style, Auditory learning style and Kinesthetic learning style in total.
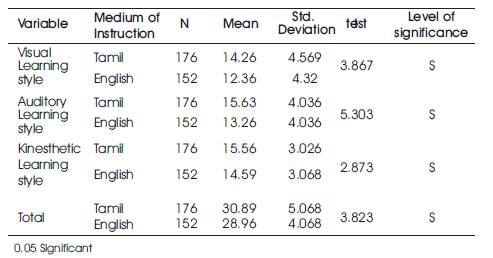
Table 3. Data and Results pf T-test: Comparison pf Tamil and English Medium Students in their Dimensions of Perceptual Learning Style and in Total
From Table 3, it was showed that, the t- value was greater than the table value 1.97, at 0.05 level of significance. Therefore, on the basis of result, Hypothesis- 3, “There is no significant difference in the mean scores of Perceptual learning style of high school students with respect to the medium of instruction in the dimensions such as Visual learning style, Auditory learning style and Kinesthetic learning style in total” was rejected. From the mean value, it was found that, Tamil medium students have more Perceptual learning style than that of English medium students in the dimensions such as visual learning style, auditory learning style, kinesthetic learning style and in total.
Hypothesis- 4: There is no significant difference in the mean scores of Academic achievement of high school students with respect to the medium of instruction.
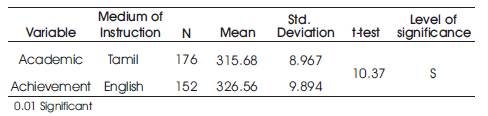
Table 4. Data and results of t-test: comparison of Tamil and English medium in their Academic achievement
From Table 4, it was shown that, the t value was greater than that of the table value 1.97 at 0.05 level of significance. Therefore on the basis of the result, Hypothesis - 4 “There is no significant difference in the mean scores of Academic achievement of high school students with respect to medium of instruction” was rejected. From the mean value, it was found that English medium students showed more academic achievement than that of Tamil medium students.
Hypothesis- 5: There is no significant correlation between the variables in total and with its dimensions to academic achievement.
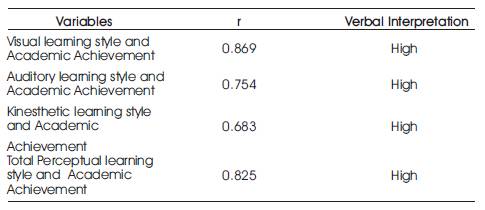
Table 5. Perceptual Learning Style and Academic Achievement
From Table 5, it was shown that, the Visual learning style and Academic achievement, Auditory learning style and Academic achievement, Kinesthetic learning style and Academic achievement and total Perceptual learning style and Academic achievement have positive high correlation.
From Table 1, it was found that, the calculated t- values for visual, auditory, kinesthetic learning styles and in total were 2.688, 3.887, 2.254 and 4.059 respectively, and were greater than that of table value 1.97 at 0.05 level of significance. Therefore, on the basis of result, Hypothesis -1 “There is no significant difference in the mean scores of Perceptual learning style of high school students with respect to gender in the dimensions such as Visual learning style, Auditory learning style, Kinesthetic learning style and in total” was rejected. From the mean value, it was found that, female students showed more perceptual learning styles than that of male students with respect to dimensions such as visual learning style, auditory learning style, kinesthetic learning style and in total.
From Table 2, the calculated t value was 2.474 which was greater than the table value 1.97 at 0.01 level of significance. Therefore, on the basis of the result, hypothesis -2 “There is no significant difference in the mean scores of Academic achievement of high school students with respect to gender” was rejected. From the mean value, it was found that, female students showed more academic achievement than that of male students.
From Table 3, the calculated t- values were 3.867, 5.303, 2.873 and 3.823 respectively for Visual learning style, Auditory learning style, Kinesthetic learning style and in total which were greater than the table value 1.97, at 0.05 level of significance. Therefore, on the basis of result, Hypothesis- 3, “There is no significant difference in the mean scores of Perceptual learning style of high school students with respect to medium of instruction in the dimensions such as Visual learning style, Auditory learning style and Kinesthetic learning style in total” was rejected. From the mean value, it was found that, Tamil medium students have more Perceptual learning style than that of English medium students in the dimensions such as visual learning style, auditory learning style, kinesthetic learning style and in total.
From Table 4, it was showed that, the t value, 10.37 was greater than that of the table value 1.97 at 0.05 level of significance. Therefore on the basis of the result, Hypothesis– 4, “There is no significant difference in the mean scores of Academic achievement of high school students with respect to medium of instruction” was rejected. From the mean value, it was found that, English medium students showed more academic achievement than that of Tamil medium students.
From Table 5, it was showed the calculated r values were 0.869, 0.754, 0.683 and 0.825 for Visual learning style and Academic achievement, Auditory learning style and Academic achievement, Kinesthetic learning style and Academic achievement and total Perceptual learning style and Academic achievement respectively. This showed positive high correlation.
From the findings of the study, following implications are proposed by the researcher.
1) This study was delimited to 8 Standard students only.
2) The size of the sample was only 328 students.
3) Students from Kanyakumari district alone were selected as samples.
From the study it was noted that, perceptual styles of learning are greater for female and Tamil medium students than that of their counter parts. Also, from the part of correlation, it was revealed that the perceptual learning styles have a high correlation with the Academic achievement of students. This finding discloses that students have their own learning styles and senses they are utilizing for their learning process is highly individualistic and dynamic. Perceptual learning is the effect of past experience on sensory perceptions. Perceptual skills are intimately involved in producing more effective response stimuli. Educators need to recognize that, individuals will have particular modes of learning that are more dominant than others. Instructors need to adopt approaches to teaching that enable students who have different learning styles to learn effectively. This means that, teaching needs to be designed to include different learning opportunities and appropriate assessments to ensure that, the learning is accessible to the largest number of students. Applying a mix of teaching approaches to the classroom and in planning the learning opportunities for students should benefit the maximum numbers of students. Even the successful language development depends on the degree of understanding of one's own learning style and on choosing appropriate learning strategies that fit his or her learning style in Oxford (1990). By the appropriate learning strategy for the student according to their learning style, produces unimaginable results and multiple opportunities for the learner to become much more competent in learning (Rekha, 2012). The competency thus gained will motivate them to build self confidence and help them to develop themselves as a great success in their world.