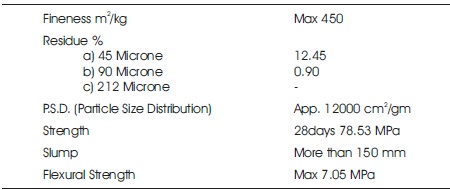
Table 1. Physical Properties of Alccofine
Black cotton soil that occupies nearly 20% of the area in India is a problematic soil. It is also called expansive soil or swelling soil, which have the tendency to increase in volume when water is present and decrease in volume when water is removed. The volume change may cause many problems in underconstruction structures. In India, the area covering the expansive soil is nearly 20% of the total area and includes almost the western Madhya Pradesh, parts of Rajasthan, Bundelkhand region in Uttar Pradesh and parts of Andhra Pradesh, Telangana and Karnataka. The swelling soil of India are commonly known by the name black cotton soil because of their color and for growing cotton. Annually waste of million tons are produced across the country, which leads to disposal problem as well as adds to health risks. Utilization of such industrial wastes and their subsidiary products as alternatives to construction materials may contribute to preservation of environmental and minimize their adverse effects on environment. In this present study, crumb rubber is used as the waste to combine with the soil so that the properties of black cotton soil were investigated in with addition of alccofine. The physical and index properties of soil which were already measured were compared with those of the experimental specimens (crumb rubber and alccofine).
Black soil is formed by the chemical weathering of rocks, such as Basalt, Gneiss, etc. Color of this soil ranges from dark brown to black. This soil is also called “Regur soil” because of its black color. The word "Regur" originates from the Latin "regurgitare", which means "to overflow". The Black soils are highly argillaceous having clay content of 40% to 60%. This soil is known for its color and suitability for growing cotton. The black soil at depth more than 1 meter is more suitable for growing cotton. It is also called expansive soil or swelling soil, which have the tendency to increase in volume when water is available and decrease in volume, if water is removed. These soils have very high capacity for holding water and poor drainage characteristics. It has low bearing capacity for construction of structures.
However, in most geotechnical projects, it is not possible to obtain a construction site that will meet the design requirements without ground modification. Therefore, it is necessary to modify the engineering properties of the native problematic soils to meet the design specifications. Nowadays, soft clays and organic soils can be improved to the civil engineering requirements. There are several methods to improve the soil capacity. Soil stabilization aims to increase the resistance by bonding the soil particles together and increasing resistance to softening by water through binding the soil particles together. Easiest stabilization methods are compaction and drainage. Soil stabilization can be achieved by different techniques, All these methods fall into two broad categories namely mechanical stabilization and chemical stabilization. As industrial wastes and their subsidiary products as alternatives to stabilizing additive may effectively contribute to environmental preservation and minimization of their adverse effects on environment. The stabilized soil have a relatively good properties as compared to the original soil.
Alccofine is a new generated, micro fine material having particle size much finer than other hydraulic materials being manufactured in India and many other countries. To enhance performance of concrete, alccofine has unique characteristics and due to it optimized particle size, distribution in soil stabilization in fresh and hardened stages is possible. The physical and chemical alccoline are shown in Tables 1 and 2, respectively. It can be used as a practical substitute for Silica Fume as it has an optimum particle size distribution not too coarse, not too finer either as per the results obtained by Count Micro fine products manufactured in the controlled conditions to produce optimized particle size distribution, which is its unique property. Alccofine is of two types namely alccofine SCM 1101 and alccofine grouting 1203 in low silica content in 1101 is also use for soil stabilization. The benefits of alccofine is to improve workable condition in soil stabilization in concrete increased flowability. Reduction in segregation can be observed in the mix. Alccofine used as mineral admixture in a concrete mix increases the initial strength of the concrete than the ordinary concrete. Alccofine is easy to use and can be added directly with cement as shown in Figure 1. The ultrafine particle present provides in it better and smooth surface finish.

Table 1. Physical Properties of Alccofine

Table 2. Chemical Properties of Alccofine

Figure 1. Alccofine
Worldwide growth of automobile industry and increased use of car has increased production of waste scrap tyres as well. Many researches carried out for the use of waste tyres in different applications of physical and chemical properties of crumb rubber are shown in Table 3. Scrap tyre is composed of ingredients that are nonbiodegradable in nature at ambient conditions. They usually produce environmental bed effects. The material is therefore used in concrete and other building products. it may cause reduction in the environmental costs of land filling and increase in landfill voids. Crumb rubber that is used on the replacement for sand, is manufactured by special mills in which huge rubbers are converted into smaller particles. In this procedure, different sizes of rubber particles may be produced depending on the kind of mills used as shown in Figure 2. According to the size of rubber particles, they are classified in meshes like 10 mesh, 20 mesh, 30 mesh, etc.

Table 3. Physical and Chemical Properties of Crumb Rubber

Figure 2. Crumb Rubber Powder
Talgotra and Sharma (2017) have researched on the stabilization of clayey soil with cement kiln dust and alccofine 1101. Earth has been utilized for working for a great many years all through the world traversing an assorted scope of atmospheres and societies. Earth itself is a multi-segment framework typically comprising of stones, sand, residue, mud, water and, close to the ground surface, natural humus. Auxiliary security of earth structures is kept up by the auxiliary trustworthiness of the sand and stone structure, by the pore filling limit of the sediment and most significantly, by the coupling characteristics of the earth, which are thus affected by the dampness substance of the dirt. Contrast and some building materials in earth can be considered to have a few disservices – it has generally low compressive quality, elasticity and scraped spot opposition. It might likewise lose a ton of its inflexibility in the nearness of water. It is exceptionally modest, generally accessible, naturally cordial, firmly connected to neighborhood societies and conventions and, with adroit development, can contribute altogether to the tasteful offer and client solace of structures.
Singh and Sharma (2018) have been conscious on Red Soil Stabilization using silica fumes and alccofine. The fundamental target of this examination work was to think about the designing attributes of red soil. The building conduct of remaining soils in the zone, got from the in-situ weathering and deterioration of parent shake, is controlled by certain physical attributes assigned as designing write mud alongside residue and fine sand. It has got its red shading because of the nearness of impressive amounts of iron oxide. It is less clayey and siltier in nature, and has low humus content. This dirt is acidic in nature and cannot hold dampness. The substance of supplements like nitrogen, phosphorous, and lime is little. Adjustment of soil utilizing bond or lime is settled. Their point here was to contemplate the impact on building properties of soil and its adjustment by utilizing Silica Fume (a modern waste) with Alccofine. Alccofine is the other progressive item created by Ambuja Cement for the adjustment purposes and to expand the quality of soil. In this examination, exploratory examinations are done to know the impact of various amount silica vapor with five Alccofine properties. Tropical and sub-tropical districts with hot, muggy climatic conditions have red soils in its most parts. It has been recommended that a mean yearly temperature of around 25 °C is required for their development, and in regular circumstances, there ought to be a happenstance of the warm and wet periods. The red soil likewise called as red earth contains kaolinite.
Sambyal and Sharma (2018) have utilized flyash and alccofine for efficient soil stabilization. The principle target of this examination work was to think about the designing attributes of earth soil. Territory in India are secured of million hectares of expansive soil. The property of these sweeping soils, as a rule, is that they are hard when in dry state, yet they lose the greater part of their quality when in wet state. In this procedure, expulsion or supplanting of the risky soil is done; substitution is finished by a superior quality material, or the dirt is treated with an added substance. In the present investigation, utilizing fly fiery debris got from Sesa, Sterlite, Jharsuguda, Odisha, adjustment of dark cotton soil got from Nagpur is endeavored. With different extents of this added substance, i.e. 10%, 20%, 30%, 40%, and half, far reaching soils is balanced out. Attributable to the way that fly fiery remains have no plastic property, pliancy record (PI) of earth fly slag blends demonstrate a decline in an incentive with expanding fly powder content. All in all, expansion of fly fiery remains brings about decline in pliancy of the far reaching soil, and increment in functionality by changing its grain estimate and colloidal response alccofine, which even in a little rate increment the quality and enhancing the building properties of extensive soils.
Dev and Sharma (2017) have researched stabilization of expansive soil with marble dust and alccofine. Far reaching or responsive soil is a dirt made transcendently out of earth. Earth experiences noteworthy volume change because of changes in the dirt dampness content. This volume change is acknowledged by swelling after wetting, furthermore, shrinkage after drying. Being built on sweeping soils, structures are every now and again inclined to extreme development caused by nonuniform soil dampness changes with subsequent breaking and harm identified with the mutilation. Precipitation and dissipation, cultivate watering, spilling water pipes, or tree root movement may trigger these dampness changes. In this study, an endeavor has been made to enhance the bearing limit of soil utilizing admixtures/Alternate materials.
Hambirao and Rakaraddi (2014) have studied soil stabilization using waste shredded rubber tyre chips. Development of building structures on frail or delicate soil is considered dangerous. Change of load bearing limit of the dirt might be embraced by variety of ground change strategies. In the present examination, destroyed elastic from squander has been picked as the fortification material and bond as restricting operator which was haphazardly included into the dirt at three unique rates of fiber content, i.e., 5%, 10%, and 15% by weight of soil. The examples were subjected to California bearing proportion and unconfined pressure tests. The tests have unmistakably demonstrated a noteworthy change in the shear quality and bearing limit parameters of the examined soil. The outcomes acquired are contrasted and unreinforced tests are drawn towards the convenience and adequacy of fiber fortification as a trade for profound or pontoon establishment and on asphalt subgrade soil as a practical approach. The low quality and high compressible delicate mud soils were found to enhance by expansion of destroyed elastic and concrete. It can be inferred that destroyed elastic fiber can be considered as a decent earth fortification material.
Sarvade and Shet (2012) have examined geotechnical properties of problem clay stabilized with Crumbed Rubber Powder. In this paper, the impact of 5%, 10%, 15%, 20%, and 25% crub rubber powder with 1%, 3%, 5% of concrete and lime include to improve the properties of mud soil. They utilize the CRP with lime and afterward after with bond and think about the test outcomes, which is the best to bear limit of risky mud soil. There is diminishment in fluid point of confinement, versatility list and dry thickness of the dirt when 1% to 5% expanding of the lime/bond. There was increment in dampness content with increment in 1% to 5% expansion of lime/bond.
Kokila (2017) had examined the test investigation on soil stabilization using rubber crumb on expansive soil. In view of the investigations did on soil with expanding level of elastic scraps powder (5%, 10%, and 15%) alongside 3% of lime as a steady the accompanying perceptions were reasoned that Increased CBR esteem with expanding level of elastic pieces at 3% of lime as consistent. Along these lines expanded California Bearing Ratio (CBR) esteem leads to decreased asphalt thickness and expanded soundness. Ideal to dampness substance and most extreme dry thickness increment with expanding level of elastic morsels powder.
In this method, to secure desired property of soil, different gradation of soils are mixed together by using different types of rollers. This process is done at site from where it can be easily transported.
In physical alteration, granular material is mixed with the expansive clay to minimize heave. The different materials like binding material or any other materials are added for the purpose of binding the soil particles.
In chemical stabilization, different type of chemicals are used for the stabilization of soil.
Chemical that have been successfully used are
As per Indian standard, Specific gravity of a substance is the ratio between the mass of any substance of a definite volume divided by mass of equal volume of water. It denotes the number of times that substance is heavier than water. Different types of soil have different specific gravities are shown in Table 4.
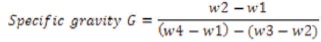
where,
W1 - Weight of bottle in gm
W2 - Weight of bottle + Dry soil in gm
W3 - Weight of bottle + Soil + Water
W4 - Weight of bottle + Water

Table 4. SP Gravity of Different Soil
As per IS, Liquid limit is defined as the moisture content at which soil begins to behave as a liquid material and starts to flow. It is important to classify the soil. Different soils have different liquid limits. Also, the plastic limit is used to determine its plasticity index. Liquid limit is used to know the stress history and general properties of the soil met with construction. From the results of liquid limit, the compression index may be estimated. The compression index value will help us in settlement analysis. If the natural moisture content of soil is closer to liquid limit, the soil can be considered as soft, if the moisture content is lesser than liquids limit, the soil is brittle and stiffer.
According to soil mechanics, Plastic limit is defined as the moisture content at which the soil can be rolled into the threads one eighth inch in the diameter without the soil breaking into pieces. This is determined by rolling out soil till its diameter reaches approximately 3 mm and measuring the water content for the soil, which crumbles on reaching this diameter.
Plasticity index (Ip) is calculated with the help of liquid limit p and the plastic limit.
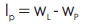
where,
wL - Liquid limit
wP - Plastic limit
According to soil mechanics, as the soil loses moisture either in its natural environment or by artificial means in laboratory, it changes from liquid state to plastic state, i.e. from semi-solid state to solid state. The volume is also reduced by the decrease in water content. But, at a particular limit, the moisture reduction causes no further volume change. A shrinkage limit test gives a quantitative indication of how much moisture can change before any significant volume change and to also indication of change in volume. The shrinkage limit is useful in areas where soils undergo large volume changes when going through wet and dry cycles (e.g. earth dams).
As per Indian Standard, the Compaction test of soil is carried out to understand compaction characteristics of different soils with change in moisture content. In this test, the soil at optimal moisture content becomes most dense and achieves its maximum dry density by removal of air voids. The results obtained from this test will be helpful in increasing the bearing capacity of foundations, decreasing the undesirable settlement of structures, Controlling undesirable volume changes, reduction in hydraulic conductivity, and increasing the stability of slope sand.
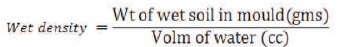
Dry density = {(1+moisture content)*wet density}/100
According to Indian Standard, the unconfined compressive strength (qu) is the compressive stress at which the remoulded cylindrical soil sample fails under simple compressive test. Due to the conditions it is not always possible to conduct the bearing capacity test in the field, therefore it is cheaper to take the undisturbed soil sample and test its strength in the laboratory and also to choose the best material for the embankment. Under these conditions, it is easy to perform the unconfined compression test on undisturbed and remoulded soil sample.

As per IS, the California Bearing Ratio test is the penetration test. it is used for the evaluation of subgrade strength of roads and pavements. The results obtained by these tests are used with the empirical curves to determine the thickness of pavement and its component layers. This method is mostly used for the design of flexible pavement. It is the ratio of force per unit area required to penetrate a soil mass with standard circular piston at the rate of 1.25 mm/min to that required for the corresponding penetration of a standard material.
The expansive soil used in the investigation has been collected from Astan near Bardoli, Gujarat. Laboratory investigation has been carried out to determine the engineering properties of soil with varying percentage of Crumb Rubber and alccofine. It is not preferable to compact expansive soil under heavy compaction conditions as it results in higher swelling. So, compaction characteristics of the soil have been evaluated from the light compaction test preferred by IS: 2720 (Part-7) – 1983. Unconfined Compressive Test (UCS) is determined on soil samples passing through 425 micron IS sieve as to know the potential effect of 5%, 10%, 15% of Crumb Rubber powder on strength and shrinkage characteristics of soil. Free swell index has been determined as the ratio of difference of the volume of pure soil using the various percentage of Crumb Rubber in distilled water and in kerosene, expressed as percentage. The specific gravity of the fresh soil has been determined. In this work, the 5%, 10%, 15% of Crumb Rubber filler material to evaluated as potential stabilizer in enhancing strength and volume change properties of soft, organic, highly plastic, and expansive soil applications.
Preparation of soil sample for proctor's compaction test was done as per IS:2720 (Part-8)-1983. The comparative study chart of Maximum Dry Density (MDD) and Optimum Moisture Content (OMC) with 5%, 10%, and 15% of crumb rubber powder and 2.5% alccofine is shown in Figures 3 and 4.
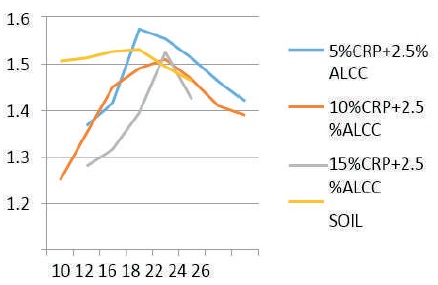
Figure 3. MDD vs. OMC of Samples
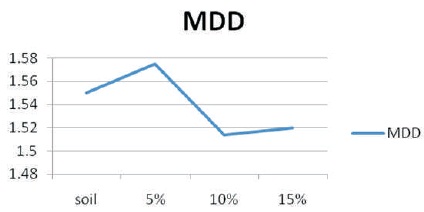
Figure 4. MDD Comparison of Soil Samples
The Maximum Dry Density (MDD) and Optimum Moisture Content (OMC) of regur soil is found as 1.55 gm/cm3 and 22.1%. The maximum dry density of soil mixed with 2.5% Alcofine and 5% Crumb Rubber was found as 1.575 gm/cm3, which represents that there is increase in maximum dry density at OMC 16%, 2.5% Alcofine and 10% Crumb Rubber was found as 1.514 gm/cm3 at 18% OMC, and 2.5% Alcofine, and 15% Crumb Rubber was found as 1.52 gm/cm3 at 18% OMC.
The UCS test was conducted on 100% expansive soil, soil + 5% crp + 2.5% alccofine, soil + 10% crp + 2.5% alccofine, soil + 15% crp + 2.5% alccofine using unconfined compression test machine as per the procedures laid down in IS:2720(part-10)-1991.
The UCS value of soil mixed with 5% of crp with 2.5% of alccofine was found as 0.31, 10% of crp with 2.5% of alccofine was found as 0.28, 15% crp with 2.5% of alccofine was found as 0.148.
The load settlement curve has been plotted for 100% soil, soil + 2.5% alcofine + 5% crumb rubber, soil + 2.5% alcofine + 10% crumb rubber, soil + 2.5% alccofine + 15% crumb rubber. To calculate the CBR value, the graph of standard load of CBR value has been referred in Figure 5. The comparison of CBR graph with different percentage of crumb rubber powder and alccofine is shown in the comparative chart of load vs. settlement.
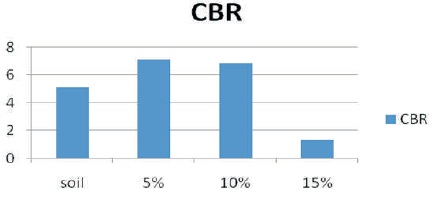
Figure 5. CBR Comparison of Different Samples
The UCS test was conducted on 100% expansive soil, soil + 5% crp + 2.5% alccofine, soil + 10% crp + 2.5% alccofine, soil + 15% crp + 2.5% alccofine using unconfined compression test machine as per the procedures laid down in IS: 2720 (part-10)-1991 are shown in Figure 7. The UCS value of soil mixed with 5% of crp with 2.5% of alccofine was found as 0.31, 10% of crp with 2.5% of alccofine was found as 0.28, 15% crp with 2.5% of alccofine was found as 0.148 is shown in Figure 8. The summary of experimental works is given in Table 5.
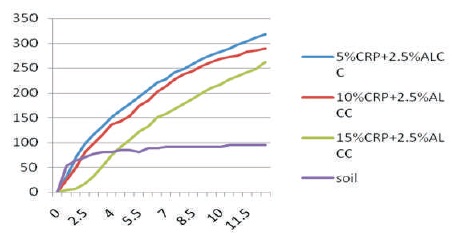
Figure 6. Load vs Penetration Graph for CBR Test
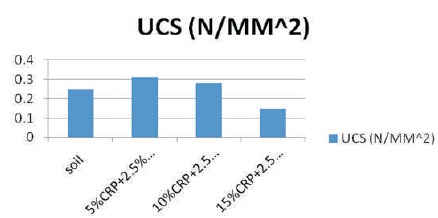
Figure 7. UCS Comparison of Different Samples
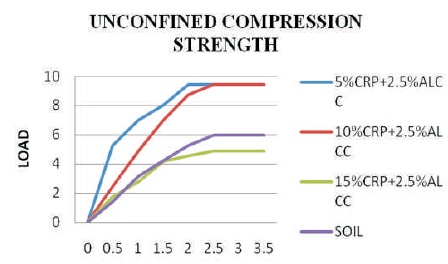
Figure 8. Load vs Penetration Graph for UCS Test
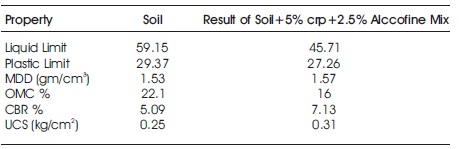
Table 5. Summary of Experimental Work
From this research work, it can be concluded that by using 5% crumb rubber powder and 2.5% alccofine, soil may be stabilized because the maximum dry density of soil is obtained at optimum moisture content so we can easily compact the soil on field at MDD and achieve a maximum strength due to good bonding between particles of soil.