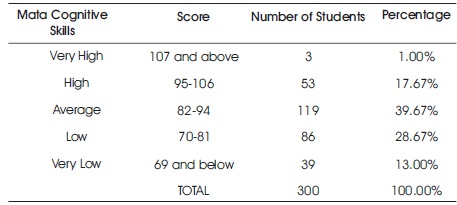
Table 1. Levels of Meta Cognitive Skills among Senior Secondary School Students
The existing research was carried out to study the meta cognitive skills among the students of school in Bhutan. This study was basically descriptive method used to acquire important and accurate information. The objective is to find the levels, gender, stream, and locality related differences in meta cognitive skills. The investigator selected 300 senior secondary school students through convenient sampling technique. For the collection of data the investigator used meta cognitive skills, tool developed by Dr. Punita Govil. The researcher used mean score, standard deviation, percentage, t-test, Pie charts, and bar graphs as statistical techniques. The result showed that 1% senior secondary school students had meta cognitive skills very high. 17.66% senior secondary school students belong to high level meta cognitive skills. 39.66% senior secondary school students had average level of meta cognitive skills. 28.66% senior secondary school students belong to low level mega cognitive skills. 13% senior secondary school students belong to very low level meta cognitive skills.
Meta cognition is way of thinking about thinking or knowing about knowing. The “meta” comes from the root of the word and it denote as beyond. The concept of meta cognitive skill has two components which are called as knowledge of cognitive processes and other is called as regulation of cognition. Knowledge of cognitive skill usually deals with all types of concept such as self-concepts and even care and study routines. Rule of thinking skill progressions which deal all type of instruments which we regulate thinking processes, which included planning, orientation, monitoring, testing, reflecting, repairing, and evaluating. Wells (1999) conducted a study on cognition and worry: A cognition model of general anxiety disorder. The researcher worked on meta-Cognitive skills on the factors of related with worry. Meta-Cognition is classified into mechanisms which implicated to relevant and other types of disturbing thought such as obsessions, at the same time the content of meta-Cognation is use of worry as coping strategy for the different from that in generalized anxiety disorder. Mokhtari and Reichard (2002) assessed students' meta cognitive awareness of reading strategies. The author described the progress and confirmation of the new self-report tool of reading strategies inventory of the meta cognitive, which is basically planned to assess adolescent. Under Meta Cognitive skills, Problem solving, support reading, and Global reading were three important Strategies for academic reading as well as school related materials. Those were three strategies of subscales or factors. Veenman, Kok, and Blöte (2005) found out that without hints, meta cognitive skillfulness is the most important forward planner of preliminary learners, at the same time intelligence also enter the regression after the per sensation of hints. Meta cognitive skills can be appeared by combining of intellectual of the persons. Kim, Park, and Baek (2009) conducted a study on using metacognitive strategies in game-based learning. The researcher found out the results involved that a marketable playing game in combination by meta-cognitive tactics has an ample positive impact to increase students in terms of learning and by playing game, which help them involved actively. However, activities like talking and observation even demonstrating are efficient and effective than lettering activities, whereby progression of the children's accomplishments in scholarship. Shamir, Mevarech, and Gida (2009) found significant differences between Meta cognition behavior in individual learning and paired learning. Ader and Erktin (2009) constructed Meta Cognition tool for assessing talented pre adolescents, it was basically divided into two types first phase and second phase. Inventory of meta cognition was developed four subscales as per the dimensions. It was included as evaluation, self-checking, awareness, and cognitive strategies, which were investigated that the first phase were included high internal consistency and adequate construct inventory. The second phase was correlation of meta cognation reading with understanding, achievement, and aptitude. The researcher concluded that it has significant and positive correlated with science course in terms of meta cognition and awareness. Johnson, Archibald, and Tenenbam (2010) found that students experienced extraneous cognitive consignment, which reduces their early presentation during their instructional actions. Nevertheless, selection of interventions had unhelpful on students' act and some inventions had shown positive late initial effects on students' performance. Liliana and Lavinia (2011) found that in general, both boys and girls utilized their meta cognitive skill in effective way of learning. The authors found out significant differences between the genders. The result was exclusively on the following dimensions, the performance of prior knowledge planning, problem solving, weaknesses and strengths of intellectual about one's own knowledge, the process of different strategies, and monitoring of learning. Roll, Aleven, McLaren and Koedinger (2011) found that meta cognitive feedback helped students to acquire better skills to transfer to learn innovative domain level content during the intervention, rather than help or looking for support was found no longer in effect. Another researcher Ahmadi in 2012 investigated that precise or specific instruction of meta-cognitive skills learnt more by using different strategies for intermediate students shown positive effect. The main reason could be their language has intermediate level were the one of these strategies in a conscious style. At the same time, learning strategies of meta cognition of the students needed to develop awareness of the conscious. Greer (2013) conducted a study on meta cognition and the music lesson. The researcher concluded that teaching and learning metacognitive strategies benefit students learning usually believed in education system that students who learn to think can do well and achieve the goals and can learn anything which acquired knowledge. The students who were learnt to think Meta cognitively show significant progress in their talent to evaluate performances. Mahadi and Subramaniam (2013) investigated that metacognitive is the strategy that students use to deals with learners' existing knowledge and experiences, which can provide teachers or instructors with clear precise course of action in what way learners can progress their autonomy in linguistic scholarship. Students enrich with adequate learning strategy to enlarge autonomous learning and become more flourishing in their learning. Nair (2014) conducted a study and found that the universal hard work enlarged to inculcate skills of thinking about the curriculum, it is component of thinking manners, and which include all instructional tactics. This skill helps student to generate the fact of knowing anything and benefit to know about a common sense of accountability among scholars. Learning activities of meta cognition submerge scholars in tough works and it creates a room for students to discuss, debate new ideas, and allows them to introspect, assess and set targets for learning. Franco (2017) conducted a study on the topic effect of negative climate for diversity on cognitive outcome of college students. The researcher found that students attending selective institutions benefitted greatly in their cognitive skills development, although unique differences were found when students' outcomes were examined by their gender. Perceived negative climate for the diversity varied depending on students' gender.
The following hypotheses were tested in the present study:
Descriptive method of research was used in the present study. The population of the study comprise of Senior Secondary School of Bhutan. Tsring and Sarbang districts of Bhutan constituted the sampling frame of the study. Stratified random sampling technique was used to select a sample of 300 senior secondary school students in different rural and urban schools of Bhutan and in (Tsring) district and (Sarbang) district. Senior secondary school boys and girls, rural and urban students were selected of all the three streams, i.e. arts, science, and commerce.
Meta Cognition Skills Inventory developed by Dr. Punita Govil (2003) was used for data collection in the current study.
The objective of the study was to find different levels of the Meta-Cognitive Skills among students of senior secondary school in Bhutan are given in Table 1.

Table 1. Levels of Meta Cognitive Skills among Senior Secondary School Students
It is obvious from Table 1 that 1% students possess very high, 17.67% students possess high, 39.67% students possess average, 28.67% students possess low, and 13% students possess very low level of meta cognitive skills. Figure 1 represents the same.
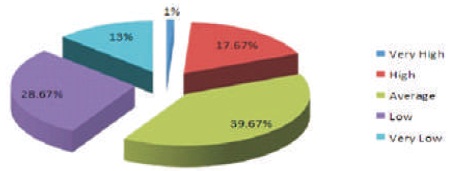
Figure 1. Graph represents the Levels of Meta Cognitive Skills among Senior Secondary School Students
The objective is to find the dissimilarity between boys and girls senior secondary school students in their meta cognitive skills. Mean scores, SDs, df, and t-value were calculated and organized in Table 2.
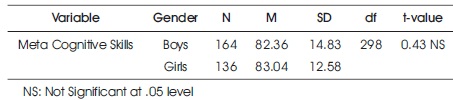
Table 2. Difference between Senior Secondary School Boys and Girls in Meta Cognitive Skills
Table 2 shows that mean score of senior secondary school boys is 82.36; mean score of girls is 83.04, the SD of senior secondary school boys is 14.83 and SD for senior secondary school girls is 12.58. For meta cognitive skills, the t-value for difference between senior secondary school boys and girls is 0.43, and it shows that it is not significant at 0.05 level. Hence, it may be interpreted that there exists no significant difference between senior secondary school male and female in their meta cognitive skills. Thus, the hypothesis that there exists significant difference between senior secondary school male and female in their meta cognitive skills was rejected. Figure 2 shows mean scores of senior secondary school boys and girls in their meta cognitive skills.
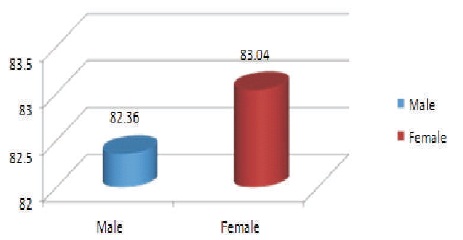
Figure 2. Mean Scores of Senior Secondary School Boys and Girls in their Meta Cognitive Skills
The second objective was to find the dissimilarity of locality differences among senior secondary school students in their Career Decision Making. Mean scores, SDs, df, and tvalue were designed and organized in Table 3.
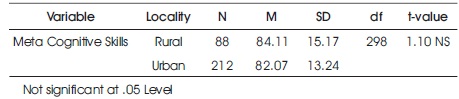
Table 3. Difference between Rural and Urban Senior Secondary School Students in their Meta Cognitive Skills
Table 3 shows that t-value (1.10) for dissimilarity between rural and urban students of school of Bhutan in their meta–cognitive skills, is not significant at 0.05 level. It means that there exists No significant difference between rural and urban students of school of Bhutan in their metacognitive skills. Further, it is obvious from above Table 3 that mean score of urban (84.11) students is greater than mean score of rural (82.07) senior secondary school students, therefore it may be concluded that urban students are more inclined towards meta-cognitive skills than their rural counterparts. Thus, the hypothesis that there exists no significance difference between rural and urban senior secondary school student in their career decision making, was rejected. Figure 3 shows mean scores of senior secondary school rural and urban students in their Meta Cognitive Skills.
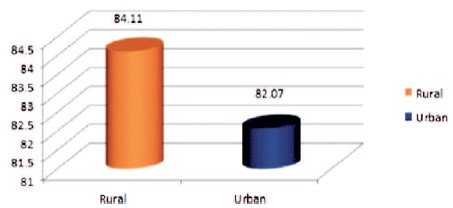
Figure 3. Mean Scores of Rural and Urban Senior Secondary Schools Students in their Meta Cognitive Skills
The objective of the current study was to find the stream related differences among students of school of Bhutan in their career decision making. Mean scores, SDs, df, and t-value was designed and organized in Table 4.
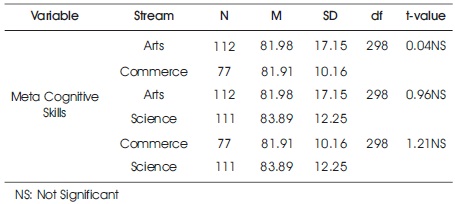
Table 4. Stream Related Differences among Senior Secondary School Students in their Meta Cognitive Skills
It is clear from Table 4 that t-value (0.04) between arts and commerce senior secondary school students for Meta cognitive skills, is not significant at 0.05 level. Similarly, t-value (0.96) between arts and science senior secondary school students for Meta Cognitive Skills is not significant at 0.05 level. Also, t-value (1.21) between commerce and science senior secondary school students for Meta Cognitive Skills is not significant at 0.05 level. Thus, it may be interpreted that for Meta cognitive skills, stream related differences among senior secondary school students are not significant. Hence, the hypothesis that there exist significant stream related differences among senior secondary school students in their Meta Cognitive Skills was rejected. Figure 4 shows stream wise mean scores of students of senior secondary school in their Meta Cognitive Skills.
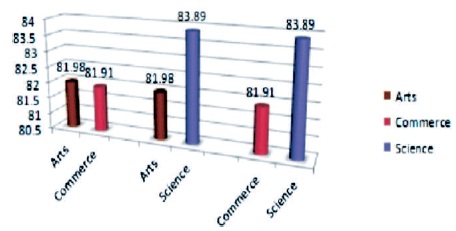
Figure 4. Stream Wise Mean Scores of Senior Secondary School Students in their Cognitive Skills
On the basis of analysis and interpretation of data of meta cognitive skills among the senior secondary school students in Bhutan, it was found that 1% senior secondary school students possess very high level of meta-cognitive skills. Further, 17.67% senior secondary school students possess high level of meta-cognitive skills. Also, 39.67% senior secondary school students possess average level of meta-cognitive skills. Whereas, 28.67% senior secondary school students possess low level of meta-cognitive skills, and 13% senior secondary school students possess very low level of meta-cognitive skills. In other words, 18.67% senior secondary school students of Bhutan possess above average meta-cognitive skills, 39.67% senior secondary school students possess average level of meta-cognitive skills, whereas 41.67% senior secondary school students of Bhutan possess below average meta-cognitive skills. Most of the students possess either low or average level of metacognitive skills. Since the researchers Kim et al. (2009), George and Kappan (2011), and Greer (2013) have found that meta-cognitive skills help in improving the academic performance of the students. Hence, it is recommended that there is a need to train senior secondary school students of Bhutan in meta-cognitive skills in order to improve their academic performance.
Based on the conclusions of the present study, it is the recommended that meta cognitive skills of senior secondary school students do not differ on the basis of gender, locality, and stream, hence it should be taken care of by the teachers, parents, and administrators that senior secondary school students should be treated equally, irrespective of gender, locality, and stream while teaching, making them learn or providing facilities to enhance their meta cognitive skills.