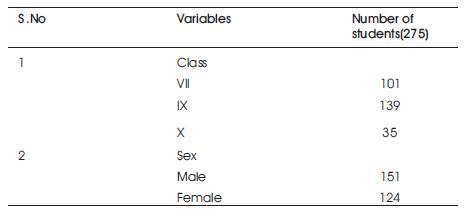
Table 1. Sample Distribution
Education is the ability to meet one's life. How the child adjusts with varying situations determines the success of life. The child's adjustment is determined by a number of factors like Home, Social, Educational and Financial adjustment. The investigator here aims to make a comparative study on the adjustment of secondary school students. The study was conducted using survey method. A total of 275 students, of which 151 were boys and 124 girls constituted the sample for the study. They were selected from eight secondary schools of Thiruvananthapuram district by giving due representation to class (VII, IX and X) and gender. Adjustment inventory prepared and standardized by the investigator was used to measure adjustment of secondary school students. Percentage analysis and t test were used as the statistical techniques for the study. The analysis revealed that level of adjustment of secondary school students is average. It was also found that significant difference exists in the emotional adjustment of boys and girls and no significant difference was found between male and female secondary school students with regard to Family, Social, Educational and Financial adjustment.
The term adjustment refers to a continual process by which a person varies his behavior to produce a more harmonious relationship between himself and the environment. The term adjustment in very strict sense denotes the results of equilibrium, which may be affected by either accommodation or adaptation. How the individual gets along or survives in his or her physical or social environment depends on adjustment. As the conditions in the environment changes constantly, every individual needs to modify or accommodate oneself with the environment. Thus adjustment is the maintenance of a harmonious relationship between man and the environment and the persons who comprise his physical or social environment, (Crow & Crow, 1956) .
Adjustment plays a vital role in the development of the child. Trow (1956) defined academic achievement as “knowledge attaining ability or degree of competence in school tasks usually measured by standardized tests and expressed in a grade or units based on pupils' performance”. As far as the academic achievement is concerned, multiple factors influence it. How the child adapts to the varying conditions of home, school, emotions, financial matters and the changing social conditions may create an impact on one's academic achievement.
In a study, Isabella (2010) explored the significant relationship between Academic achievement and socio Economic status of B.Ed students.158 student teachers were randomly selected for the study. Modified Kuppuswamy's Socio Economic status scale was used to collect data. It showed that there was no significant relationship existing between Academic achievement and Socio economic status of B.Ed students. Mohanraj and Latha (2005) investigated the relationship between family environment, home adjustment and academic achievement in adolescents. The study was homogeneous in age and home environment. The sample was assessed using Moos and Moos family environment scale and Bell's adjustment inventory. Family environment seemed to influence home adjustment as well as academic performance. Another study conducted by Reddy (1976) using Rao's academic achievement inventory and sentence completion device found that the academic adjustment is significantly related to scholastic achievement of students. Raju and Rahamtulla (2007) found that adjustment of school children primarily depends on the school variables like the class in which they study, medium of instruction and type of management of the school. Parental education and occupation of the school children were also found to influence the adjustment of students.
The following were the objectives formulated for the study:
The following were the hypotheses formulated for the study:
Methodology is the procedure or the technique used to conduct the research study. The survey method was found most appropriate for the study.
Representative samples of 275 secondary students (Boys =151 and Girls=124) selected from eight secondary schools of Thiruvanathapuram district were taken for the study. Due representation was given to factors like gender of students. The breakup of the sample is shown in Table1 respectively.

Table 1. Sample Distribution
Adjustment inventory prepared and standardised by the investigator was used to measure adjustment of secondary school students. This inventory consists of five dimensions viz. family, school, finanacial, personal and social adjustment. The reliability coefficient was found to be 0.74.
The investigator used the following statistical techniques for the study.
1. Percentage analysis
2. T test
As per the preliminary analysis, percentage distribution of level adjustment of students as grouped by their classes was determined.
It can be inferred from Table 2, that 53% of class VII, 52 % of class IX and 54 % of class X students show moderate level of family adjustment while 40 % of class VII, 10 % of class IX and 12 % of class X students show low level of family adjustment. It can also be seen that 7% of class VII, 38 % of class IX and 34 % of class X students show high level of family adjustment. Thus majority of the respondents were in the moderate level of family adjustment. The low level of family adjustment in the students of class IX and X indicates that they were exposed to familial problems.
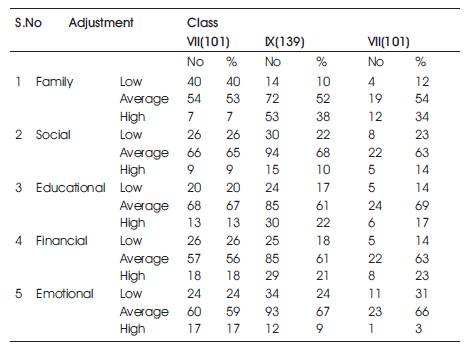
Table 2. Percentage of adjustment of secondary school students
It can be inferred from Table 2, that 65 % of class VII, 68 % of class IX and 63 % of class X students show moderate level of social adjustment while 26 % of class VII, 22 % of class IX and 23 % of class X students show low level of social adjustment. It can also be seen that 9% of class VII, 10 % of class IX and 14 % of class X students show high level of social adjustment. Thus majority of the respondents were found to be in the moderate level of social adjustment.
From Table 2, 67% of class VII, 61 % of class IX and 69 % of class X students show moderate level of educational adjustment while 20 % of class VII, 17 % of class IX and 14 % of class X students show low level of educational adjustment. It can also be seen that 13% of class VII, 22 % of class IX and 17 % of class X students show high level of educational adjustment. Majority of the respondents were found to be in the moderate level of educational adjustment. The lower levels of school adjustment can make serious impact on the academic achievement of students' as mentioned in the study by Adhiambo, Odwar and Mildred (2011) as the differences in the school adjustment can manifest between the high and low achievers.
It can be seen from Table 2, that 56% of class VII, 61 % of class IX and 63 % of class X students show moderate level of financial adjustment while 24 % of class VII, 24 % of class IX and 31 % of class X students show low level of financial adjustment. It can also be seen that 18% of class VII, 21 % of class IX and 23 % of class X students show high level of educational adjustment. Majority of the respondents were found to be in the moderate level of financial adjustment.
It can be inferred from the Table, that 59% of class VII, 67 % of class IX and 66 % of class X students show moderate level of emotional adjustment while 26% of class VII, 18 % of class IX and 14 % of class X students show low level of emotional adjustment. It can also be seen that 17% of class VII, 9 % of class IX and 3% of class X students show high level of emotional adjustment. Majority of the respondents were found to be in the moderate level of emotional adjustment. The lower level for emotional adjustment indicates that many subjects in this study may be subjected to strain, mental stress, unhealthy competition, cooperative works and so on.
Table 3 shows a significant difference in the emotional adjustment of boys and girls(t=2.04 >1.96). No significant differences were found in the family, social, educational and adjustment of boys and girls. This result concurs with the study of Ganai et.al (2013) that male and female students show no significant difference with reference to family, social and educational adjustment. The result is this study is different from Ganai et.al (2013) as significant difference was found between boys and girls for the emotional adjustment. The study shows that male students have better emotional adjustment than female. The difference may be due to the fact that girls are compelled to subdue emotions, at times become introvert and may hesitate to speak freely. Yellaiah’s (2012) study also noted that boys and girls differ significantly in their emotional adjustment.
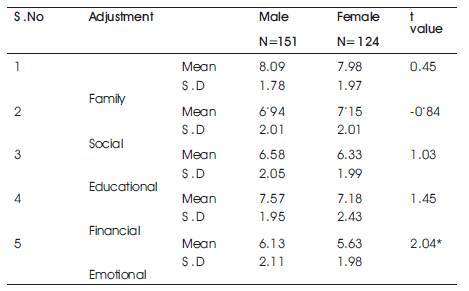
Table 3. Difference in adjustment of male and female students
1. The level of adjustment of secondary school students is average.
2. There is a significant difference in the emotional adjustment of boys and girls.
3. No significance difference was found between male and female secondary school students with regard to family, social, educational and financial adjustment.
4. Boys possess better emotional adjustment than girls.
Teachers can play a crucial role in increasing the adjustment of students. Yoga and meditation, healthy group activities, various programs like NCC, cultural competitions, sports etc. can be incorporated into the school curriculum in order to improve the emotional adjustment of students.
The study calls for school authorities to initiate adjustment programs for the secondary school children. Orientation programs, social activities, student organizations should be arranged in the school environment itself to promote overall adjustment in children. Hence a positive, free, open and friendly atmosphere for students to interact freely with the teachers should be maintained. A good school climate thus gains much significance in making the students a better individual who can meet the challenging demands of life. A range of programs according to the diverse student needs should be oraginsed in the schools. Parents should be made aware about their role in making the child better adjusted personalities. Guidance and Counselling center, academic advisor, financial aid programs, and tutoring programs should be offered to address various student needs. Providing adequate rest, socializing, physical activity and recreation can improve the wellbeing and adjustment of students.
Adjustment is the process by which a living organism maintains a balance between its needs and the circumstances that influence the satisfaction of these needs. It is the process by which an individual attempts to deal with stress, tensions, conflicts etc., to meet one's needs. The individual in the due course can maintain harmonious relationships with the environment in the process of adjustment. The study concluded that for this study population, despite the fact that there were no differences between male and female secondary school with regard to family, social, educational and financial adjustment, boys showed more emotional adjustment than girls. The percentage analysis reveals that secondary school students possess only a moderate level of adjustment for all dimensions of adjustment. A higher level of adjustment in every dimension of adjustment is shown only for a small number of students and this has to be seriously taken for the successful wellbeing of the individual. The study thus urges the need to develop and implement adjustment programs for the secondary school children. The difference in the emotional adjustment of male and female secondary schools students can manifest both the behavior and academic achievement of students.