
Figure 1. Components of Power System
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are emerging technologies that are increasingly being used to improve various aspects of power systems. In particular, AI-based relaying algorithms have the potential to revolutionize the way power systems are protected from faults and failures. Relaying algorithms play a critical role in ensuring the stability and reliability of power systems. However, traditional relay protection algorithms face several challenges, including difficulty handling complex and dynamic systems, limited fault detection accuracy, and slow response times to changing conditions. AI-based relaying algorithms can address these challenges by leveraging the power of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning. This paper presents an overview of AI-based relaying algorithms and their potential applications in power systems. It explores the use of AI techniques such as Artificial Neural Networks (ANN), Decision Trees (DT), and expert systems for improving the accuracy and reliability of relay protection. It also discuss the steps involved in AI-based relaying algorithms, including feature extraction, classification, and result output. This paper highlights the importance of further research and development in this field to fully realize the benefits of AI-based relaying algorithms.
Energy plays a crucial role in daily life and in the functioning of modern societies. It is a fundamental resource that powers homes, businesses, transportation systems, and industries. Access to reliable and affordable energy is essential for economic growth and development and has a direct impact on people's quality of life. Energy also plays a significant role in the global economy and is a key factor in determining a country's competitiveness in the world market.
An electrical power system is a network of components and devices used to generate, transmit, distribute, and utilize electrical energy. It includes power plants, transmission networks, substations, and distribution networks that supply electricity to homes, businesses, and industries.
Figure 1 shows the main components of an electrical power system (Weedy et al., 2012). They are as follows,

Figure 1. Components of Power System
The goal of an electrical power system is to provide a reliable and stable supply of electrical energy to meet the demands of customers while maintaining the safety and stability of the system.
Power system protection is an important research area in the electrical power industry, focused on ensuring the stability and reliability of power systems. Power system protection research focuses on protecting power systems from various types of faults and failures, including short circuits, overloading, and system instability (Paithankar & Bhide, 2022). Power system protection research is essential for ensuring the safe, reliable, and efficient operation of power systems and meeting the growing demand for electrical energy.
Relaying algorithms are mathematical algorithms used in power systems to protect the system from faults and ensure its stability and reliability. These algorithms analyze power system data, identify faults, and then trigger protective actions to isolate the faulted section of the system.
Relaying algorithms can use various techniques, such as Artificial Neural Networks (ANN), Decision Tree (DT), Fuzzy Logic, Genetic Algorithms (GA), Wavelet Transforms (WT), expert system and Support Vector Machines (SVM). The use of these algorithms can significantly improve the accuracy and reliability of power system protection, reducing false alarms and increasing the overall efficiency of the system (Phadke & Thorp, 2009).
In recent years, there has been an increased focus on the development of advanced relaying algorithms that use Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning. These algorithms can provide more accurate and faster fault detection and isolation, allowing for a more efficient and stable operation of the power system. Relaying algorithms play a crucial role in ensuring the safe and efficient operation of power systems, and the continued development of advanced relaying algorithms is essential for the future growth and stability of the power industry.
The primary objective of relaying algorithms in power systems is to provide accurate and reliable protection against faults and ensure the stability and reliability of the power system. The specific objectives of relaying algorithms can include the following.
The continued development of advanced relaying algorithms is essential for meeting the growing demand for electrical energy and ensuring the stability and reliability of the power grid. The effective implementation of relaying algorithms in power systems will help to achieve these objectives and ensure the long-term health and sustainability of the power industry.
Advanced protection algorithms for power systems use Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML). These algorithms aim to improve the accuracy and reliability of power system protection by using data analysis and pattern recognition to identify faults and trigger protection measures more quickly and accurately. The use of AI and ML in power system protection can also help reduce false alarms and improve the overall efficiency of the power system (Warwick et al., 1997).
The need for Artificial Intelligence (AI) in power systems is driven by the increasing complexity and interconnectivity of the power grid, as well as the growing demand for more accurate and reliable protection. Some of the key benefits of using AI in power systems as follows.
There are several Artificial Intelligence (AI) techniques that can be used in power systems (Gao et al., 2019) as follows,
Figure 2 shows the steps involved in using Artificial Intelligence (AI) in power systems (Farhoumandi et al., 2021). The steps involved are as follows.
The first step is to collect data from various sources, such as sensors, Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) systems, and databases. The data should be representative of the system conditions and sufficient for the AI algorithm to make accurate predictions and decisions. The collected data should be cleaned and pre-processed to remove any errors or inconsistencies and ensure that the data is in a format suitable for the AI algorithm.
In power systems, feature extraction is an important step in the application of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) algorithms. The goal of feature extraction in power systems is to identify and extract the most relevant features or attributes in the data that are critical to making predictions and decisions related to power system protection, operation, and control.
In power systems, classification is often used to identify and categorize different types of faults and events in the system. Some of the classification problems in power systems discussed as follows.
The resulting output of an AI or ML algorithm in a power system is typically a predicted class label or a probability distribution over a set of class labels. The quality of the output depends on several factors, including the quality and quantity of the data used to train the algorithm, the choice of algorithm, and the choice of features used as input to the algorithm. The final output of a power system AI algorithm should be reliable, actionable, and easy to understand so that it can be used to improve the safety, reliability, and efficiency of the power system.
Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs) have the potential to play a significant role in the operation and protection of power systems. ANNs are able to process large amounts of data and perform complex computations, making them well- suited for use in power systems. There are several key applications for ANNs in power systems, including fault detection, load forecasting, state estimation, optimization, and relaying algorithms.
Regarding fault detection, ANNs can undergo training to identify specific patterns within electrical signals that signify the presence of a fault. This information can be used to isolate quickly the fault and prevent damage to the power system. Load forecasting is another important application for ANNs in power systems, as they can analyze historical data to predict future demand and optimize the operation of the system accordingly.
State estimation is another key area where ANNs can play a role in power systems. By analyzing real-time electrical signals, ANNs can estimate the state of the system and identify any potential problems before they cause significant damage. This information can also be used to optimize the operation of the power system and improve its overall efficiency. Figure 3 shows how ANN is used in power restoration (Bretas & Phadke, 2003).
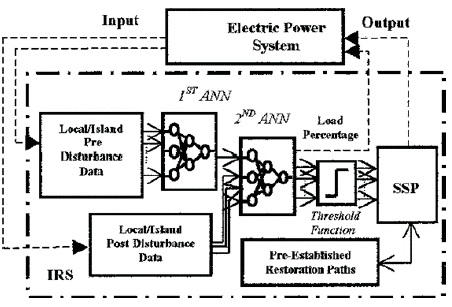
Figure 3. ANN in Power Restoration
ANNs can also be used to develop advanced relaying algorithms for power systems. These algorithms can detect and isolate faults with high accuracy and reliability, helping to ensure the stability and security of the power system. Overall, the use of ANNs in power systems has the potential to improve the accuracy, efficiency, and stability of these systems and will likely play an increasingly important role in the future of power systems.
Decision Trees are a Machine Learning technique that can be used in power systems to help with a variety of tasks, including fault diagnosis, load forecasting, and system optimization. It works by making predictions based on a series of decisions, or splits, in the data. At each split, the decision tree algorithm evaluates a specific feature of the data and makes a decision based on whether the feature is above or below a certain threshold (Liu et al., 2013). Figure 4 shows an example of how the Decision Tree helps to classify the overhead transmission line in the power system (Al Mtawa et al., 2022).
Tree helps to classify the overhead transmission line in the power system (Al Mtawa et al., 2022).
In the context of power systems, Decision Trees can be trained on historical data to make predictions about future system behavior. For example, it can be used to predict the likelihood of a fault occurring based on past system behavior, allowing for proactive maintenance and improved system reliability. They can also be used for load forecasting, allowing the system operator to better plan for future demand. It can be used to optimize the operation of power systems by making predictions about the most cost-effective way to generate and distribute energy. This can be done by analyzing various factors such as fuel prices, renewable energy availability, and demand patterns.
Decision Trees offer a powerful tool for improving the efficiency, reliability, and stability of power systems. By making predictions based on historical data, Decision Trees can help system operators make informed decisions about system operation and maintenance, ultimately leading to a more reliable and efficient power system.
Expert systems, also known as knowledge-based systems, are computer programs that use Artificial Intelligence to simulate the problem-solving abilities of a human expert. They can be used in power systems to provide decision support, automate routine tasks, and improve system reliability and efficiency (Styvaktakis et al., 2002).
In the context of power systems, expert systems can be used for a variety of tasks, including fault diagnosis, system optimization, and predictive maintenance. For example, an expert system can be designed to diagnose faults in power systems by using a knowledge base of rules and a database of past faults and their causes. The system can then make recommendations on how to resolve the fault, allowing for faster and more accurate fault resolution. Figure 5 shows how an expert system can make decision support in electric power system operation (Filho et al., 2012).
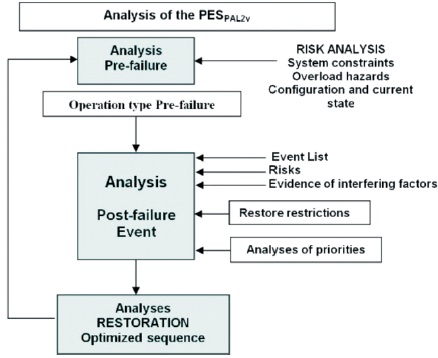
Figure 5. Expert Support in Making Decision
Expert systems can also be used to optimize the operation of power systems. For example, an expert system can be trained on data from past energy demand patterns, renewable energy availability, and fuel prices to make predictions about the most cost-effective way to generate and distribute energy. This can help reduce energy costs and improve system efficiency. It is used in fault diagnosis and system optimization; expert systems can be used for predictive maintenance. By using data from sensors and other monitoring systems, an expert system can identify potential equipment failures before they occur, allowing for proactive maintenance and improved system reliability.
Expert systems offer a powerful tool for improving the efficiency, reliability, and stability of power systems. By providing decision support, automating routine tasks, and making predictions based on historical data, expert systems can help system operators make informed decisions about system operation and maintenance, ultimately leading to a more reliable and efficient power system.
This paper concludes that, the use of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) in power systems has the potential to revolutionize the way power systems are protected from faults and failures. AI-based relaying algorithms offer several advantages over traditional relay protection algorithms, including improved accuracy, better handling of complex and dynamic systems, and faster response times.
This paper has provided an overview of AI-based relaying algorithms and their potential applications in power systems. The potential benefits of AI-based relaying algorithms are significant, there are also challenges that need to be addressed. These include ensuring the safety and security of AI systems, ensuring the reliability of AIbased relaying algorithms in real-world applications, and the need for further research and development in this field. The use of AI-based relaying algorithms in power systems has the potential to enhance the stability and reliability of the power system. Further research and development in this field is crucial for realizing the full benefits of AI-based relaying algorithms.