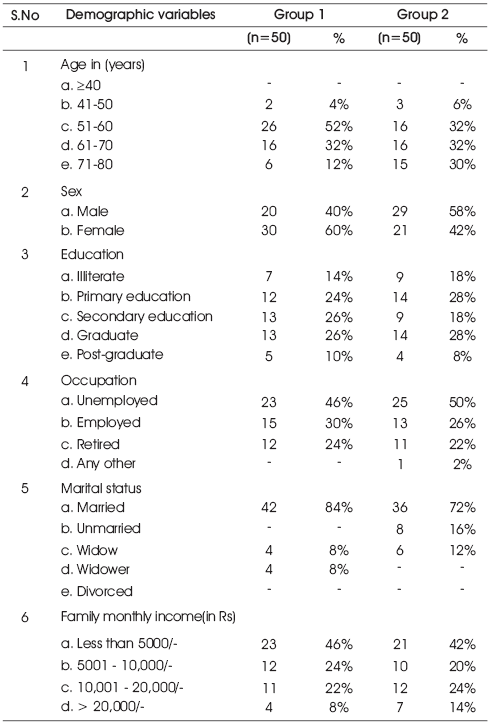
Table 1. Demographic variables of the sample from Group 1 and Group 2
It is well documented that hospitalisation for surgery is associated with increased anxiety (Dodds 1993). This study investigates the effectiveness of preoperative Nursing teaching module versus patient to patient teaching on anxiety among patients subjected to coronary artery bypass graft (CABG). Using non probability convenience sampling method a total of 100 surgical patients subjected to CABG were selected for the study from selected hospitals of Punjab. The study utilized quasi experimental design which consisted of Group1: 50 patients who received Preoperative Nursing Teaching Module and Group 2: 50 patients who had interacted with post operative CABG patients pertaining coronary artery disease and perioperaive care of CABG. Anxiety was assessed at two time points, preoperatively and postoperatively using State Trait Anxiety Inventory (STAI). A pretest was conducted to assess the baseline level of anxiety scores of both the groups (Group 1 and Group 2) of the patients using the State Trait Anxiety Inventory (STAI) followed by Preoperative Nursing Teaching Module for Group 1 and Patient to Patient teaching Method for Group 2. The posttest was carried out approximately after 3 days after the administration of Preoperative Nursing Teaching Module and Patient to Patient teaching Method. In pretest, the Group1, 5(10%) patients were having mild anxiety, 45 (90%) were having moderate level of anxiety; out of the 50 patients in Group 2, 8(16%) patients were having mild anxiety and 42(84%) were having moderate level of anxiety. Whereas during posttest, among 50 patients of Group1, 36(72%) patients were having mild level of anxiety followed by 14(28%) were having moderate level of anxiety. In group 2 out of 50 patients 9(18%) were having mild level of anxiety and 41(82%) were having moderate level of anxiety. The mean post test anxiety scores of the Group 1 patients were significantly lower (p<0.001) compared to their pretest anxiety scores, after administration of the Preoperative Nursing Teaching Module. On the contrary, the Group2 posttest mean anxiety scores were not significantly reduced compared to their pretest scores. Hence the Preoperative Nursing Teaching module is more effective in reducing the levels of anxiety among the patients subjected to CABG as compared to the Patient to patient teaching method. Association between the post test Level of anxiety of the patients and their demographic variables was found to be statistically insignificant.
More than 60% of the global burden of heart diseases occurs in developing countries. It is on the rise and has become true pandemic that respects no borders. Out of all the heart diseases prevalent, Coronary artery disease has become one of the leading causes of death among cardiac disorders. Although several alternative treatments for coronary artery disease exist which include:
Both PCI and CABG are more effective than medical management at relieving symptoms, (e.g. angina, dyspnea, fatigue). CABG is superior to PCI for some patients with multivessel CAD. Patients treated with CABG had lower rates of death and myocardial infarction than treatment with a coronary stent. Coronary Artery Bypass Graft surgery (CABG) is a procedure that uses patient's own veins or arteries to bypass narrowed areas and restore blood flow to heart muscle. Thus, bypass surgery can effectively relieve chest pain for most patients, and can prolong their life. Coronary Artery Bypass Graft (CABG) is the ultimate choice of the treatment.
Coronary Artery Bypass Graft has now become one of the most common types of surgery in developing countries like India with more than 500,000 surgeries performed each year. In the year 2008 more than 1,314,000 CABG's were done around the world and an average of more than 1000 CABG surgeries are done every year in selected hospitals in Punjab.
The main purpose in conducting this surgery is to:
Coronary Artery Disease is a chronic condition, in which the coronary artery become clogged with calcium and fatty deposits. The deposits, called plaques, narrow the arteries that carry blood and become clogged with calcium and fatty deposits. The most common signs and symptoms of CAD are chest pain or chest discomfort, heart palpitation, lightheadedness or dizziness, syncope, fatigue, lethargy or daytime sleepiness, shortness of breath. Although several alternatives treatments for coronary artery disease exist, the most effective one is Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG). CABG has now become one of the most common types of surgery in developing countries like India with more than 500,000 surgeries performed each year. In the year 2008 more than 1,314,000 CABGs were done every year in selected hospitals in Punjab. The patients undergoing CABG surgery deserves to have confidence that the professional nurse is knowledgeable, caring, efficient and effective in providing necessary preoperative care. Nurses have shown to play a crucial role in reducing the anxiety of the patients undergoing CABG. A study conducted by Asilioglu et. al.to assess the effect of preoperative teaching method on anxiety levels of patients undergoing cardiac surgery stated that the intervention group were satisfied with the preoperative teaching given by the researcher.
The research design that is chosen for this study was Quasi-experimental study. The study was conducted in three leading cardiothoracic hospitals situated in the city of Jalandhar, Punjab. A Convenience sampling technique was used to select a sample of 100 patients, 50 each for experimental and control groups.
The tool used in this study consists of two sections. Section-I contain demographic variables. Section-II contains State and Trait Anxiety Inventory “Y” Form Y1 &Y2.
State Trait Anxiety Inventory is a 4 point Likert scale which has 20 items in state anxiety and 20 items in trait anxiety. The items include both positive and negative state of mind. The items which are considered as positive state had reverse scoring. The negative state had direct scoring.
The data were analyzed using descriptive (frequency, percentage, mean and standard deviation) and inferential statistics ('t' test and chi square).
Table 1 illustrates the distribution of demographic variables of 100 patients, which includes 50 patients (Group 1) who received preoperative nursing teaching module and 50 patients (Group 2) who received preoperative teaching from post CABG patients.
Figure 1 depicts the comparison of mean scores in the level of anxiety among patients subjected to CABG in Group 1 and Group 2.
Table 2 shows the association between demographic variables and the level of anxiety with the effect of preoperative nursing teaching module and patient to patient teaching on perioperative care of CABG among patients subjected to CABG. (N= 100).
This concluded that the association between the post test anxiety level scores of patients undergoing CABG and demographic variables in both the groups did not reach the level of significance (p>0.05).

Table 1. Demographic variables of the sample from Group 1 and Group 2
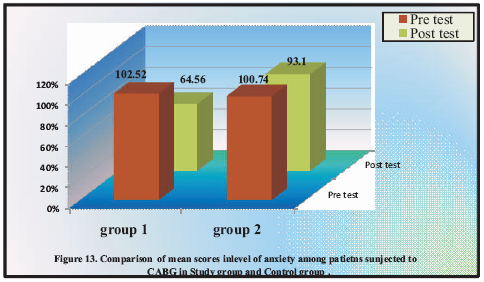
Figure 1. Comparison of mean scores in level of anxiety among patients subjected to CABG in Group 1 and Group 2
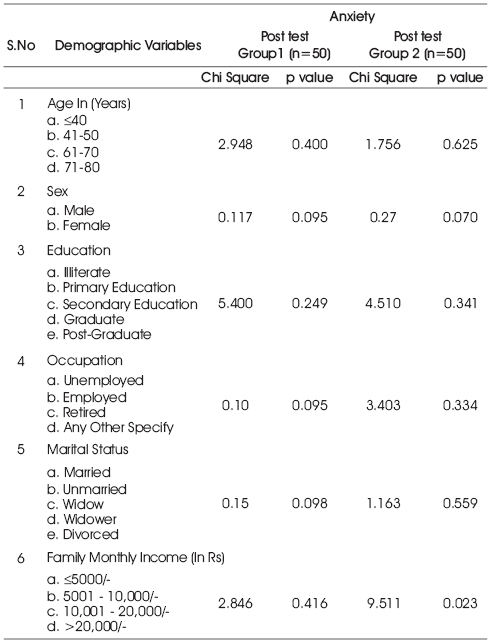
Table 2. Association between Demographic Variables and the Level of Anxiety
The results of this study showed that:
The findings were supported by an experimental study done by Klinik and Poliklinik (2008) on effect of patient education in the form of written material among patients undergoing coronary artery bypass graft. The results revealed that there was a positive effect of the patient education programme in the form of written material given to the patients before surgery. It was recognized as an effective tool to reduce the level of anxiety and maintain physiological parameters in the post operative period.
Patient education is one of the most important responsibilities of the nurse in all health care setting. The results of this study demonstrate that the effect of preoperative teaching module and patient-patient teaching between the group1 and group2 showed group1 had a greater reduction in the level of anxiety from moderate to mild than group2. There was no association between demographic variables and level of anxiety in both the groups.