Table 1. Specification of Sheet Materials
The objective of this experiment is to find out the cupping index of different sheet metals in different thickness using ERICHSEN cupping testing machine (Model ET-20, least count of 0.01 mm) in metal forming operations (stretching). In the ERICHSEN cupping test, the sheet metal test piece is clamped under a pressure of 1000 ± 100 kgf between a blank holder and a die. This test is a type of stamping test, which uses a polished steel ball or a spherical punch of a standard size mounted on a plunger to penetrate into the specimen with a constant force until the specimen produces first crack. The machine is to be operated at 4.8 r.p.m. by handwheeel. Under the action of the force, the specimen sheet forms a cup-like structure, hence known as the 'ERICHSEN cupping testing.
The production of the first crack may either be detected by Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) like Visual Test (VT) or Liquid Penetration Test (LPT). A total force of around 10 KN was applied on the sample sheet metals until the specimen finally cracked. Then the work piece is pressed into the die by a ball shaped indenter (20mm diameter) until the cracks begin to occur in the specimen. The measure of the length of penetration in mm, indicates the ERICHSEN Number which gives a measure of the ductility of the sheet in the plane of drawing under biaxial stress conditions. The ERICHSEN no is the penetration of the die given in millimeters to the nearest decimal point, upto the point at which cracks occur (end point).Finally NDT method was used to find out formability Characteristics of different sheet metals.
Sheet metal formability is the ability of sheet metal to undergo desired shape change without failure. Formability is the ability of a given metal work piece to undergo plastic deformation without being damaged. The plastic deformation capacity of metallic materials, however, is limited to a certain extent, at which point, the material could experience tearing or fracture (breakage).
Forming operation of a sheet metal can be classified in four types, which are: (i) deep-drawing which is also called shrink flanging, by which a large formed height can be secured by pouring the material effectively in between the punch and the die as represented by cup forming. (ii) Stretching, in which the material is stretched in a manner to inflate a balloon by thinning the material. (iii) Stretch flanging in which the cutting edge of materials experiences a large tensile deformation in a manner to expansion of pieced hole and (iv) Bending which is the plastic deformation of metals about a linear axis with little or no change in surface area.
Tensile strength of a material is important in determining which forming operations are appropriate. Sheet metal is often anisotropic-properties vary with direction and orientation. Majority of failures during forming occur due to thinning or failure. Strain analysis can be used to determine the best orientation for forming.
The formability property of a metal is very important to the layout and design of any industrial forming process. Sheet metal also has applications in car bodies, airplane wings, medical tables, roofs for buildings (Architectural) and many other things. Sheet metal of iron and other materials with high magnetic permeability, also known as laminated steel cores, has applications in transformers and electric machines.
The Erichsen cupping test is used to assess the stretch formability of sheets. This test can be classified as a stretch forming test which simulates plane stress biaxial tensile deformation. For the Erichsen test a sheet specimen blank is clamped firmly between blank holders, which prevent the in-flow (feeding) of sheet volume from under the blank holder into the deformation zone during the test.
From literature survey it is seen that Y.I. Kim, J.H. Kim, Y. Kim, M.Y. Lee, Y.H. Moon, D. Kim (et al.2011,pp no-568-574) worked on tailor-welded blanks of boron steel sheets by Erichsen cupping test at elevated temperature. H. Danesh Manesh, A. Karimi Taheri (Journal of Alloys and Compounds 361 (2003) 138–143) researched on bond strength and formability of an aluminum-clad steel sheet, they found that formability of an Al-clad steel sheet depends on the annealing time at constant annealing temperature. The intermetallic phase thickness increases with increasing annealing temperature at constant time. A. Karimi Taheri, T.M. Maccagno, J.J. Jonas worked on effect of quench aging on drawability in low carbon steels, (Mater. Sci. Tech. 11(1995) 1139). Islahuddin (2009) thesis work give the information that magnesium was the most ductile followed by aluminum and brass using finite element method or to be more specific using ALGOR software. According to F. Hosford et.al (1983), Erichsen cupping tests were performed as following the standard procedure DIN 50 101 the biaxial tension deformation. J.C. Wright (1974) et al. gives information on cold bond between the sheet metal layers. The previous work done was mainly related to characterize stretch formability of sheets metals due to elasticity and plasticity during Erichsen cupping testing. This was mainly done in order to find the sheet metal with the best formability for a particular sheet metal forming process (Edwards et al.1990) and the sheet metal with the higher Erichsen number was more suited for forming process.
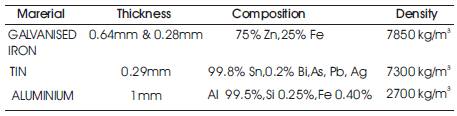
For this experiment the authors have taken two different thickness galvanized iron, one tin and one aluminum sheet in Erichsen cupping testing. The composition, thickness and density of all sheet metals are given in Table 1.

Table 1. Specification of Sheet Materials
Erichsen test is a very popular test which gives an excellent account of current metallurgical practice in producing pressed and deep drawn components. In the Erichsen test, the punch is pressed into the sheet until fracture occurs, at which point the test is stopped immediately and the depth of the bulge noted. This depth (mm) gives the Erichsen number. The Erichsen number obviously gives a measure of the ductility of the sheet in the plane of drawing under biaxial stress conditions. The Erichsen cupping testing machine with specification and principle of the testing is given in Figures 1, 2 and Table 2.

Figure 1. Erichsen Cupping Testing Machine
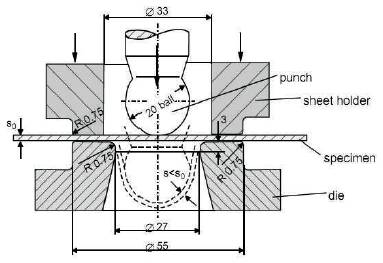
Figure 2. Different Parameter of Cupping Test
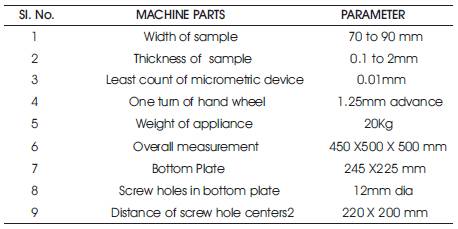
Table 2. Specification of Erichsen cupping testing machine
Detection of crack was done by Non destructive testing method (V.T and L.P.T). Picture of crack detection surface in different two method have been given separately from Figures 3 to 10. And results of the experiment have been shown in different graphs from Figures 11 to 13.

Figure 3. Cupping of Aluminium (VT)
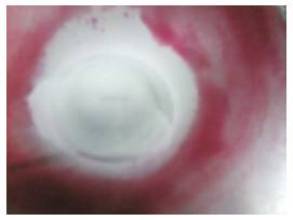
Figure 4. Cupping of Aluminium (LPT)
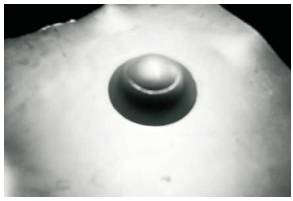
Figure 5. Cupping of Galvanised Iron-2 (VT)

Figure 6. Cupping of Galvanised Iron-2 (LPT)
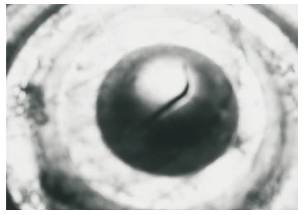
Figure 7. Cupping of Tin (VT)
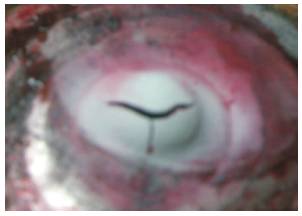
Figure 8. Cupping of Tin (LPT)

Figure 9. Cupping of Galvanised Iron-1 (VT)

Figure 10. Cupping of Galvanised Iron-1 (LPT)
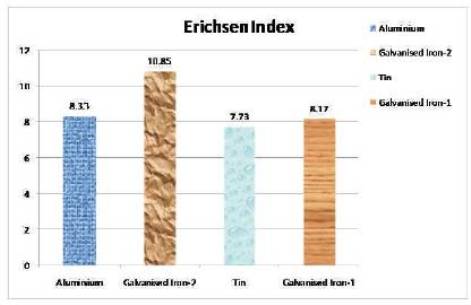
Figure 11. Variation of Erichsen index with different thickness sheet materials
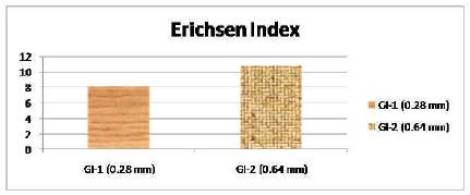
Figure 12. Variation of Erichsen index with thickness of two GI sheets taken
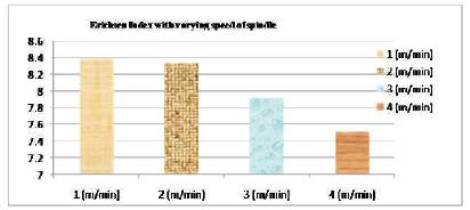
Figure 13. Variation of Erichsen index with varying speed of spindle
In this experiment the authors have taken four sheets of material of different thickness. We have taken Aluminum sheet of thickness 1mm, two GI sheets GI-1 and GI-2 of thickness 0.64mm and 0.28 mm respectively and tin sheet of 0.29mm thickness. After conducting the experiment we have found that Erichsen Index no. of Aluminum sheet to be 8.33, 8.17 and 10.85 of GI-1 and GI-2 sheet and 7.73 of Tin sheet. Thus from Table 3 we have found that for same material sheet (GI-1 and GI-2) Erichsen Index no. decreases with decrease in thickness. More the Erichsen Index No. more good stretching formability property of the material is. For different materials Erichsen index no. varies with thickness of the sheet depending on the material properties. We have done two tests to determine the stretching formability property of materials. These are Visual Testing (VT) and Liquid Penetration Testing (LPT). From the pictures we see that Crack is most generated in the tin sheet.
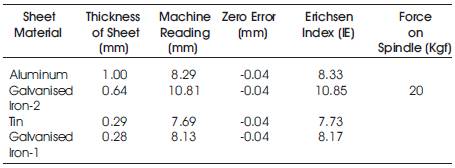
Table 3. Result of Erichsen Cupping testing for different sheet materials
Of the two Galvanized Iron sheets GI-1 and GI-2 taken crack is generated most in GI-1 which is of thickness 0.28mm with respect to GI-2 of thickness 0.64 mm. The least thickness out of four sheets taken is of GI-1.The Erichsen Index of two sheets are 10.85(GI-2) and 8.17 (GI-1).Thus we see that with decrease in thickness Erichsen Index decreases and Crack generated is more for material of lower thickness and Erichsen index .Thus more the Erichsen index and thickness more good the stretching formability property of the material. From graph we see that Erichsen Index is most for Galvanised Iron -2 sheet and least for Tin sheet. Thus Erichsen index depends on the property of the material of sheet like density, hardness, thickness etc. Of the two GI sheets Erichsen Index is more for GI-2 (10.85) which has more thickness than GI-1 (8.17).Thus more the thickness more the index no and more good the stretching formability property of material. There is also variation of Erichsen Index with speed as shown in graph. Erichsen Index decreases with increase in speed.
From the experiment they concluded that more the Erichsen Index of a material more the stretching formability property of the material and is more suitable for general use than ones with lower index. The stretching formability property of the material varies with thickness, speed of spindle and temperature of the four sheet materials. we have used thickness is most for aluminum sheet and least for GI-1.Erichsen Index is most for GI-2 and least for tin sheet. Thus GI-2 has best stretching formability property and tin has worst stretching formability property.
The authors would like to thank all the staff members of Automobile Engineering Department especially Head of Dept. AUE, Mr. Manik Chandra Das for providing them support to conduct this experiment. They also thank the lab instructor Mr. Arijit Ghosh and Mr. Jyotirmoy Das for giving their precious time in helping them to conduct the experiment and clearing their doubts instantly. They also wish to thank the college Management for providing the materials and space which they needed to conduct the experiment.