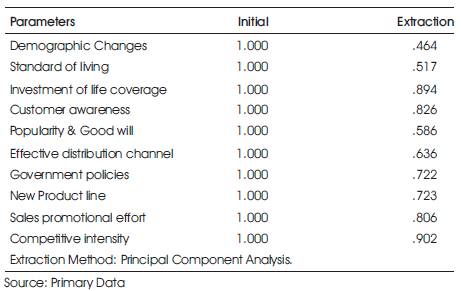
Table 1. Communalities
A breakthrough in the Indian life insurance sector witnessed after the liberalization process which is nearly a decade old. The first major milestone paved after long discussions by political parties, conferences and other key contributors were came into reality through the passing of Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority Act by Government of India in 1999 thereby opening its doors for private players with foreign collaboration. Hence the monopolistic spell of the public giant Life Insurance Corporation of India had been swiped away to a diminishing percent. As a result of this growth phase, new range of products, better and competent customer service, tremendous employment opportunities and acceleration in insurance penetration and density were ameliorated in Indian life insurance sector. A serious concern on the 80 percent of the untapped population of India, a cogitate step has taken to consider 'God's own country'- Kerala - the land of latex, lakes and literacy into the prime limelight for this study as it is the one of the key emerging market in India out of the 28 States and 7 Union Territories. Au contraire, keeping in mind the fact whether the insurer is old or new, private or public, expanding the market and increasing the magnitude of sales will provide enormous challenges and opportunities. This paper sheds light on the significance of different factors that influence the sales promotion efforts in Kerala.
The deep rooted history of Indian life insurance and its ranking as the second largest population power with 1.2 billion people according to the global population statistics. Out of the total insurable population in the country, only 20 percent is insured in various life insurance schemes. In the last few decades technology has brought a stupendous change in the field of insurance through the internet penetration which has shockingly increased in India Tantal Nitin (2006). People in all fields of their life would like to get things fast and at their finger tips. Whilst considering all the factors, it is evident that priorities in the sale of life insurance products changes day by day. Identifying the key sales indicators and focusing on taking advantage of those indicators outlines the utmost success of any life insurance company. Moreover, the speedy growth of life insurance sector has made it a colossal one. It is proud to see the transformation of life insurance sector in India with steady growth has become a boon for the economic and infrastructural development of the country.
One of the beginning milestones in life insurance business was achieved through the Indian Life Insurance Act of 1912 for regulating the life insurance business. Later, in 1928 another step was taken forward by the government through the Indian Insurance Companies Act for sanctioning the government to collect the statistics of life insurance business. Moreover, an amalgamation of Insurance Act was made in 1938 for protecting the interest of the insured population. A remarkable achievement in the history of life insurance was taken place by the central government by merging 245 Indian and foreign players and provident societies. In 1956 life insurance business was nationalized and brings forth the formulation of Life Insurance Corporation of India who held the monopoly of Indian market for over 40 years.
According to the latest updated list published by IRDA (2011) , there are a total of 23 registered private life insurance players along with the state owned giant LIC of India on the fore front. The global economic melt down has not affected the Indian economy much and keeps it comparatively stable because of the strong back bone of the Indian financial sector. Keeping pace of the fastest growing market of Kerala, new companies are launched every other day that makes it extremely competitive and it is tough for companies to sustain their market position. The purchasing power[India: The Next Insurance Giant, 2008] of the buyers has become extremely high as they can negotiate with companies and has a loop of choosing as many substitutes offering the same service. At this point companies should act stringently by forming various sales strategies that are appealing for the potential customers.
The Associated Chambers of Commerce and Industry of India reported the growth capacity of life insurance stratum from the view point of macro economic variables such as the ratio of premium to the Gross Domestic Product is relatively low [Indian Insurance Business Projected to US $ 60 Billion, 2010] . The annual report (2008- 2009) of Insurance Regulatory Authority (IRDA) shows ample details on India's insurance density as USD 47.4 which has prolonged to be beset by life insurance business (USD 41.2). Whilst the insurance penetration (insurance premium as per cent of Gross Domestic Product) show the level of insurance activity comparatively to the size of the economy. Further, as the GDP per capita elevates, it is anticipated that the individuals extend to buy more insurance. The latest Swiss Re report reveals that the insurance penetration in India was 4.6 per cent in 2008 consisting of 4.0 per cent in life business and 0.6 per cent from non-life business, unchanged from 2007[IRDA Annual Report 2008-09 (2009)] .
According to the 2001 census record of the Government of Kerala, the state has a population of around 319 millions (31,838,619) people which is approximately 3.44 per cent of the India's total population. Moreover, the density of population in Kerala is 819 persons per square kilo meter which is three times higher than the national average of India [Kerala Population and Census (2001)]. Further, Kerala has a significant place in adult literacy in Indian sub continent with an amazing rate of 100 percentages. Considering a holistic picture of Indian market, Kerala opens a cascade of scope for life insurance players with its immeasurable growth potential.
Philip Kotler (2000) highlighted the fact that in modern marketing, developing a good product is not enough. On the other hand it has to be decorated well with good pricing and make it accessible for customers. Every company is inevitably deputing themselves into the role of communicator and promoter. There are five major Marketing Communication Mixes as advertising, sales promotion, public relations and publicity, personal selling and direct marketing. Considering all these elements, sales promotion plays a vital role in any of the marketing communication activities. Obviously, sales promotion is a variety of short term incentive to encourage trial or purchase of a product or service.
A focus group discussion was conducted among twenty officials in an unstructured and natural way where respondents were free to give their views, perceptions, attitudes and beliefs to identify the different variables which were the key components / factors that influence the sale of life insurance products in Kerala. The identified key variables are given as follows:
The study focuses on eight leading life insurance players (Life Insurance Corporation if India Ltd., Allianz Bajaj Life Insurance Co. Ltd., ICICI-Prudential Life Insurance Co. Ltd., Reliance Life Insurance Co. Ltd., SBI Life Insurance Co. Ltd., Birla Sun-Life Insurance Co. Ltd., HDFC Standard Life Insurance Co. Ltd., & Tata AIG Life Insurance Company Ltd.) in Kerala which has been ranked from the business performance statistics provided by IRDA reports of march 2010. For this study, a sample size of 200 life insurance officials were selected using quota sampling method through a distribution of 25 officials (Sales Officers & Advisors) respectively from each of the above mentioned players to understand the factors influencing the sale of life insurance products in Kerala. The tool used in this analysis is Factor Analysis (PCA) method. The factor analysis is used as structure detection rather than a data reduction, so that the underlying (latent) relationships between the variable are identified. This will enable to understand the factors that play a primary role in influencing the sale of life insurance products. For structure detection, the extraction method goes one step further by adding the assumption that some of the variability in the data cannot be explained by the components. As a result, the total variance explained by the solution is smaller; however, the addition of this structure to the factor model makes these methods ideal for examining relationships between the variables. The study tries to identify how many components (factors) are needed to represent the sale of insurance products and what do these components represent. In order to understand the relationships among variables that hang together a Principal Component Analysis (PCA) method was used. PCA mathematically derive a relatively small number of variables to use to convey as much of the information in the observed/measured variables as possible. This will result in analysis of a manageable subset of the predictors.
Using SPSS the survey sample N=200 of data was analyzed using the factor analysis (PCA) method using principal component extraction which is then rotated for ease of interpretation. Components with Eigen values greater than 1 are taken for analysis. The Table 1 on communalities indicate the amount of variance in each variable that is accounted for.
From Table 1, the initial communalities are estimates of the variance in each variable accounted for by all components or factors. For principal component extraction, this is always equal to 1.0 for correlation analysis. Extraction communalities are estimates of the variance in each variable accounted for by the components. The communalities in this Table 1 are almost high, which indicates that the extracted components represent the variables well.
The total variance explained by the initial solution, extracted components and rotated components is displayed in the Table 2. The section1 of the Table 2 provided shows the initial Eigen values.
From the Table 2, the total column gives the eigen value, or amount of variance in the original variable accounted for by each component, the % of variance gives the ratio expressed as a percentage of variance accounted for by each component to the total variance in all the variables. The Table 2 extracts four principal components with eigen values greater than 1. The second section of the table shows the extraction components. They explain nearly 71 % of the variability in the original ten variables, thus considerably reducing the complexity of the data set. The rotation maintains the cumulative percentage of variation explained by the extracted components, but that variation is now spread more evenly over the components.

Table 1. Communalities
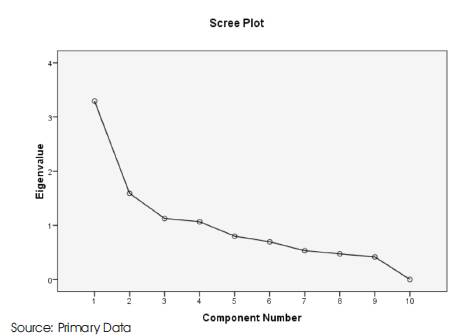
Figure 1. Eigen value of each Component
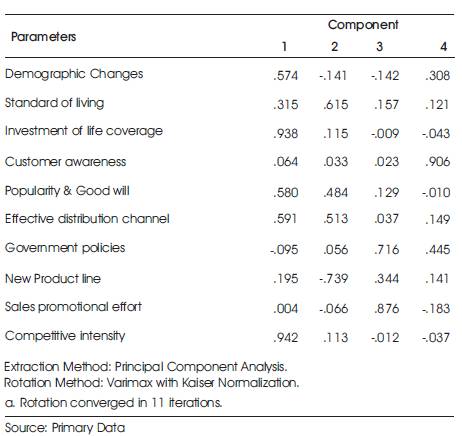
Table 3. Factors Influencing Sale (factor Analysis) Of Life Insurance Companies Rotated Component Matrix
Figure 1 provides the scree plot which will help in determining the optimal number of components. The Eigen value of each component in the initial solution is plotted. The component on the steep slope is extracted as the shallow slope contributes little to the solution. The rotated component matrix which helps in determining the component represented on the parameter analyzed and is given (Table 3).
In the rotated component matrix the magnitude of loading on the first component is competitive industry. The second component which is highly correlated is the Standard of living and the third component highly correlated is sales promotional effort. The fourth component most highly correlated with is the customer awareness about the company and the products.
After the rotated component matrix is inferred, the component score is computed for each case and each component by multiplying the case's standardized variable values (computed using list wise deletion) by the component score coefficients. The resulting four component score variables are representative of the entire initial variables.
The 4 components thus derived represent the original 10 factors and the components are not linearly correlated with each other. Thus it can be concluded that Competitive intensity, standard of living, sales promotional efforts and customer awareness about the company and products play a critical role in the sale of life insurance products.
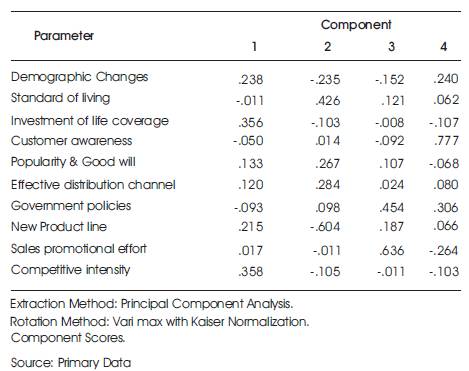
Table 4. Factors influencing sale (Factor Analysis) of Life insurance companies Component Score Coefficient Matrix
From the analysis the major findings were deducted which was the main intention behind the article. The main factors generated from the study are competitive intensity, standard of living, sales promotional efforts and customer awareness about the company and products which play a critical role in the sale of life insurance products in Kerala. This reveals the facts of concentrating the sales promotion efforts in the specific areas to boost the sales of life insurance products in Kerala.
From the rotated component matrix the magnitude of loading on the first component is competitive industry. The second component which is highly correlated is the Standard of living and the third component highly correlated is sales promotional effort. The fourth component most highly correlated with is the customer awareness about the company and the products. The total variance explained by the initial solution, extracted components and rotated components used to identify the variables in connection with the sales of life insurance products in Kerala. The rotated component matrix which helps in determining the component represented on the parameter as Competitive intensity, standard of living, sales promotional efforts and customer awareness the major factors contributing the study.
The component score is computed for each case and each component by multiplying the case's standardized variable values by the component score coefficients was considered which also showed that the 4 components derived represent the original 10 factors and the components are not linearly correlated with each other. Thus it can be concluded that Competitive intensity, standard of living, sales promotional efforts and customer awareness about the company and products play a critical role in the sale of life insurance products in Kerala.
The landscape of life insurance in India is changing colour rapidly. For more than four decades, LIC was holding the monopoly of Indian market. However, IRDA opened a turning point by lifting all the entry restrictions for private insurance players to sow their maiden seed in Indian soil. Creating successful sales strategies has become the key thoughts for all companies by creating innovative products, smart marketing and aggressive sales and distribution systems to walk into the hearts of Indian customers. Through the present study, considerable efforts were taken to identify the various factors that contributed for sales of life insurance products in Kerala and it was unanimously identified as the factors like competitive intensity, standard of living, sales promotional efforts and customer awareness of the company and products play a critical role in the sale of life insurance products in Kerala.