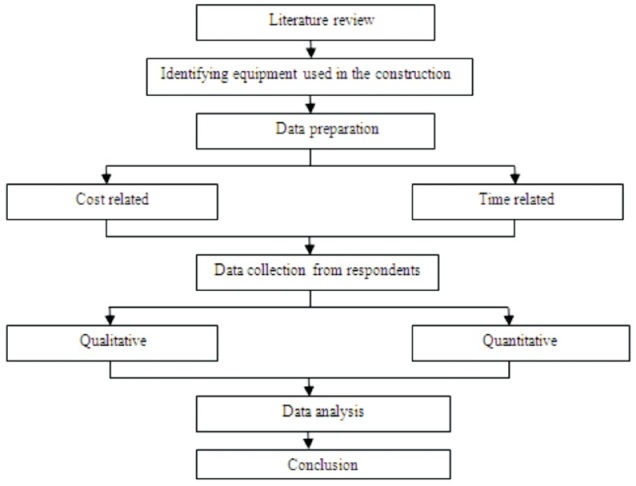
Figure 1. Flow Chart Showing the Methodology of the Study
Construction sector relies on the effective utilization of resources. Equipment is one of the major resources which leads to cost and time overruns if they are not managed properly. So the equipment should be accurately managed as they form a substantial portion of the project. Due to intricacy of projects, unavailability of manual labour and the need to complete projects in time, utilization of equipment is on an increase. Before procuring equipment, it is necessary to perform useful life analysis for the equipment and select the equipment best suited for the project. The method of procurement of construction equipment also needs careful consideration. If construction equipments are idle or breaksdown frequently, the project suffers cost and time overruns. In this study, qualitative and quantitative data are gathered to identify the most commonly used construction equipment in Indian infrastructure projects and also the critical reasons which need to be avoided or improved upon to ensure efficient equipment management. In conclusion, the paper presents the critical reasons for cost and time over-run due to mismanagement of equipment and also suggests the proactive measures to be taken to overcome idle equipment and equipment breakdown.
Construction equipment is a major resource in a construction project. In any construction project, the cost of the equipment covers 10% to 30% of the total budget of the project, depending upon the extent of mechanization. There are many projects in which the cost of equipment is above 30% due to site constraints and time limitations. With most infrastructure and real estate projects expecting a profit margin of 8% and 12% respectively, efficient equipment management is necessary.
Generally equipment are employed to complete the project within the given time and mainly, within the project schedule. With proper planning, selection, procurement, installation, operation and maintenance, and equipment replacement policy the equipment management wing of the project can be turned into a profit centre instead of a cost centre. Emphasis on reducing downtime, achieving optimum equipment utilization and increasing the production at the minimum cost is the goal of the equipment management wing.
Before starting any project, the planning of equipment should be done with great care, as the efficiency of the entire project largely depends on its planning. The planning should involve the extent of mechanization, equipment planning, equipment management, and execution planning. Even during the execution of the construction project, continuous evaluation of the equipment fleet is necessary to ensure that the equipments are optimally utilised. The construction equipments fleet need to be continuously evaluated to determine whether new equipment is needed or any of its part need replacement. There are many construction equipments which can handle multiple tasks that are ideal for one or more tasks. Similarly, some construction equipment may be suitable only for one or two specific tasks. The equipment manager has to take decisions to ensure maximum benefits with minimum costs to the company. The automobile industry has achieved considerable savings in cost and time through improved workshop layout, automation of the manufacturing and assembly process and enhancing labour efficiency. Equipment management offers a similar window for construction companies to enhance profitability.
The construction equipment manager also needs to decide whether it makes sense to buy, lease or rent the equipment. Some equipments may be required for full length duration of a project while other equipments may only be required for specific durations. Some equipment may be required for multiple projects being undertaken by the company while other equipment may be site or project specific. The transportation and operating costs of equipment, versatility of the equipment to function effectively in different terrains, water logged situations and sites with overhead high tension electrical lines require consideration.
The high failure rate and extreme competitiveness of the construction industry has forced the industry to adopt new ways to reduce construction cost. Many construction companies seek to have a competitive advantage by increasing preventive measures and controlling losses. One way that companies in the construction industry have found effective in increasing profit margins is by preventive equipment maintenance rather than breakdown repairs.
Equipment procurement and its management involve several risks. Many projects have reported major variations between the estimated and the actual quantities, which make the equipment owning and operating costs analysis redundant. In certain projects, the equipment commitment may be greater than the project returns. Projects and equipment usage are also dependent upon labour regulation and agreements, safety regulations, weather dependence, unforeseen pandemic situations and the like.
In India, more than 70% of the projects are facing cost and time overruns due to various factors, among them improper planning and maintenance of the equipment is one of the topmost factors. Construction equipment planning and management play a major role in the success of construction companies. Inadequate planning and selection of equipment and the individual decision of equipment managers, usually result in major cost and time overruns of the project.
In this study, factors which are responsible for the cost and time overruns of the project due to equipment mismanagement in a real-time construction project are identified and suggestions are made for better management of these vital resources.
This study is limited to the information collected from thirteen respondents regarding the time and cost overruns for a period of one year. Among the various equipment used in construction sector, commonly used equipment is selected for the study. Further the data were collected only from projects that are located in India.
The choice of construction equipment depends on the method of doing the work, the time to complete the work, and the cost of construction (Day & Benjamin, 1924). Ibbs and Terveer (1984) stated that maintenance of heavy construction equipment is a vital requirement for increasing construction efficiency. Frimpong et al. (2003) identified the significant factors that cause delay and cost overrun; among them project financing factors ranked highest, while the labour category was ranked lowest. Ramanathan et al. (2012) stated that usage of unsuitable construction equipment leads to time overrun. Lenin et al. (2014) found that unsuitable and inefficient construction equipment affects the productivity causing delay in project and resulting in cost overrun. Waris et al. (2014) hinted that selection of right equipment has always been a key factor in the success of any construction project. Adik and Bobade (2018) noticed that substantial loss of time and cost is attributed to breakdown of equipment. Prasertrungruang and Hadikusumo (2007) observed that poor training of equipment operators is a major cause of equipment related accidents. Thus, quality output can be partly achieved through skillful operators working with machines that are in good operational condition. Phadatare et al. (2016) have shown that the overall equipment efficiency improved with less idling, low machine breakdown and minimized accidents at sites. Randunupura and Hadiwattege (2013) stated that proper construction equipment management helps in minimizing the effects on time and cost overrun of the project. Odeyinka and Yusif (1997) identified 16 major factors that caused delays and cost overruns in Nigeria, of which equipment management was one of the major causes of delay and cost overrun in Nigerian construction projects. Majid and McCaffer (1998) identified that the factors such as equipment breakdown, improper equipment selection, slow mobilization of equipment, and equipment allocation as the major contributors of construction time overrun. Long et al. (2004) identified inadequate modern equipment as a factor causing time overrun of construction projects. Manikandan et al. (2018) stated that use of new site specific equipment and innovative construction methods have made possible wholesale changes in construction technologies in recent decades. Based on the method of Relative Importance Index (RII), they identified significant factors such as frequent equipment breakdown, maintenance of equipment, insufficient number of equipment etc., affecting the cost and time overrun in a project. Prajeesh and Sakthivel (2016) stated that inefficient manual process of equipment management and the subjective decisions of equipment managers result in major losses in construction projects.
In this study, qualitative and quantitative data were gathered through personal interaction with equipment managers, construction managers, site in-charge and other field personnel on the usage of different construction equipment on specific construction projects, method of procurement of the equipment (buy, lease or rent), hours of usage and period of usage, idle time, frequency of breakdown of equipment and other details. Literature study and questionnaire analysis helped in gathering this information. Several construction projects in Andhra Pradesh and Odisha states were visited for gathering this information. The projects are not mentioned in this paper to maintain confidentiality. The collected data were analysed on a five point scale of Relative Importance Index (RII) to determine the factors of construction equipment management responsible for construction time and cost overruns. The flow chart of the methodology of the study is shown in Figure 1.

Figure 1. Flow Chart Showing the Methodology of the Study
In this study, both quantitative and qualitative data were collected. The data were gathered through questionnaires, interviews and from company websites. In the quantitative analysis real-time equipment managers and senior site engineers were interviewed and the cost and time overruns were determined for a particular time period. The qualitative data were analyzed by using RII method.
The data were collected from few construction companies involved in infrastructural development works like roads, highways and commercial spaces, in India.
The details of the major equipment used, type of ownership (Rent, Lease or Purchase), number of hours the equipment was employed and number of idle hours, and cost details were collected to determine the impact of equipment management efficiency on the project. Based on the time value of money (TVM) approach and fuel cost per day, the operating cost of equipment was determined. The difference between the actual cost of work and estimated cost of work gives the overrun cost of the project and idle time represents the time which equipment is nonproductive, due to which there is a time overrun in the project. Table 1 shows the details of the major equipments used and the impact of the equipment management efficiency in completing the work within the project schedule and at the estimated cost.
It can be seen from Table 1 that the idling/breakdown of the equipment has resulted in both cost and time overruns. Column (6) of Table 1 gives details of the additional time (6) the equipment has to be used on the work to make up for the lost time due to idle time of the equipments. Table 2 gives details of the cost overrun and the percentage cost overrun for each of the equipment. It can be seen that the cost overrun ranges from 4.87% to 36.95%. It is evident that the impact of these overruns on the project schedule and cost would be considerable. Column (10) of the Table 1 shows the actual cost spent on the equipment due to the additional time it has to be used on the work to make up for the lost time [Actual cost = Estimated cost of work + (No.of hrs idle x Operating cost per hour)].
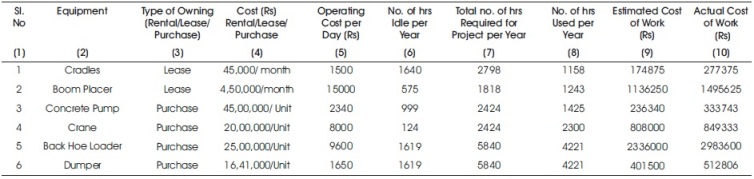
Table 1. Equipment Usage, Time and Cost Details
Column (6) of Table 2 gives the percentage of additional cost spent on the equipment in real-time projects [Cost overrun = (Actual Cost of work - Estimated Cost of work) / Actual Cost of work]
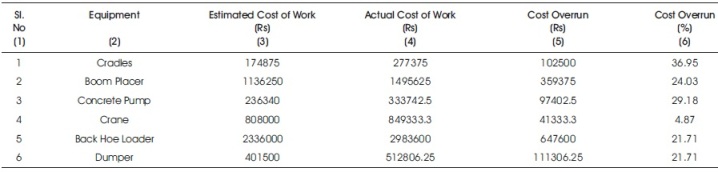
Table 2. Cost Overrun Due to Idling/break Down of Equipment
Eight issues related to equipment planning and management came up as important based on literature review and interaction with equipment managers, project managers and other field staff. The Relative Importance Index (RII) method was employed to determine the relative importance of these problems that affect the productivity of equipment on construction projects. These issues were ranked based on the value of the RII.
To calculate RII, a five-point scale of 1 (very low), 2 (low), 3 (medium) and 4 (high) and 5 (very high) was adopted to determine the RII. The Relative Importance Index (RII) is calculated using the formula
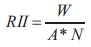
where,
W= sum of weightages given by the respondents for each critical reason
A= Weightage value 1-5
N= No. of respondents (13)
Data collected from 13 respondents were analysed using the RII method. The higher the value of RII, the more significant the problem is. These rankings made it possible to cross-compare the importance of major equipment planning and management problems as perceived by the different companies. The survey data collected from the 13 construction companies are given in Table 3. The calculated RII value of equipment planning and management problems are depicted in Table 3. These RII values explain how far the construction equipment planning and management problems affect the performance of the construction project.
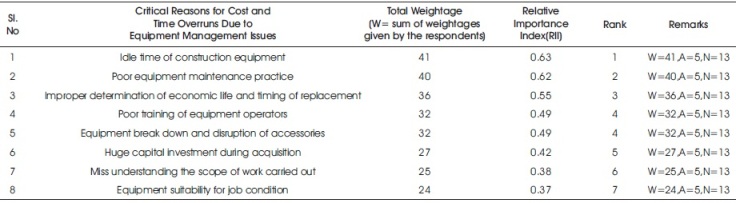
Table 3. Ranking of Critical Reasons for Cost and Time Overruns
As can be seen from Table 3, 'idle time of construction equipment' with a Relative Importance Index (RII) of 0.63 is the most critical reason while 'equipment suitability for job condition' with a Relative Importance Index (RII) of 0.37 has the lowest critical importance. It can also be seen that 'poor training of equipment operators' and 'equipment break down and disruption of accessories' are considered equally important critical reasons responsible for cost and time over-runs. Figure 2, illustrates the ranked construction equipment planning and management problems based on the survey data.
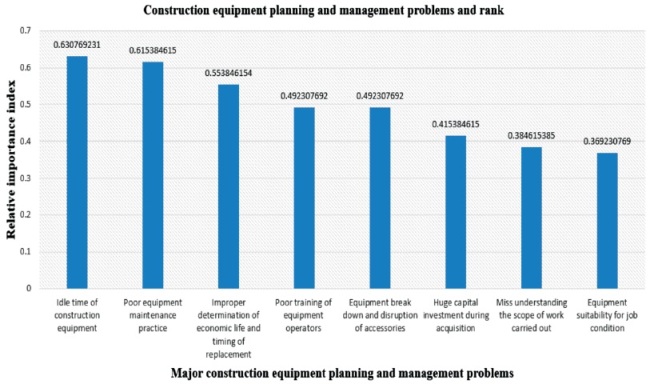
Figure 2. The Ranked Construction Equipment Planning and Management Problems Based on the Survey Data
The result state that idle time, poor equipment maintenance practices, equipment breakdown, improper determination of economic life and timing of replacement, poor training of equipment operators, huge capital investment at the time of the acquisition, misunderstanding the scope of work carried out and equipment suitability for job condition are the major problems that affect construction equipment planning and management on projects during the planning and construction process.
From the study, it is seen that equipments play an important role in the profitability of projects and help in reducing cost and time overruns. For the projects investigated, the cost overrun ranged from 4.87% for cranes to 36.95% for cradles. It is evident that the impact of these overruns on the project schedule and cost would be considerable. The qualitative analysis has suggested eight critical reasons for cost and time overruns from equipment. Hence, proactive equipment management techniques have to be adopted to reduce equipment idling and breakdowns.