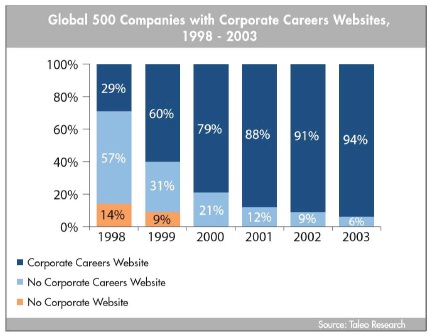
Figure 1. Global 500 Companies with Corporate Career Websites 1988-2003
This paper explores the conceptual inquiry on recruitment and selection in the digital age. The corporate career website, commercial websites, and social media are widely used in recruitment process throughout the world. An analytical research provides factual inquiry on trends in e-recruitment and selection practices globally. This paper identifies the reason for online recruitment such as reduction of recruitment costs, availability of more number of candidates, effective use of social media tool for employee referrals, and availability of top talented persons across geographical locations. The challenges faced by an organization in e-recruitment process include restriction on use of social media, content on the digital application, too much information about the candidate, and efficiency in response time is too low. Commercial websites and social networking sites are key to the recruiter in reduction of recruitment process due to usage of e-recruitment and selection practices.
Recruitment and selection is a continuous function of Human Resource management. Use of technology helps the company in maintenance of human resource information system to make effective decision on recruitment and selection to get an advantage over traditional practices (Barber, 1998). Human Resource Information System (HRIS) explores the possibilities of storage, analysis, retrieval, and distribution of information about workforce in an organization (Kavanagh, Gueutal, & Tannenbaum, 1990). The recruitment process conducted through web-based tools like Internet site or intranet of business organization is called as E-recruiting (Kerrin & Kettley, 2003). Alternatively, e-recruitment and selection in the digital age is the process of recruiting and selection of candidates through use of career websites, commercial websites, and social media. The selection of the job aspirant is shortlisted by Human resource personnel and before a consensus arrived through decision support system with multiple criteria and group discussion of the potential applicants (Shih, Huang, & Shyur, 2005). This implies the automatic selection of the job aspirant for a given job.
A research on content analysis of 'online job application form' conducted on 76 companies in 2005 and 66 companies in 2009 that are listed in Spanish Stock Exchange, reveals certain issues related to discrimination on hiring decision and data privacy of applicants information (García-Izquierdo, Aguinis, & Ramos-Villagrasa, 2010). A study reveals that collection of applicant information pertains to 24 categories through online application remains stable, i.e., these have not been revised, which led to lawsuit on hiring companies due to discrimination on hiring decisions and violates the privacy of applicant information. The study concludes negative aspects of e-recruitment such as discrimination in hiring decisions and violation of applicant privacy. In automated e-recruitment system that works on 'Analytical Hierarchy Process' ranks the candidates based on credible criteria. The criteria include education, work experience, and personality (Faliagka, Tsakalidis, & Tzimas, 2012). The e-recruitment system consists of job application module, where the candidates have to login to the Linked in profile. Linguistic Inquiry and Word Count Analysis measures candidate personality traits from his/her blog. Weightage is given to candidates based on analysis of LinkedIn profile (education, experience), blog (to measure personality on linguistic usage), and then a rank is assigned by comparing between the candidates through Ranking module of 'Analytical Hierarchy Process'. An experimental test was conducted by a researcher on technology industry of unnamed IT Company with three different positions. Hundred candidates have been selected who are bloggers along with a LinkedIn profile to test e-recruitment system. It reveals that selection of candidates with extroversion has an error of fewer than 1.5 grades in grading scale of 0-5 for 80 percent and a correlation coefficient of 0.63 between recruiters and systems core. There is an average error of ±4 positions of candidate errors. The e-recruitment system finds it difficult to get accuracy for domain-specific work experience. It concludes that experimental test on Big five personality other than extroversion is to be conducted to make the e-recruitment system automatic in the selection of candidates for personal interview for the posted jobs.
The Objectives of the study include the following.
To obtain the facts or information, an analytical research methodology have been applied to collect, analyze, and know the facts.
Secondary data has collected from Surveys, Journals, and reports of the consulting solutions on internet recruitment and selection in the digital age.
The Investigators conducted an exploratory study on 40 e- Recruiting websites of large companies belongs to different industries in the Netherlands (Furtmueller, Wilderom, & Tate, 2011). Seventeen recruiters have interviewed to understand requirements on digital resume. The contents analysis of the e-recruiting website of companies and recruiters’ interviews reveal the personal and contact information, education, work experience, extra activities, skills, references in resume have identified as requirements for the interviewers in the selection of the potential applicant. The researchers added career status and the desired jobs to the existing online content of e-recruitment website. 25% of recruiters are dissatisfied due to unnecessary information in digital resume of candidates that were obtained through erecruitment websites. They concluded that the online application of e-recruitment website should be designed to select the applicant as per the job advertisement. This has become the challenging task to the users of present e-recruitment website.
The research on use and success of corporate and commercial recruitment methods in the UK reveals that there is a gradual increase in usage of internet recruitment by large-scale organizations (Parry & Tyson, 2008). The exploratory study conducted through survey and interview method indicates that website based recruitment is not suitable for blue-collar and senior-most personnel in small organization. The perceived success of online recruitment compared with other recruitment methods such as corporate website, commercial website, national newspapers, regional newspapers, professional magazines, employment agencies and recruiters gives an insight on dependence of organizations on the other methods depending on the recruiter's requirement. Metrics of success on successful use of corporate and commercial websites such as costs reduction and enhancement of efficiency. However, pooling of the right applicant for the job from the online recruitment has become a challenging task to the recruiters.
Factual inquiry on pursuance of e-recruitment from various organizational responses (Kerrin & Kettley, 2003) indicates: improvement of employer profile and corporate image (80 percent), Reduction of recruitment costs (78 percent), Reduction of administration burden (62 percent), and Better tools for recruitment team (62 percent). Further, shorter recruitment cycle (56 percent), Expectation/preference of candidates (51 percent), and Better fit (screening large pool) (33 percent). Major challenges in implementing in e-recruitment, include cultural approach, Lack of knowledge, Internet usage, senior management commitment, inadequate software, and security.
Figure1 in the Annexure depicts The Taleo Research Report on the Global 500 group of companies on recruiting website conducted in 2003 as complies by Fortune Magazine, reveals usage of 'corporate career websites' between 1998 to 2003 has shown an increase from 29 percent to 94 percent. 'No corporate career website' during 1988 to 2003 has drastically declined to 6 percent from 57 percent. It implies that trend in erecruiting has been increased by the large firms using corporate career websites (Global 500 website Recruiting 2003 Survey, 2003).
The Global Recruiting Trends 2016 conducted by LinkedIn Talent Solutions on talent leaders value quality of hires to be better performance (by 39 percent), employee referral programme to be long-lasting trend (by 26 percent), top priority is employee retention over the next 12 months (by 32 percent), employer brand investment is more than last year (by 59 percent).
Figure 2 in Annexure depicts the Organizations give top priority in brand value and a proactive brand strategy. 62 percent respondent of talent leaders give employer brand priority and 55 percent have proactive employer brand strategy, such as social media, online professional networks, and company website. The investment in improvement of employer branding has significantly increased to 59 percent compared from 2012 to 2015 (Abbot, Batty, & Bevegni, 2016). The organization uses Company websites and social media as effective branding tools than compared with online professional networks (68 percent, 61 percent, and 47 percent). There is a significant increase in use of social media for effective employer branding.
Figure 3 in Annexure depicts increasing trends in Hiring volume from 2012 to 2015 (42 percent to 62 percent). Similarly, there is no consistency in hiring budget, as there is fluctuation. This acts as an obstacle in attracting of top talent arising from competition with the peers.
The Global recruiting Survey 2016 conducted on 998 recruiting professionals survey by Social Talent and Alexander Mann solutions reports successful methods of recruitment takes places on social media (by 37 percent), paid job board (by 26 percent), other option by 12 percent), direct applications or companies career site (by 11 percent). Further, Internal referrals or Alumni (by 9 percent), Recruitment Agencies (by 3 percent), Non-paid job boards (by 3 percent). The response of recruiters towards search results, response from job aspirants when contacted is poor. There needs an improvement in the online sourcing tools.
Figure 4 in Annexure represents The LinkedIn networking tops recruiters choice for sourcing the applicant during 2015 (97 percent) and 2014 (96 percent) than compared with Twitter, Facebook and Google Plus (2016 Global Recruiting Survey, 2016).
The Factual inquiry on the ways recruiters try to contract the top talent or job aspirant are as follows: 81 percent of recruiters either send an Email or add a passive candidate as a LinkedIn connection in order to engage with candidates. Only 14 percent take the time to find an email address, and only 5 percent pick up the phone to try to reach the talent. The recruiters are using Message apps in the recruitment process by 65 percent i.e., 55 percent used Skype, 25 percent WhatsApp to contact and engage with applicants.
The literature shows there is an increase in online recruitment practices in the organization throughout the world. The reasons for internet recruitment benefits reduction of recruiting costs, availability of more candidates, and efficiency in the process. The content analysis of e-recruiting website creates a challenging task for the recruiters due to unnecessary information of candidates for selection through e-recruiting websites. This has created a potential threat to the litigation on the privacy of candidate information. Another challenge is that selection of candidates becomes time-consuming. The developer of the e-recruitment website such as commercial, corporate website, and social networking sites has to be designed based on advertised jobs or on company requirements. There is an increased investment in company branding to attract the top talent across geographical locations. The employee referral schemes by organization mostly preferred platform through social media preferable LinkedIn followed by Twitter and Facebook. For communication, recruiters are using message apps as successful e-recruitment tools preferable Skype, followed by WhatsApp to contact and engage with candidates. Hence, automated selection of candidate to source through e-recruitment websites for all the industries is required to reduce the time and efficiency as per the advertised job.

Figure 1. Global 500 Companies with Corporate Career Websites 1988-2003
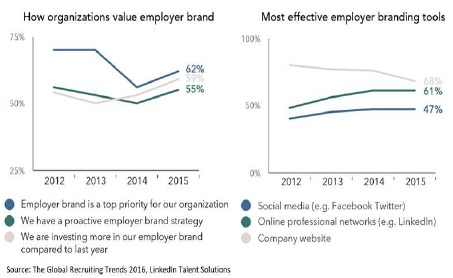
Figure 2. Trends in Organization value Employer Brand and Branding Tools
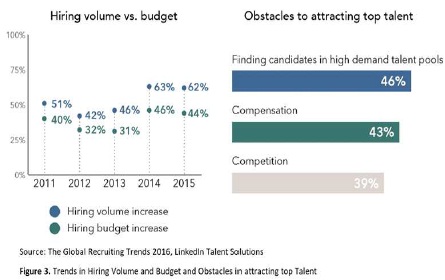
Figure 3. Trends in Hiring Volume and Budget and Obstacles in Attracting top Talent
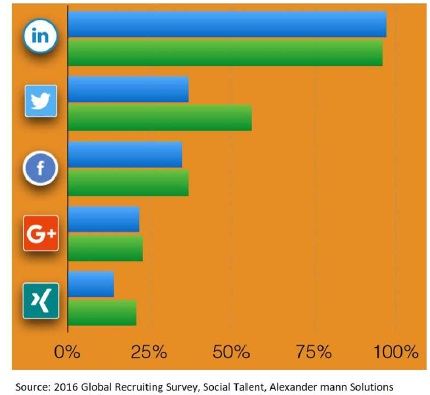
Figure 4. Successful Methods of Recruitment takes place on Social Media