Table 1. Validity Test of Cluster Analysis Variables
Any indirect tax will have an impact on the consumer spending ability. Even direct taxes will affect the consumer spending ability but confines more to the tax payers. Goods and Services Tax (GST) has also affected the purchasing capacity of the consumers. This is because any economic reform will result in short term or medium term inflation which will reduce the purchasing power of the consumers. This research seeks to group the consumers based on the spending ability after goods and services tax implementation. Cluster analysis is a most commonly used analytical technique to classify homogeneous groups. The study classifies consumers into three major clusters and tries to explain each of these cluster characteristics by indicating priorities of the clusters based on their spending ability. While there are many type of cluster analysis being followed, this study uses K-means clustering to classify homogenous groups. Finally, the study arrives at a meaningful conclusion and can be used as a basis for further researches relating to taxes and consumer choices.
Understanding the consumer behavior is important for every marketing firm. There are many factors that will influence the consumer behavior. Consumer behavior is complex in nature and identifying the target market is a key task for any marketing manager. However research studies found that though consumer behavior is complex to understand, consumers of similar characteristics exhibit similar kind of purchase behavior.
Goods and Services Tax (GST) is the new indirect tax introduced in India which subsumed many of the multiple indirect taxes previously existing in the country. Taxes and consumer choices have a significant relationship with each other. In fact many countries use taxes as weapons to modify the behavior of consumers or to alter unfavorable demand prevailing in the market which can lead to rising inflation level. Likewise, goods and services taxes also affect the consumer behavior.
Many research studies have been carried out regarding the impact of goods and services tax on the spending ability. Research studies focusing on the consumer perception and brand preferences after goods and service tax implementation have been carried out. However, no research study seeks to classify the consumers based on spending ability which will pave way for market segment research.
Hence there is a research gap which needs to be fulfilled and hence this research study is carried out. Goods and services tax can be defined as the destination based taxation system whereby the taxes accrues on the place of consumption rather than the place of manufacturing with a new unique feature input tax credit attached to it. Various studies were carried out before the implementation of GST on how it will work and benefit the Indian economy. Dr. R. Vasanthagopal (2011) stated that GST will be a positive step in booming the Indian economy. Vinod Kumar (2017) also stated that GST will be a benefit for the end consumer as the GST will reduce the overall tax burden on the goods and services in the country (Kumar, 2017). With this background on GST and consumer behavior, this paper seeks to use cluster analysis to classify consumers based on their spending ability after goods and services tax implementation.
Kumar (2014) in his study entitled “Goods and Service Tax- A Way Forward” and concluded that implementation of GST in India helps in removing economic distortion by current indirect tax system and expected to encourage unbiased tax structure which is indifferent to geographical locations.
Pinki, Supriya Kamma and Richa Verma (July 2014) in their studt entitled “Goods and Service Tax- Panacea For Indirect Tax System in India” concluded that the new NDA government in India is positive towards implementation of GST and it is beneficial for central government, state government and as well as for consumers in long run if its implementation is backed by strong IT infrastructure.
Gupta (2014) in his study titled “Goods and Services Tax and its impact on Indian Economy” stated that implementation of GST in the Indian framework will lead to commercial benefits which were untouched by the Value-Added Tax (VAT) system and would essentially lead to economic development. Hence GST may usher in the possibility of a collective gain for industry, trade, agriculture and common consumers as well as for the Central Government and the State Government.
Ahmad et al., (2016) conducted a study on “Awareness and perception of tax payers towards Goods and Service Tax implementation" and concluded that consumers in Malaysia have high negative perception to the GST due to its impact on their purchasing power.
Barhate (2017) in his study tiltled “An Analytical Study of Awareness and Perception towards GST among traders in Rural areas” concluded that the benefits of GST can be enjoyed by correcting the problems in the way it is implemented and consumers can enjoy the real benefits of GST.
Agarwal (2017) in his paper titled “People Perceptions about GST” concluded that GST has increased legal compliances, increases the price level in the country but a good tax reform for the country on long term basis. Increase in price level will affect the spending ability and small businesses.
Ramkumar (2017) in his study titled “Impact of GST on consumer spending ability in Chennai City” concluded that consumers are left with less money after GST, rise in inflation level and fall in prices of certain goods after GST implementation. He further concluded that GST rates will have a significant impact on the spending ability of the consumers and suggested that benefits of input tax credit must be transferred by the companies to the consumers.
Ramkumar (2018a) in his study titled “Consumer perceptions towards Goods and Ser vices Tax Implementation – An Economic approach” concluded that four tier system of goods and services tax will help in taxing the luxury items at a higher level and certain revisions made after the initial implementation of goods and services tax has reduced the burden of consumers and concluded that it will take time to evaluate whether the new tax system has benefited India or not.
Ramkumar (2018b) in his research study titled “A Study on factors influencing the purchase decision of young adults after goods and services tax implementation in India – with special reference to FMCG products” identified two major factors influencing the purchase decision of consumers namely consumer oriented factors and seller oriented factors. He concluded that goods and services tax is expected to make India one common economic market but to ensure greater transparency suggested that separation should be given like cost, profit and then tax charged which will benefit the consumers.
Ramkumar (2018c) in his study titled “A Study on the spending ability of FMCG Consumers after GST Implementation” concluded that goods and services tax introduced recently in India has a significant impact on the spending ability of the consumers. He further concluded that spending ability of fast moving consumer goods (FMG) consumers have decreased after the implementation of goods and services tax due to effects of multiple economic reforms in the shorter period of time.
From the above it is clear that while the research studies on goods and services tax focus on the impact of it on the economy, consumer perceptions and so on, none of the studies focused on how the goods and services tax will modify consumer behavior. This can be done through grouping the consumers based on their homogeneous characteristics. Hence a research study needs to be carried out to group consumers which can be done through cluster analysis. Thus, the present study will contribute significant to indirect taxes research studies.
Goods and services tax is considered to be an important tax reform in the country. With the destination based tax, it has a significant impact on the spending ability of the consumers. As a result, the purchasing behavior of the consumers changes due to multitier system of goods and services tax in the nation. It is important to understand the consumer behavior as it will have an impact on the profits of the company. The success of marketing efforts of companies depends on the better understanding of consumer behavior. Only then they can create, deliver and communicate value to the customers. Hence there is a need to conduct a research study which groups consumers based on the spending ability which will benefit the marketing firms and also helps in understanding the consumer behavior.
The novelty of the research indicates the uniqueness of the research study being carried out. Several research studies have been conducted on the goods and service tax. Some research studies focused on the impact of goods and services tax on different sectors of the economy while some other researches focused on how the goods and services tax will impact the consumers and their spending ability. This research study is unique because instead of focusing on the impact of goods and services tax on spending ability, it focuses on classifying the consumers based on their homogeneity after goods and services tax implementation.
The main objectives of the study are as follows:
This research study will benefit the following
This study will benefit the marketing managers by providing them an idea about how the consumers can be classified based on their spending ability after goods and services tax implementation. Further this will enable them to direct their marketing efforts according to the appropriate needs of different class of customers. Similarly, this study will also benefit the marketing managers as they can use the results of the study for market segmentation and then create, communicate and deliver value according to respective market segments they are dealing with.
This research study will also help marketing researchers. The marketing researchers can improve this study by classifying the consumers based on their factors affecting purchase decision. Further they develop research study in this area by focusing on marketing strategies for the consumer segments classified by the study. The results can also be used to conduct market segment researches.
The data required for this study is collected from both primary and secondary sources.
This research study is a quantitative research study. A quantitative research study is a study where a problem which is being studied by the researcher is supported by generating data which can be later converted into usable statistics giving meaningful conclusion.
6.2.1 Primary Data
Primary sources are the sources that are collected originally rather than being already made available. The data obtained from these sources are called primary data. The primary data for the study is collected through survey method using structured questionnaire. The primary data often is available in raw form which is then processed to make itself suitable for further analysis to arrive at meaningful conclusion.
6.2.2 Secondary Data
The secondary sources represent those data made available in a suitable form to lend itself for further analysis. Often they do not require any processing and can be used for analysis purpose. The secondary data for the research is collected through journals, magazines and books relating to economic effects of taxes on the economy.
6.3.1 Sample Size
The sample size for the study is 150 respondents from Chennai city. The sample size for the study is arrived through G-power statistics 3.1 software which helps in determining the sample size based on the analytical tool used for the study.
6.3.2 Sampling Technique
This research study is based on simple random sampling method. This sampling technique gives each element an equal and independence chance of being selected rather than pre-determining the samples to be selected.
6.3.3 Sampling Unit
The sampling unit for the study is the consumers of FMCG products. Industrial consumers do not represent the sampling unit for the study.
The analysis for this study has been carried out through IBM SPSS Version 22 Software. The analytical tool used for the study is cluster analysis. K-means clustering analysis is used to classify the consumers based on their spending ability. K-means cluster analysis is a cluster analysis technique which helps in grouping the observations into K clusters based on their association with the nearest mean value. This is the most widely used and common method of cluster analysis whose results can be used as a basis for further research studies.
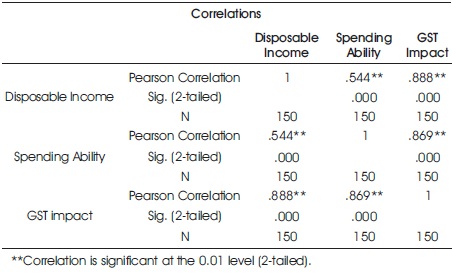
E. Croarkin (2004) states correlation as one of the ways to study the validity of the research instruments. Table 1 shows the validity testing of instruments intended to measure the GST impact. From the table, it is clear that all the instruments have a significance influence on the GST impact. Since the values are highly significant at 1% level, the instrument used for measuring the GST is valid for 88.8% in case of GST aspects, 86.9% in case of GST Implementation and 81.5% in case of GST rates.

Table 1. Validity Test of Cluster Analysis Variables
6.5.1 Reliability Test
Table 2 shows the reliability statistics of the measures used for cluster analysis. Since the calculated 0.842 which is more than the standard value of 0.5, it has the highest reliability on the constructs used for the study.
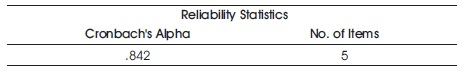
Table 2. Reliability Statistics
The various limitations of the study are as follows
Table 3 shows the initial cluster centers. Table 4 shows the iteration history which tells the number of iterations carried to achieve the convergence. Table 5 shows the final cluster centers which is of significant importance in analyzing the results of cluster analysis. Table 6 shows the ANOVA table. Table 7 shows the number of cases in each cluster. The results of final cluster analysis are represented in the form of the diagram shown in Figure 1.
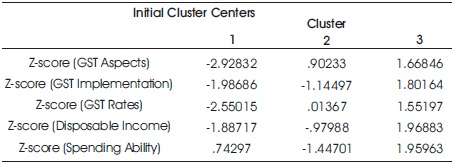
Table 3. Initial Cluster Centers
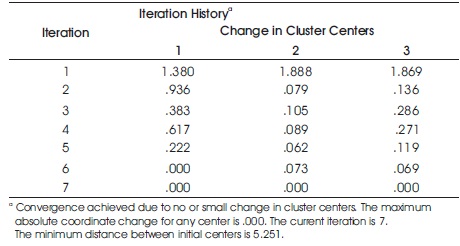
Table 4. Iteration History
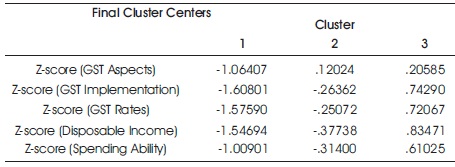
Table 5. Final Cluster Centers
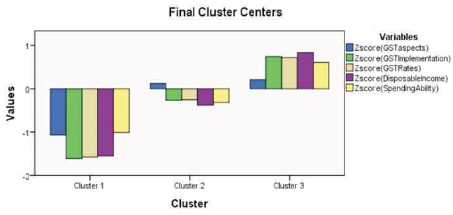
Figure 1. Final Cluster Centers
The tables show the results of cluster analysis through various sub tables. The study groups the consumers based on the spending ability. To classify the consumers based on the spending ability, the various independent variables influencing the spending ability is also considered. Table 3 shows the initial cluster centers. This initial cluster centers show the allocation of consumers to different clusters before any iterations or convergence. This table is often generated along with cluster analysis and do not have much significance in interpreting the results of the analysis. Table 4 shows the iteration history which tells the number of iterations carried to achieve the convergence. Generally iterations to maximum of 10 is considered acceptable. In other words, if the convergence is achieved before 10 iterations, then it means that the data is very well suitable for the cluster analysis. In this case, the iterations have been achieved within 7 iterations, thus indicating the data is very well suitable to conduct the cluster analysis. Table 5 shows the final cluster centers which is of significant importance in analyzing the results of cluster analysis. The results of final cluster analysis are represented in the form of the diagram in Figure 1. Based on Table 7 and Figure 1, it is clear that GST aspects, rates, implementation, disposable income and spending ability have a weak or low relationship or significance in the cluster 1 and cluster 2. However it should be noted that, in cluster 2, the degree of weakness is far reduced than in cluster 1. It should also be noted that all the variables are positively significant in cluster 3 and it shows that many of the consumers fit in the cluster 3 based on the variables used for the study. Table 6 shows the ANOVA table. This table is also of significance importance as it helps in deciding whether the variables used for cluster analysis is suitable to group the consumers based on the cluster analysis. Based on the results of the table it is clear that all the variables are significantly suitable for cluster analysis as the computed values are much less than the significance value both at 1% level and 5% level.
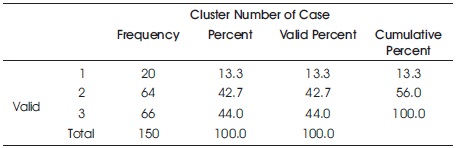
Table 7. Number of Cases in Each Cluster
Table 7 shows the number of cases in each cluster. The clusters are labeled as follows:
Cluster 1 – Low spending ability
Cluster 2 – Moderate spending ability
Cluster 3 – High spending ability
7.2.1 Low Spending Ability
Based on Table 7, it is clear that 13.3% of the respondents have low spending ability after GST implementation. Though this percentage is slightly lesser compared to other clusters, it should be given importance. GST may have reduced the spending ability of these consumers because increase in the prices of products may not been offset by the increase in their disposable income. Thus with increase in prices accompanied by stagnant income level of the consumer can result in low spending ability. There can also be several controllable and uncontrollable factors that might have affected the spending ability of the consumers. These respondents often spend based on the importance and requirements and seeks to satisfy the basic needs due to low spending ability.
7.2.2 Moderate Spending Abilit
Based on Table 7, it is clear that 42.7% of the respondents have moderate spending ability after GST implementation. There is significant proportion of the consumers falling under this cluster. This shows that GST has impacted the different sections of the consumers in different ways. The moderate spending ability can be due to many reasons. One, the rise in prices of certain goods may not be felt as a significant increase by the consumers and may have little impact on their disposable income. Second, only prices of certain goods have increased and these might have been less consumed by these consumers. Third, moderate spending ability can also be due to increased prices being offset by a slight increase in income. These respondents spend considerable amount of money in comforts as satisfying the basic needs is not a problem and purchases comfort goods when surplus is available with them.
7.2.3 High Spending Ability
Based on Table 7, it is clear that 44% of the consumers have high spending ability after GST implementation. This may be due to the increase in their disposable income. Just before few months of implementation of GST, the income tax slab was brought down to 5 %. This might have resulted in significant increase in their spending ability. Due to high spending ability, they will be in a position not only to purchase comforts but also to spend on luxury goods.
The findings of the study are as follows:
To conclude, goods and services tax is an important tax reform taken place in the country. Understanding the consumer behavior is important as the success of companies depends on their consumers. Identifying the market segment is also important for marketers. A marketing firm cannot satisfy the needs of all market segments. The study classifies the consumers into three clusters and gives an insight into how spending ability of consumers change with GST and how their purchasing behavior will be. The study can be used as a basis for market segmentation using spending ability as base of segmentation from taxation perspective.