A Study on Factors Affecting Purchase Decision of Young Adults after GST Implementation in India – with Special Reference to FMCG Products
Gowtham Ramkumar
PG Scholar, Madras Christian College, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India .
Abstract
Goods and Services Tax (GST) is considered to be a major and important indirect tax reform in India. It has affected almost all the sectors of the economy. It has also affected the economic growth. Consumers are not exception to the impact of GST. Fast Moving Consumer Goods (FMCG) industry has witnessed a price rise in certain goods. Purchase decision of consumers play an important role in determining the volume of business by FMCG companies. This is the reason companies undertake various marketing programs and activities to influence consumers towards purchasing their products. This study focuses on factors influencing the purchase decisions of young adults after GST implementation as this major tax reform has affected each and every citizen of the country. For this purpose, 100 respondents are surveyed and collected data are analyzed through SPSS 21 version software. The study identifies and groups the variables into two major factors, namely consumer oriented and seller oriented factors. Finally, this study provides a meaningful conclusion and provides a scope for further research in this area.
Keywords:
- Tax Reform,
- GST,
- Price Rise,
- Purchase Decision of Young Adults
Introduction
Taxation plays a major role in the economy of any country. Tax revenues are the major source of income for governments. In fact major social welfare and development schemes are funded through the revenues generated by taxes in various forms. Tax policies not only exerts its importance at domestic level, but also determines the international competitiveness of the country. For example, in case of imports and exports, tariff rate is considered as an important factor. Similarly, foreign investors also consider the tax rate prevailing in a nation before they take the decision of investing in that particular. A country, in order to attract foreign investment may give tax holidays, say for five years, but this is not enough for foreign investors. The factor they consider is that after five years, the amount they have to pay as tax and its procedural formalities. While this is an important consideration from the economy point of view, any tax reform will affect the final consumers in the domestic market. While various preliminary research studies are carried out regarding the expected benefits of GST and its drawbacks, now GST is implemented. This requires a need to study the purchase decisions of the consumers after GST implementation, as GST has affected almost all the sectors. This study tries to identify the factors influencing purchase decision of young adults after GST implementation. Before proceeding with the study, it is important to understand the conceptual framework for GST which discusses what GST is really all about, its features and why it is needed for the country.
1. Goods and Services Tax (GST)
1.1 Goods and Services Tax - Meaning
Goods and Services Tax is a destination based tax on consumption of goods and services, where tax will be levied at all stages from the stage of manufacturing till the final consumption and set off is allowed in the form of input tax credit to the business parties involved in the process (Central Board of Excise and Customs New Delhi, 2017).
1.2 Features of GST
- Dual GST
This is one of the unique features of GST in India. The proposed GST is to be levied in two forms, namely Central Goods and Services Tax (CGST) and State Goods and Services Tax (SGST). The term CGST refers to the GST charged on the behalf of central government and SGST refers to the GST charged on behalf of the state government. The Indian constitution gives power for both central and state government to levy and collect taxes. Thus a dual GST model is proposed. CGST will be administered by central government and SGST will administered by the state government. Thus both governments will generate revenue through GST
- No Distinction between Goods and Services
The new proposed GST treats goods and services same. In other words, both are on the same page. The law does discriminate between goods and services. Both goods and services will be taxed at the same rate. The law also gives clear explanation on; what constitutes goods and what constitutes services.
- Tax Rates
Uniform tax rate is another distinguishing feature of GST. Though four different rates are proposed, a group of sector comes under the same tax slab. Unlike the present system of different taxes, GST abolishes them and will have a uniform tax rate across the nation.
- Destination Feature
This is the fundamental feature of the GST. The destination feature indicates that the tax will accrue at the place of consumption, i.e. the place where goods or services will be received.
- Interstate Transactions
Interstate transactions are governed by Integrated Goods and Service Tax (IGST), which is a combination of CGST and SGST. The interstate transactions will also attract additional tax. IGST will be administered by the central government.
- Barter Transactions are also Taxable
Any interstate transactions which involve the nature of exchange of goods and/or service for another goods and/or service, they are also subject to IGST under the new tax system.
- Input Tax Credit
As indicated earlier, GST will be levied right from the stage of manufacturing till stage of consumption. This means that at each stage GST will be levied. In each of these stages, GST paid will be allowed to set off against the GST paid in the next stage.
- Mechanism of Set off
Set off is allowed only with the respective GST. For instance, the credit of CGST can be adjusted only with CGST and similar mechanism for SGST.
- Compensation
The present tax system does not give any compensation for the loss arising in generating tax revenue. But the present proposed GST law on recommendation by GST council will compensate the losses incurred by the state due to new tax regime for five years.
- Treatment of Exports and SEZ
Exports will be zero rated as currently they are. But in case of Special Economic Zones (SEZ), it will be zero rated only when if the supply of goods and/or service is meant for consumption in processing zone.
1.3 Need for GST
The GST is required for the following reasons:
- To stimulate economic activity: Though the economic activity is increasing over the years, it has not contributed significantly to our GDP when we compare ourselves with developed nations like US. Due to differentiated tax system, some sectors look attractive compared to others. Thus, when GST comes into effect it is expected that economic activity will increase at higher rate. When economic activity increases we can expect a increase in development activities in the country.
- To reduce cost: In GST, input tax credit helps in reducing the value added at each stage as seen earlier. Thus it helps in reducing the cost added at each of business activity.
- To reduce government expenditure: If we take at national level, government needs to spend a considerable amount in collecting taxes. Since we have a varied tax system now, it will cost high. But when there is one common tax for all, these expenses are expected to reduce to some extent.
- To remove state barriers: With common tax system, the barriers to enter different states will be removed as all the states will be governed by uniform tax rate system.
- To make easy compliance: Instead of following procedural formalities for excise, customs and services tax respectively, with the help of GST, these procedural complexities will be the reduced ones making it easy for both business houses and government to administer.
- Equality of states: GST through the destination feature treats states equally. The consuming state will be benefited by the tax revenue and the law also compensates the loss of supplier state. Thus, equality is maintained in revenue generation though the amount of revenue varies.
- Ease of doing business: Ease of doing business is an index used by World Bank to measure how attractive a country is to attract foreign investment. GST will make India one common economic market, which will contribute to ease of doing business index. Thus the international competitiveness improves.
- To generate employment: It is expected that GST will help in attracting foreign investments. More the foreign investments, more employment opportunities will be created. Through exports and imports, Foreignexchange (FOREX) reserves are also expected to increase.
- Transparency: GST ensures transparency, as total tax element is reflected on the invoice given to the consumer. There is also seamless tax credit in the value chain, i.e. mechanism of tax credit is same at all stages.
1.4 Drawbacks of GST in India
1.4.1 Change in Business Software
Different business software packages are now used by the companies. These packages are already preloaded with different taxes and service tax already incorporated in them. After the introduction of GST, the businesses are required to update their software and much confusion was also prevailing on the mechanism of the GST. This is the additional cost for the businesses as the software packages are costly.
1.4.2 GST Compliance
SMEs and several other businesses are not totally aware of the new tax regime. Understanding the mechanism is important as it directly affects the pricing and several aspects of business about which the businesses are not completely aware of. Many complexities involved in compliance at various stages like filling returns, invoices, etc., makes the process further complicated. Small scale businesses find themselves difficult to adapt to digital mode of compliance which GST mandates for business transactions.
1.4.3 Increase in Operating Costs
Previously small businesses filed their returns on their own and preferred to pay taxes on their own without the assistance of the tax professionals. However, now they are required to avail the services of the tax professionals as the tax regime is completely new for them. Though it will benefit the tax professionals in the country, it has now become the additional cost for these small businesses as they are now forced to hire the services of these tax experts. Also, businesses will need to train their employees in GST compliance, further increasing their overhead expenses.
1.4.4 Online Procedure
GST compliance, return filing and payments all have to be done online. Many small businesses are not techsavvy and do not have the resources for fully computerized compliance. Even as the rest of the nation gets ready to go digital, businesses in small cities across India face a huge technology problem in the days ahead.
1.4.5 Clarity on Tax Holidays
Before introduction of GST, different industries are given tax holidays and several other monetary and other supports from the government. After the introduction of GST, whether such benefits will be still provided is a question to be answered. In case of suspension of these benefits, it will be an additional cost for the business and these costs will be ultimately transferred to the customers.
1.4.6 Disruption to Business
Many unorganized sectors are getting affected by the new tax reform in the country. Many protests and many small scale businesses announced strikes to reduce the tax rates charged for the goods related to their respected business. This is not only relevant for a particular country like India. Even other countries faced similar problems when they introduced goods and services tax. For example, when Malaysia introduced GST in 2014, the government witnessed similar protests and strikes. Tackling such issues is a biggest challenge for the Indian government.
1.5 GST Working Mechanism
The GST working mechanism is explained below with an example:
Consider a manufacturer producing coffee seeds. Lets say the cost of producing coffee seeds is  1000 inclusive of taxes at 12%. So the tax includes
1000 inclusive of taxes at 12%. So the tax includes  120. He will now add, say
120. He will now add, say  200, to the cost as his profit. So now the total cost of price
200, to the cost as his profit. So now the total cost of price  1200. Lets say the GST applicable is 12%, composed of 6% as SGST, and 6% as CGST. So the GST now paid by the manufacturer will be 144, i.e. 12% of
1200. Lets say the GST applicable is 12%, composed of 6% as SGST, and 6% as CGST. So the GST now paid by the manufacturer will be 144, i.e. 12% of  1200. This includes
1200. This includes  72 as SGST and
72 as SGST and  72 as CGST. Now the total cost of the manufacturer is
72 as CGST. Now the total cost of the manufacturer is  1344. He will now avail input tax credit of
1344. He will now avail input tax credit of  120. So total tax paid by the manufacturer for the government at this stage is
120. So total tax paid by the manufacturer for the government at this stage is  24.
24.
Now he will sell this coffee seeds wholesaler at  1368 (inclusive of GST) and manufacturer will charge wholesaler 12% on
1368 (inclusive of GST) and manufacturer will charge wholesaler 12% on  1368. Now the wholesaler will pay GST as
1368. Now the wholesaler will pay GST as  164.16. In the first stage, he has paid
164.16. In the first stage, he has paid  24 as GST to the manufacturer. Now wholesaler can avail
24 as GST to the manufacturer. Now wholesaler can avail  24 as input tax credit. Therefore GST of wholesaler
24 as input tax credit. Therefore GST of wholesaler  140.16 will be paid to the Government.
140.16 will be paid to the Government.
Now the total cost incurred by the wholesaler will be  1368 plus 140.16, which is equal to
1368 plus 140.16, which is equal to  1508.16. Now the wholesaler will sell the coffee seeds to the retailers at
1508.16. Now the wholesaler will sell the coffee seeds to the retailers at  1508.16. Now the retailer has paid
1508.16. Now the retailer has paid  140.16 as GST to the wholesaler. Assume now he adds his profit margin
140.16 as GST to the wholesaler. Assume now he adds his profit margin  192. After adding this lets say approximately the value comes to
192. After adding this lets say approximately the value comes to  1700. Now GST will be charged at 12% on
1700. Now GST will be charged at 12% on  1700. So the GST will be
1700. So the GST will be  204. Now he will avail
204. Now he will avail  140.16 as input tax credit. So the total GST paid by the retailer is
140.16 as input tax credit. So the total GST paid by the retailer is  204 -
204 -  140.16 which is equal to 63.84. So the final price for the consumer will be
140.16 which is equal to 63.84. So the final price for the consumer will be  1763.
1763.
1.6 Conceptual Framework of the Study
Figure 1 shows the conceptual framework for the study. Conceptual framework gives the outline of the researcher's plan for the research study. Olivola and Sussman (2015) in their review of taxes discussed that indirect taxes have a significant impact on the spending ability of the consumer. Thus, GST being an indirect tax in India, will also impact the spending ability. Gowtham Ramkumar (2017) in his paper also concluded that GST has an impact on consumer spending ability. This spending ability influences the purchase decision of the consumers. This paper thus seeks to come out with the factors influencing the purchase decision of the young adults after GST implementation (Ramkumar, 2017)

Figure 1. Conceptual Framework of the Study
2. Review of Literature
The review of literature for this study is presented in two different forms as direct literature on relationship between GST and purchase decision is not available for the study. Therefore literature review is presented in the form of inferences of pros and cons of GST to the economy in general and some inferences of research studies relating to relationship between indirect tax and consumer purchase decision.
Ramkumar (2018) in his study titled “A Study on the spending ability of FMCG Consumers after GST Implementation” concluded that goods and services tax introduced recently in India has a significant impact on the spending ability of the consumers. He further concluded that spending ability of fast moving consumer goods consumers have decreased after the implementation of goods and services tax due to effects of multiple economic reforms in the shorter period of time.
Ramkumar (2017) in his study titled “Impact of GST on consumer spending ability in Chennai City” concluded that consumers are left with less money after GST, rise in inflation level and fall in prices of certain goods after GST implementation. He further concluded that GST rates will have a significant impact on the spending ability of the consumers and suggested that benefits of input tax credit must be transferred by the companies to the consumers.
Esmaeel (2013) in his study titled “The impact of directindirect taxation on consumer” stated that any indirect tax will push up the prices and decreases the consumption level. As a result, it will reduce the effects of negative externalities such as damages caused to the environment. He further states that indirect taxes are the solution to problems in demand fluctuations resulting out of consumer being charged the full social cost.
Karat and Karat (2017) in their research study titled “Impact of Goods and Services Tax (GST) on the Buying Behaviour of FMCG Consumers in Alanalloor Grama Panchayath, Palakkad (Dt)” stated that GST has affected the prices of products of daily use. However this study concludes that GST has not affected the buying behavior of the consumers for essential commodities of daily use and concluded that GST has increased the sales volume of some products in rural area.
Parashar et al. (2017) in his study titled “Exploring the influence of transition to GST on consumer behaviour related to FMCG in India” concluded that GST has significant impact on the purchase decision. The authors conclude that it can result in postponement of purchase decision by the buyers. Further he also identifies bargaining position of buyers as the new factor affecting the purchase decision.
Goolsbee (2000) in a research study on “In a world without borders: The Impact of taxes on internet commerce” stated that people tend to purchase more on online as the indirect tax increases and their future decisions will be based on the comparative prices of the product in the market and online.
Chaurasia et al. (2016) in their study on, “Role of Goods and Services Tax in the growth of Indian economy” concluded that it will help in the development of Indian economy and expected to increase the GDP by two percent.
Kumar (2014) in his paper titled “Goods and Service Tax in India-A way forward” stated that GST will be charged for all the goods and services except for those items that are exempted from the GST. The author further stated that the proposed GST will be implemented as dual model GST. The author further states that various central taxes will be subsumed under the new tax regime and points out the various benefits that can be expected from the goods and services tax.
Vasanthagopal (2011) in his paper “GST in India: A big leap in the Indirect taxation system” discussed the impact of GST on different sectors and key economic indicators, and concluded that GST will help in development of the economy.
Overall, many researches have been carried out in India to explore the benefits and challenges that the GST will bring to the various sectors in the economy and also the common man. Some studies have compared the Indian GST and GST across the other countries at the time of proposal of new tax reform. But between the time gap of proposal and implementation of GST, many changes have come up which should be taken into account by the researchers. It is almost nearly a year since GST has been implemented, and within this one year many revisions have been brought by the central government. It should be noted that most of the research studies on GST are secondary in nature and few studies which are primary in nature also focused on the spending ability of the consumers. There is a scope for further research in GST operating in India extending the existing studies. The primary objective of this paper is to identify the factors influencing the purchase decision after GST implementation among young adults.
3. Statement of the Problem
GST is considered to be an important indirect tax reform for the nation. Various changes are implemented by the government of India under the name of economic growth. GST is also considered to be an important economic reform by the government. This new tax regime subsumes various types of indirect taxes that prevailed in the country and seeks to eliminate cascading effects of taxes and double counting problem in calculating the national income.
Fast Moving Consumer Goods (FMCG) industry is one of the most outperforming industries in India today and considered to be most impacted by the GST. The four tier GST rate system has significant impact on the FMCG products. The industry is also experiencing those changes in the past eight months. GST has significant impact on consumer purchase decisions. GST rates have revised consumer's product selection and purchase criteria. Consumers have been shifting their brands due to rise in prices of various products.
This necessitates to carry out a study on the factors affecting the purchase decisions of consumers after implementation of GST, and to study the impact of GST on consumers purchase decisions which involves measuring the spending pattern and product selection criteria. This study seeks to measure the impact of GST on consumers of FMCG products and arrives at a meaningful conclusion and suggestions that will benefit the key players in FMCG industry.
4. Rationale of the Study
Several research studies have focused on different aspects of GST introduced in India. These studies focused on determining the impact of GST on various sectors like FMCG, manufacturing, pharmaceutical, etc. While very few research studies focused on the impact of GST on consumers. This study is aimed at identifying the factors affecting the purchase decision of young adults after the implementation of GST and how it has changed their way of spending. In this way, this study is a unique one as it considers two diversified aspects: purchase decision related to the field of marketing and GST related to finance. This study will further help in better understanding of consumer psychology towards purchase options after the implementation of GST.
5. Objectives of the Study
The objectives of the study are as follows:
- To understand the concept of GST.
- To identify the factors influencing the purchase decisions of young adults after implementation of GST.
- To offer suggestions about how factors identified can be used for designing marketing programs and activities.
6. Scope of the Study
The study titled “A study on factors influencing purchase decisions of young adults after GST implementation – with special reference to FMCG products” is limited to the respondents in Chennai city, India. Further this study considers only young adults falling within age group between 21 and 30. The study considers both employed and unemployed young adults within Chennai city. This study is conducted during last week of September 2017 and concluded at the beginning of second week of November 2017. Further this study limits its scope to identify the purchase decisions of young adults towards FMCG products and other sectors are not considered.
7. Significance of the Study
This study will benefit companies operating under FMCG sectors as it will help them in designing their marketing programs based on their consumer perceptions and government of India will benefit from this study as it will help them in understanding the impact of GST on consumers with special reference to FMCG products through spending pattern of consumers.
8. Research Methodology
The data required for this study is collected from both primary and secondary sources.
8.1 Research Design
This research study uses exploratory and descriptive research design to find out the factors influencing the purchase decision of young adults after GST implementation.
8.2 Primary Data
The primary data for the study is collected through the structured questionnaire with close ended questions.
8.3 Sampling Design
Sample size for the study is arrived through G Power 3.1 software. The sample size consists of 100 respondents from Chennai city. Stratified random sampling technique is used for the study. It is a sampling technique where researcher will divide the population into different subgroups and then selects at random one particular group for the research study. Thus for this study, the FMCG consumers is divided into four strata based on age group, namely 21- 30, 31 - 40, 41 - 50, and above 50. Based on lottery method, this stratum was selected. Therefore the stratum is named as young adults.
8.4 Statistical Design
The statistical design used in this study is factor analysis with Varimax rotation. Factor analysis is the multivariate analysis technique that helps in reducing the dimensions of the variables used for the study. It groups the variables into different factors. The rotation is based on Varimax, a part of Principal Component Analysis. The grouping of factors is based on Eigenvalues and variances.
8.5 Validity and Reliability Testing
Table 1 shows the output of reliability statistics. Reliability analysis is a statistical technique to test internal consistency of the variables used for the study. Cronbach's Alpha is considered to be the standard measure of variable reliability. Alpha value of above 0.5 is acceptable. The table shows a value of 0.880 which indicates a higher level of internal consistency of the scores generated by the variables used for the study.

Table 1. Reliability Statistics
8.6 Limitations of the Study
The various limitations of the study are as follows:
- The study uses the data collected from both primary and secondary data. Therefore limitations of these sources apply to this study.
- The study deals with the data made available and therefore it may not judge the entire scenario. ·
- The study is mainly focused on young adults in Chennai city and therefore results can vary when the same study is conducted in any other geographical locations. ·
- This study focuses only on FMCG products and so results may vary when the study is carried on in different sector.
9. Data Analysis and Interpretation
9.1 Interpretations
While Tables 2, 3 and 4 show the output of important components of factor analysis, namely KMO test, communalities, and rotated component matrix, the subjective interpretation for the variables shown in these tables are discussed below.
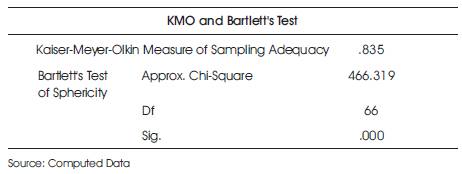
Table 2. KMO and Bartlett's Test of Sampling Adequacy
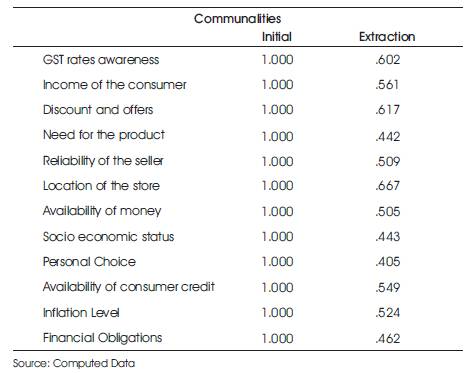
Table 3. Communalities
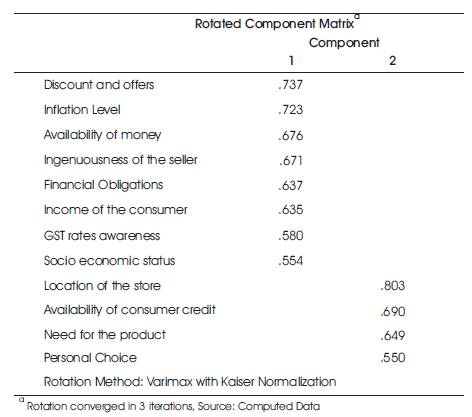
Table 4. Rotated Component Matrix
9.1.1 Factor I : Consumer Oriented Factors
Discount and Offers play an important role in purchase decision of young adults after implementation of GST. Many marketers have started using GST itself as a promotional tool for selling their products. Because GST has resulted in rising prices, many businesses started giving offers and discounts in order to attract customers.
Inflation level, in other words, consistent rise in general price level also influences purchase decision of young adults. This is because consumers are price sensitive. More young adults look to purchase products within their allocated budgets.
Availability of money is another important factor in purchase decision. More the money, higher will the expenditure and vice versa.
How far the seller is genuine also influences the purchase decisions. Issues concerned with bills with no GST rates and other transparency issues came after implementation of GST. Though these issues are being addressed gradually, it is also an important factor in purchase decision of the young adults in Chennai.
Financial obligations are also an important factor to be considered in purchase decision. Each person will have their own financial commitments and family commitments. Financial obligations may include loans, Equated Monthly Installments (EMIs), etc. Income left after spending for these activities will be used for shopping and other purposes.
Income is one of the major factors which influences purchase decision of young adults and also other people whether it is before or after GST. Employed young adults will have to consider this factor and their purchase decision like choice of a brand, etc. depending on their income.
GST rate awareness is another important factor considered in purchase decision after implementation of GST. Now there is four tier GST implemented in India. Consumers who are aware of GST rates prefer to buy products with less GST than those which are charged high GST.
Socio-economic status of the young adults also influences purchase decision of the young adults. One of the socioeconomic factors is education. The purchase decision also depends on the education level of the consumers. The educated customer will buy products after proper analysis of product information and GST rates, whereas it may not be the same in case of educated customers. Similarly there are many socioeconomic factors which will be considered by the young adults before making the purchase decision.
9.1.2 Factor II: Seller Oriented Factors
Location of the store is also considered by the customer in purchase decision. This is because price may vary according to the location of the store. For example, prices of perishable products will be less in stores that are located near the central market from where these products are procured compared to the store that is located far away from the market. This is due to transportation cost. This also influences the purchase decision of the young adults.
Availability of consumer credit is also an important factor in purchase decision of young adults. This is because credit facilities attract more consumers rather than cash based sales.
Need for the product also influences purchase decision of the consumers. Need for the product depends on how well the consumer feels that he actually requires the product on one side and how the product is promoted as an essential commodity for the consumer by the seller. Personal choice of the young adults also influences the purchase decision of the young adults after GST.
Thus from the above analysis, it is clear that after the implementation of GST, few new considerations are added to the factors influencing the purchase decision of the young adults. These include genuineness of the seller, availability of consumer credit, and GST rate awareness, which is the bottom line of this study.
10. Findings
The findings of the study are as follows:
- The factors influencing purchase decision of the young adults after GST implementation centers around two factors, namely consumer oriented factor and seller oriented factor.
- Discounts and offers are the major consumer oriented factors which influence purchase decision after GST implementation. ·
- Location of the store is the major seller oriented factor which influences purchase decision after GST implementation due to the impact of transportation cost in the prices of the commodity.
Conclusion
To conclude, GST is considered to be an important tax reform in the country. It has affected almost all areas of study like finance, marketing, etc. Practically it has impacted many small businesses and also consumers. GST is expected to make the nation as one economic market. It has almost affected the prices of all daily products and even outputs of many other industries. Prices of some goods have gone up while others remained same. Many prices are now shown as inclusive of GST. But if separation is given as cost, profit, and taxes, greater transparency can be ensured and it can result in identified malpractices happening through GST. Though there are standard factors like income which will affect the purchase decision of the consumer, any change happening in the business environment can bring a new consideration in the purchase decision. This study identifies some new factors like reliability of the seller, store location, GST rate awareness, etc., which will have a significant impact on purchase decision of young adults which will be of immense help to marketers. Finally, the study enabled to get practical touch with the topic and helps in understanding the various dimensions of GST.
Suggestions
This study identifies two major broad categories of factors that will have an impact on purchase decision, namely consumer oriented factor and seller oriented factor. Marketers can consider these factors in developing their marketing program. More emphasize can be given on discounts and offers to attract more customers and transparency in GST for the goods and services can contribute to the sales growth of the company. Further steps are to be taken by the retailers to provide credit facilities for the consumers to increase repetitive purchases in the store.
Scope for Further Research
- The study can be replicated by identifying the factors affecting purchase decision with different population as the target group.The study can also be conducted with consumers as general target group.
- The study can also be repeated with studying purchase decision of consumers in different sectors.
- The study can also be conducted by studying the impact of GST on consumers’ spending pattern.
- The study can also be conducted with different geographical locations with the same group as the target population.
- The study can also be conducted studying the scenario of health care services after GST implementation and comparing it with international scenario.
References
[2]. Chaurasia, P., Singh, S., & Sen, P. K. (2016). Role of
Good and Service Tax in the Growth of Indian economy.
International Journal of Science Technology and
Management, 5(2), 152-157.
[3]. Esmaeel, E. S. (2013). The impact of direct-indirect
taxation on consumer. IOSR Journal of Engineering, 3(6),
8-13.
[4]. Goolsbee, A. (2000). In a world without borders: The
impact of taxes on Internet commerce. The Quarterly
Journal of Economics, 115(2), 561-576.
[5]. Karat, R., & Karat, P. (2017). Impact of Goods and
Services Tax (GST) on the Buying Behaviour of FMCG
Consumers in Alanalloor Grama Panchayath, Palakkad
(Dt). Journal for Advanced Research in Applied Sciences.
4(5), 61-65.
[6]. Kumar, N. (2014). Goods and Services Tax in India: A
way forward. Global Journal of Multidisciplinary Studies,
3(6).
[8]. Parashar, N., Joshi, D., & Chopra, P. K. (2017).
Exploring the influence of transition to GST on consumer behaviour related to FMCG in India. Int. Journal of
Management and Development Studies, 6(4),50-57.
[9]. Ramkumar, G. (2017). Impact of GST on consumer
spending ability in Chennai city. Primax International
Journal of Commerce and Management Research
(PIJCMR), 5(3), 2321-3612.
[10]. Ramkumar, G (2018). A study on the spending ability
of FMCG consumers after GST implementation.
Conference Proceedings of National Conference on
Goods and Services Tax – Impact and Prospects 2018
Loyola College (Autonomous), Nungambakkam, ISBN
No: 9788193 377703.
[11]. Vasanthagopal, R. (2011). GST in India: A big leap in
the Indirect Taxation System. International Journal of
Trade, Economics and Finance, 2(2), 144-146.
 1000 inclusive of taxes at 12%. So the tax includes
1000 inclusive of taxes at 12%. So the tax includes  120. He will now add, say
120. He will now add, say  200, to the cost as his profit. So now the total cost of price
200, to the cost as his profit. So now the total cost of price  1200. Lets say the GST applicable is 12%, composed of 6% as SGST, and 6% as CGST. So the GST now paid by the manufacturer will be 144, i.e. 12% of
1200. Lets say the GST applicable is 12%, composed of 6% as SGST, and 6% as CGST. So the GST now paid by the manufacturer will be 144, i.e. 12% of  1200. This includes
1200. This includes  72 as SGST and
72 as SGST and  72 as CGST. Now the total cost of the manufacturer is
72 as CGST. Now the total cost of the manufacturer is  1344. He will now avail input tax credit of
1344. He will now avail input tax credit of  120. So total tax paid by the manufacturer for the government at this stage is
120. So total tax paid by the manufacturer for the government at this stage is  24.
24.



