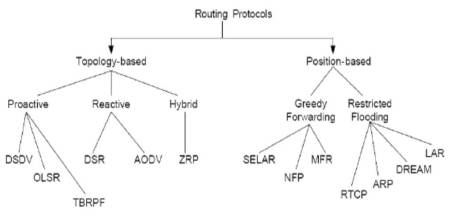
Figure 1. MANET Routing Protocols [7]
Mobile Ad Hoc Network (MANET) is a wireless, infrastructureless network where each node acts as a router, transmitter, and data sink. The objective of this paper is to evaluate the performance of reactive, proactive, and hybrid routing protocols of Mobile Ad-Hoc networks (MANET's) for Custom application. The authors’ have evaluated three routing protocols, i.e. AODV, OLSR, and ZRP by using NETSIM simulator tool. The performance of these routing protocols is examined by two application metrics: throughput and delay. The study of protocols will be carried out and finally the results will be presented as to which routing protocol is a better one for MANET.
Mobile Ad Hoc Network (MANET) is a continuously selfconfiguring, infrastructure-less, multi-hop network of mobile devices connected wirelessly. Every device in MANET is free to move independently in different direction, change links to other devices frequently and must forward traffic unrelated to its own use and therefore be a router. MANET is equipping devices to continuously maintain the information required to properly route traffic. Such types of networks may operate by themselves or may be connected to the larger Internet. MANET consists of a selfhealing, peer-to-peer, self-forming network.
The growth of laptops, tablets, and 802.11/Wi-Fi wireless networking have made MANETs a popular research topic since the mid-1990s. People evaluating protocols and assuming varying degrees of mobility within a bounded space, their abilities, usually with all nodes within a few hops of each other. Performance is evaluated using various protocols based on metrics, such as the packet drop, end-to-end packet delays, network throughput, Average Jitter, ability to scale, etc. [8].
In the next generation of wireless communication systems, there will be a need of rapid deployment of independent mobile nodes. Mobile Ad Hoc Networks (MANETs) provide communication between various nodes in the network topology without the presence of any centralized authority, instead all nodes can function as routers. It gives MANETs two of its most desirable characteristics such as adaptable and quick to deploy [1].
In this paper, the main focus is on evaluating the performance of three types of routing Protocols, such as Ad-hoc On-Demand Distance Vector (AODV), Optimized Link State Routing (OLSR), and Zone Routing Protocol (ZRP) which are reactive, proactive, and hybrid routing protocols. These routing protocols are compared in terms of performance metrics such as Throughput (Mbps) and Delay (microseconds).
The main objectives of this paper are,
Topology based routing protocols in MANETs are categorized into three categories: reactive, proactive, and hybrid routing protocols. This section explains the main characteristics of three protocols, such as AODV (Ad Hoc On-Demand Distance Vector Protocol), OLSR (Optimized Link State Routing), and Zone Routing Protocol (ZRP) deeply examined by employing NETSIM Simulator. An ad-hoc routing protocol is a standard that enhances the scalability of wireless networks in comparison of infrastructure based wireless networks due to its decentralized nature. Figures 1 shows different types of MANET Routing Protocols.

Figure 1. MANET Routing Protocols [7]
Figure 2. Setup of MANET Scenario having 6 Mobile Nodes and Application
In reactive routing protocols, the route is calculated when a node needs to send data to an unknown destination. Thus, route discovery is initiated only when needed. It saves overhead in maintaining unused routes. It may lead to larger initial delays. In route discovery, the query is flooded into the entire network and the reply from the destination (or intermediate nodes) sets up the path between the source and destination. AODV and DSR are examples of Reactive Routing Protocols.
AODV Routing protocol is used in mobile ad hoc networks (MANETs) and other wireless ad hoc networks. It was jointly developed by C. Perkins, E. Belding-Royer, and S. Das on July 2003 at Nokia Research Center, University of California, Santa Barbara and University of Cincinnati [7] AODV is a purely reactive routing protocol. The Ad hoc On- Demand Distance Vector (AODV) algorithm enables selfstarting, dynamic, multi-hop routing between participating mobile nodes that want to establish and maintain an ad hoc network. AODV obtains routes to mobile nodes quickly for new destinations and it does not need nodes to maintain routes to destinations that are not active for communication. AODV enables mobile nodes to respond if there is a link breakage and change in network topology in a timely manner. AODV is loop-free and it offers quick convergence when the ad-hoc network topology changes [3]. When links of AODV break down, the set of affected nodes need to be notified so that they are able to validate the routes using the lost link. AODV is also used in ZigBee Technology. There are various implementations of AODV, such as MAD-HOC, Kernel- AODV, AODV-UU, AODV-UCSB, and AODV-UIUC.
In Proactive (Table-driven) routing protocols, each node maintains a table of routes to all destination nodes in the network at all times. This requires periodic exchange of control messages between nodes. Since the route from source to every destination already exists, there is little or no initial delay when first sending data. DSDV and OLSR are examples of Proactive Routing Protocols.
OLSR is a proactive link state routing protocol based on the following three mechanisms:
As a proactive protocol, OLSR maintains information about network topology by means of exchange link state information. Every OLSR node sends HELLO messages in predefined time intervals for constructing its 1-hop and 2- hop neighbor sets and topology control message for completing link state information, so the routing table can be calculated. Link failures in OLSR are detected this way. OLSR uses multipoint relays (MPRs) in order to reduce message overhead in network. OLSR's MPR set of a given node is a subset of its neighbors which can forward its control messages. The neighbors which a given node A selects as MPR are called MPR nodes of A. When all neighbors are MPR nodes of a given router, OLSR spreads control messages similarly to classical flooding mechanism. On the other side, MPR decreases network per formance due to overhead introduced for constructing and repairing MPR set.
Hybrid routing is a combination of proactive and reactive routing which was proposed to combine their advantages.
In ZRP routing, the nodes have a routing zone which defines a range in terms of hops that each node is required to maintain network connectivity proactively. Therefore, nodes within the routing zone, routes are immediately available for communication. Nodes that lie outside the routing zone, routes are determined ondemand with the help of reactive feature and it can use any on-demand routing protocol to determine a route towards the required destination. The advantage of ZRP is that it has significantly reduced the amount of communication overhead when compared to pure proactive protocols. It also has reduced the delays associated with pure reactive protocols such as DSR, by allowing routes to be discovered faster. To determine a route to a node outside the routing zone, the routing only has to travel to a node which lies on the boundaries of the required destination. Since, the boundary node would proactively maintain routes to the destination. The disadvantage of this protocol is that for large values of routing zone, the protocol behaves like a pure proactive protocol, while for small values it behaves like a reactive protocol.
NetSim is a network simulation tool that allows creating network scenarios, model traffic, and studying performance metrics. NetSim provides simulation of various protocols working in various networks as follows: Internetworks, Advanced Wireless Networks, Cellular Networks, Cognitive Radio Networks, Legacy Networks, BGP Networks, MPLS Networks, Wireless Sensor Networks, Personal Area Networks, and LTE Networks. Different experiments can also be analyzed using the analytics option in the simulation menu [4]. The steps of methodology of work are as follows:-
The simulation concentrates on the performance of the routing schemes to respond on the various scenarios in MANET. In this paper, the performance is measured in terms of Throughput (Mbps) and Delay (microseconds).
The simulation parameters are defined in Table 1. It permits the users to plan and study on communication networks, protocols, devices, and applications with efficiency, scalability, and flexibility.
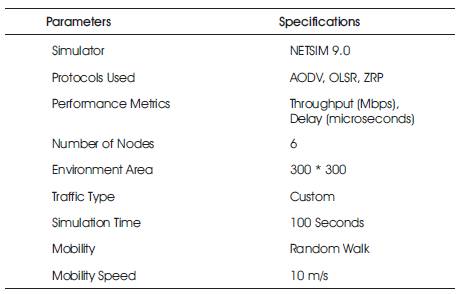
Table 1. Simulation Parameters
The simulation is done on NETSIM Simulator 9.0. The results indicate evaluation in performance by taking MANET routing protocols, such as AODV, OLSR, and ZRP. Under these protocols, Throughput (Mbps) and Delay (microseconds) are used as performance metrics. The simulations are performed with 6 nodes over environment area of 300 * 300 meters. In each scenario, node 2 and node 6 is used as source node and as destination node for sending and receiving data. Figures 3 and 4 show the throughput and delay of this network with respect to total simulation time which is considered as 100 seconds for which the simulation was performed. In this simulation, the network is adjust to 15 and 30 nodes, the traffic type is custom.
Throughput is the most important metric to examine the performance of routing protocols. Throughput is a measure of how fast data packet successfully reaches a receiver node. It is measured in Mbps and should be more for the network. Unreliable wireless channels, frequent topology changes, and limited resources affect throughput in MANETs [2]. Mathematically it is represented as follow 6:
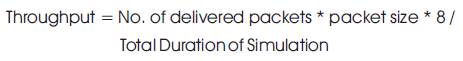
Figure 3 shows the simulation results of Throughput containing 6 nodes by taking MANET routing protocols such as AODV, OLSR, and ZRP.
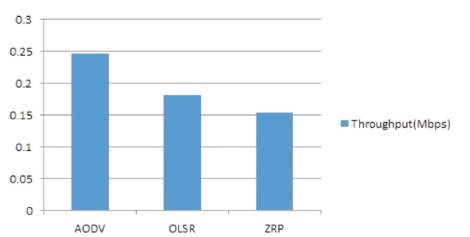
Figure 3. Comparison of AODV, OLSR, and ZRP in terms of Throughput (Mbps)
Results of all the three protocols are easily analyzed from this figure. Performance of AODV is better as compared to OLSR and ZRP in the scenario of throughput. OLSR performs better than ZRP. Throughput of AODV, OLSR and ZRP is .245747, .18104, and .154293 as shown in Table 2.

Table 2. Comparison of AODV, OLSR and ZRP
Delay is the time that packet takes to traverse the network from source to destination. It is the time from the generation of data packet by source to destination nodes and expressed in seconds. It is measured in ms (microseconds) and should be less for the betterment of network. Different types of delays are included during the transmission of packet from source to destination, such as buffering during the route discover y process, retransmission at MAC layer, propagation delay, and transfer time [2]. Mathematically, end-to-end delay can be shown as:
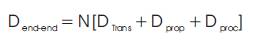
It includes all the delays, i.e. end-to-end delay is the combination of N time Transmission.
Delay (DTrans ), Propagation Delay (Dprop ), and Processing Trans prop Delay (Dproc).
Dend-end = End-to-End Delay.
Dproc = Processing Delay
Dtrans = Transmission Delay.
Dprop = Propagation Delay.
Figure 4 shows the simulation results of Delay in microseconds containing 6 nodes by taking MANET routing protocols, such as AODV, OLSR, and ZRP.
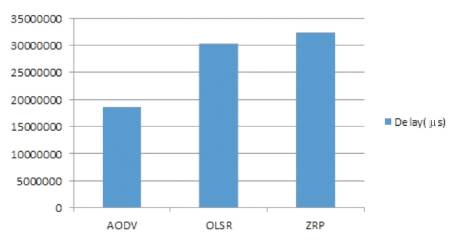
Figure 4. Comparison of AODV, OLSR, and ZRP in terms of Delay (microseconds)
The results of AODV, OLSR, and ZRP protocols are easily analyzed from this figure. Performance of AODV is better as compared to OLSR and ZRP in the scenario of delay. OLSR performs better than ZRP. Unlike Throughput, Delay should be less for the betterment of the network. Delays of AODV, OLSR, and ZRP are 18680503.82, 30174552.32 and 32427148.69, respectively as shown in Table 2.
This paper has described the evaluation routing protocols in MANETs. There are many routing protocols, such as AODV, DSR, OLSR, GRP, ZRP, DSDV, TORA, etc. Three Ad-Hoc Protocols, such as Ad-hoc On Demand Distance Vector (AODV), Optimized Link State Routing (OLSR), and Zone Routing Protocol (ZRP) which are reactive, proactive, and hybrid routing protocols were used with respect to their throughput in Mbps and delay in microseconds as their performance metrics.
In terms of reliability and efficient use of network resources for MANET, the selected performance metrics were subjected to identify protocols effectiveness and suitability in the network. AODV, OLSR, and ZRP were implemented in the scenario having 6 mobile nodes network. In each scenario, node 2 and node 6 was used as source node and as destination node for sending and receiving data. According to results, the authors have analyzed and proved that AODV is a more reliable protocol in terms of delay and throughput than OLSR and ZRP.