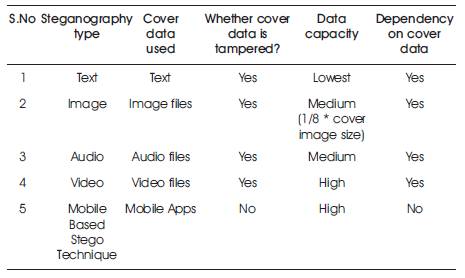
Table 1. Broad comparison of Our Proposed Steganographic technique and other existing Steganographic techniques
Nowadays for data transfer from one place to another in whole world, internet is the best solution. But data transfer using internet is a very risky affair. In this context, data security has become a critical area, because private network is not the solution of data security all the time and none of the medium used for data transfer is fully secured. These challenges encouraged data hiding techniques like Encryption and Steganography. One advantage of steganography over cryptography is that, cryptography protects the contents of a message only, whereas steganography can protect both messages and communicating parties. In this paper, the author are going to implement a Mobile Apps Based Steganography Technique in a mobile application and compare the results based on various criteria like Robustness, Noise Resistance, Imperceptibility, Payload Capacity and Real time with all other audio Steganographic techniques like LSB, Parity, Eco hiding, Phase coding and Spread Spectrum. Millions of Mobile Apps are downloaded on mobile phones daily from all parts of world. This technique has been implemented on J2ME platform with; Mobile Application being a Maze game and it is tested on Nokia Supernova 7610 series phones.
Steganography is an art of secret transfer of data, that has became popular in recent years, mainly aimed to hide data within a cover data such that other individuals fail to observe their existence [3]. While implementation of this method, the main aim is to hide data in a cover media like text, image, audio and video such that except sender and receiver, any other person will not notice that such important information is hidden inside the cover file. The main difference between Steganography and cryptography is that in steganography, individuals will not notice that data exists in the sources [4]. Cover file in most of Steganographic techniques is used as images, video clips, text, music and sound files [5]. These techniques have been developed for variety of targeted systems such as computers and mobile phones [6]. The steganography method, apart from application in covert exchange of information, is also used in fields like copyright protection, preventing e-document forging, etc [7,16].
On basis of their cover file data type, the Steganographic technique can be categorized as Text, Image, Audio, Video and Protocol [1,9]. In order to evaluate the capability of any Steganographic technique performance, some of the major criteria are Invisibility, Payload capacity, Robustness against statistical attacks, Robustness against cover data manipulation, Independent of file format and Unsuspicious files [1]. Most of Steganographic techniques do not fulfill all of above requirements. Hence a trade off must be selected, depending on the requirement of application at hand [2], [15].
On the other hand, in last few years, mobile phones have become a-life-line for human being in urban areas because of its all facet development and its enhanced capability in field of Utility,Entertainment, Communication, Data transfer rate, Interactive services etc. Millions of mobile applications are downloaded and installed daily from all over the world. An application in Mobile phone is written using languages which are specialized in dealing with the software and hardware specifications and limitations of the mobile phones. Some of the most commonly used programming languages are C++, Java and J2ME (Java 2 Micro Edition), which is an embedded version of Java language for low end devices such as set top box, mobile devices and PDAs (Personal Digital Assistant) and some of the widely used mobile operating systems are Symbian, Android, Bada, Linux variant, iOS for iPhones and latest is Tizen.
In any existing Steganographic technique, for hiding data, the approach used is that we hide secret information/ data inside a cover file (Text, Image, Audio or Video File) by embedding secret information bit pattern into cover file or by modifying cover file specific property in which change is difficult to be detected or observed by normal human senses, like echo, phase in audio, small variation in color pattern of consecutive pixels etc. As a whole, the existing method of hiding information in steganography is by tempering/ modifying the cover file as per secret data at sender’s end and at receiver’s end and finding these modifications for extraction of secret information.
Following problems were present in the previous Steganographic techniques:
A detailed analysis of Mobile application based Steganographic technique and some of the previous Steganographic works implemented on mobile phones are presented. Various types of steganography on mobile phones are basically based on SMS [8,11,12,13,14], MMS [10] and mobile apps based steganography [17], [19]. SMS can be used to send Text data or binary image data and hence used by text steganography and image steganography techniques respectively [20].
All problems mentioned in Table 1 were solved by the Mobile apps based Steganographic techniques [17, 19, 21]. In this technique secret data is image type and its file format can be any type. This secret data is hidden inside the JAR file which is executable file in case of J2ME based platform. Then this JAD/JAR files are downloaded to mobile phones from server or a website directly on the mobile phone and then installed on it. In order to recover the secret image from application user has to use his secret key and it will recover. User can again hide image by using his secret key. The basic problem of existing techniques was the approach of tampering of Cover file for hiding information inside it, which causes limited and dependent payload capacity and distortion in Cover file after embedding process. These problems were solved by adopting a new approach in methodology in case of Mobile Application Based Steganography [17], [19], [21] which is discussed in next section. But this technique has no way of user authentication check and real time interactive communication. For enhancing the capability of mobile apps based Steganographic method and improving its security, we implement SMS module [18] concept on it.

Table 1. Broad comparison of Our Proposed Steganographic technique and other existing Steganographic techniques
In all type of Steganographic techniques secret information is embedded into some Cover file, based on some algorithm. These methods alter cover file's properties to hide Secret information based on its Steganographic Algorithm, either in spatial domain or in transform domain by taking caution of its invisibility. Because of this process of altering in cover data, first disadvantage is that the amount of payload is limited and also dependent on the size of cover data and changes in cover data caused noise production in cover image. Table 1 shows the differences in approach of various existing techniques text, audio, video and Image steganography with Mobile Application Based Steganography.
The steps for Mobile Application based Steganography
1. ----- Download Stego Mobile Apps from Website and its
Installation
2. ----- Optional services facilitated on Client Application
for Covert Interactive Communication, IMEI Number cross
check during installation and mobile application
activation password exchange using SMS Module [18].
In case of Mobile Application Based Steganography technique of image hiding in mobile application the secret image is mixed with mobile application resources in such a way that it cannot be retrieved from any other means except by using Mobile Apps in running state [17,19,21]. The control flow diagram is shown in Figure 2. The proposed technique is implemented on J2ME enabled device and run & tested on Nokia C5 phone.
Figure 1 presents the simplest implementation model of Mobile Application based steganography. Here in general, Mobile stego Apps can be uploaded on any website server either by sender or first party who wants to transfer some secret data (image) and at reciever end the second or concerned party can download it from that website on their mobile and install it on mobile. In order to recover the secret data (image) in application, user need to run application and apply specific secret key on mobile phone; which is shared between both party using a secured media.
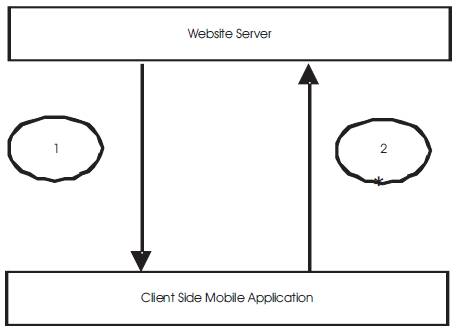
Figure 1. The Simplest Model of Mobile based Steganography
Two different models can be implemented like,
In order to achieve this flow of control shown in Figure 2 is implemented in a Mobile Application which can be any utility like Paint Brush or any entertainment application like any Mobile Game. In our case the utility application is Maze mobile game. The results obtained are shown in Figure 3 and Figure 4 and Tables 2 and 3 show list of devices on which stego game is tested and its various mode of installation on device.
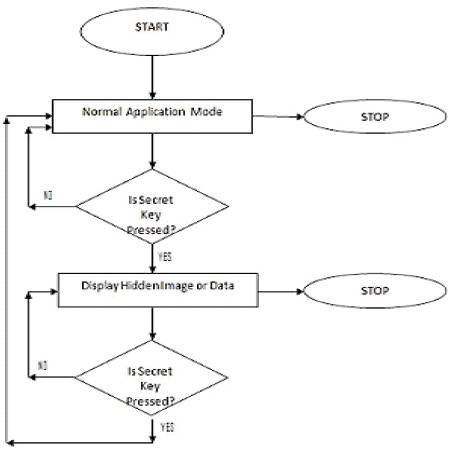
Figure 2. Control flow diagram of technique [17]
Figure 3. Maze Game App in Normal Mode
Figure 4. After Applying Secret Key, Image Display Mode
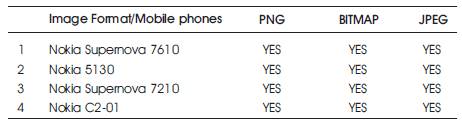
Table 2. Testing various phones with different Image format
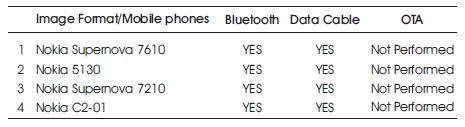
Table 3.Testing on various devices with different Modes of installation
Table 2 shows the list of mobile devices in which Mobile Apps Based Stego Application is installed and tested with different image formats. Devices are Nokia Supernova 7610, Nokia 5130, Nokia Supernova 7210, Nokia C2-01 and different image formats used are PNG, BITMAP and JPEG. Table 3 shows the various ways of installation of mobile apps on mobile devices.
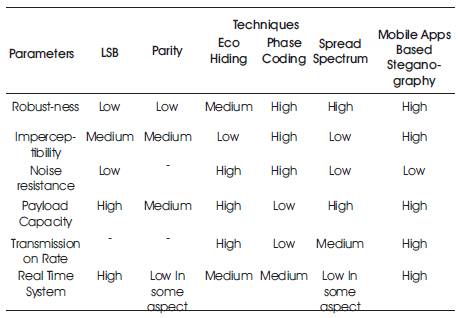
Table 4. Comparison of our techniques with other existing audio Steganographic techniques
Abdulaleem et.al [22] present a comparison of various existing techniques in Audio steganography based on various criteria like Robustness, Imperceptibility, Noise resistance, Payload Capacity, Transmission Rate, Real Time System etc. Authors use this comparison in assessment of Mobile application Based steganography capabilities based on same criteria and present a comparison between existing audio steganography techniques and Mobile technique. The results are shown in Table 4.
In this work the authors tested the Mobile Application Based Steganographic technique and different existing audio Steganographic techniques from the point of view of Payload capacity independence, and establish fact that this technique makes payload capacity, imperceptibility, noise resistance, transmission rate and real time system better. As mobile applications are quite normal these days, its transfer does not catch attention. Because of novelty in selection of cover file, we find extra ordinary results as compared to audio stego techniques, as mentioned in Table 4. It is clear that payload capacity of Mobile Apps Based steganography technique is independent from the dependency on Size of Cover File. This technique has limitation that the secret information can be exposed to hacker if he has doubt that a mobile application contains an embedded data image inside it. Recovering the image file will require connection of mobile phones to PC and specialized software. It has a risk of code reverse engineering. Both of these short comings can be paramount by using Obfuscated code and Binarized resource data.