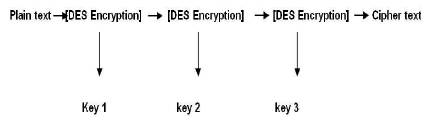
Figure 1. 3DES Structure
Security is the most difficult angle in the system correspondence framework. In system correspondence framework, trade of information data for the most part happens on arranged PCs, remote telephone, and other web based electronic contraptions. Cryptography is the one of the primary PC securities that proselytes data from its ordinary structure into a disjointed structure by utilizing encryption and decoding strategies. The security of remote systems principle acknowledges and the procedure of encryption and decoding assumes as an imperative part to give security to the remote systems. Unsecured information goes through numerous kinds of result. The cryptography strategies used to just an approve individual can have the capacity to open and read the first message. Various cryptography methods are created to accomplish the security in the system correspondence framework. There are essentially two sorts of cryptography systems, viz. symmetric key and Asymmetric key. In Symmetric key systems, the same key is utilized to encryption and unscrambling information. An awry key procedure is utilized to illuminate the key circulation. In Asymmetric keys, are utilized in two keys particular open key and private key. In this, the Public key is utilized for encryption and the private key is utilized for decoding. This paper gives a contrast between the cryptography calculations on various settings of information parcels and utilizing the different calculations (DES, AES, Blowfish, RSA, RC6, RC4, and TRIPLEDES). In this paper relative investigation of the DES, AES, Blowfish, RSA, RC6, RC4 and TRIPLEDES calculations, for example, distinctive size of information squares, diverse key sizes, and encryption /decoding speed are done. Various symmetric and lopsided calculations are proposed in reason situation. Numerous favourable position and weakness are in calculation. This paper is a review of the better than ever Security based calculations in system security.
The word cryptography originates from the Greek words covered up or mystery and composing. Cryptography calculation is the method utilized for secure data from undesirable people by changing over it into muddled structure [1]. Cryptographic frameworks are portrayed along three autonomous measurements, for example, the sort of operations utilized for [Transforming plain text to figure message, the quantity of keys utilized, the path in which the plain text is processed]. In advanced time, assessment of systems administration and remote systems has approached to allow correspondence anywhere. Web and system applications are developing quickly, so the significance and the estimation of traded information over the web or other media sorts are expanding in the correspondence system [2]. Cryptography calculations is a mystery message writing in unique message is essentially encoded in some nonmeaningful arrangement [3]. A number of cryptography methods are produced to the network correspondence framework. There are essentially two keys utilized- Symmetric key strategies and unbalanced key techniques [2], [4]. Symmetric key cryptography utilizes single key for both encryption and decoding. The symmetric key calculations are DES, AES, and RC4, Blowfish, RC6 and 3DES. The uneven key calculation known has RSA.
Plain text→Encryption→Cipher text→Decryption→Plain text
Manoj Kumar Pandey and Deepty Dubey have performed information safety which is the one important in data communication. The multiphase encryption is a new encryption technique used include number of such phase which are strongly protected due to many encryption in each phase [1].
Ranjeet Masram et. al, evaluated the dynamic selection of symmetric key cryptographic algorithms AES, DES, 3DES, RC2,RC4, Blowfish and Skipjack Experimentations show that for all block cipher algorithms analyzed, there is increase in key size and encryption time, rather than there is reduction with the increase in key size for RC4. The fastest block cipher is advanced Encryption Standard (AES), although RC4 shows to be the fastest among all analyzed ciphers [2].
Ezeofor C.J, and Ulasi A.G, discussed that different data block sizes and time response are taken through records encryption. Advantage of RSA and AES algorithms in conditions of the processing moment in time and speed. This paper analyzed altering key size and higher key size leading to clear change in the battery and time consumption [3].
Rajdeep Bhanot and Rahul Hans discussed the strength of both the encryption algorithms depending upon the key management, type of cryptography and the number of bits used in a key. ECC algorithm uses the small key distance which shows the way to fast encryption speed and less power consumption [4].
Sunil Mankotia and Manu Sood analyzed DES 3DES AES, IDEA, Blowfish and RC2 by taking different parameters to outline the strength and weaknesses' of various algorithms. They also found that 3DES requires always more time than DES because of its triple phase encryption characteristic [5].
Pratap Chandra Mandal, concluded that the triple data encr yption standard has the smallest amount performance. In data communication blowfish is the very secure cipher and fastest block cipher [6].
Jawaharlal Thakur, and Nagesh Kumar show a comparison between DES, AES and blowfish algorithms.
The algorithms analyzes the processing speed, block range and key size. Cipher feedbacks demonstrate better presentation than electronic code book. Cipher block chaining requires processing time than the cipher feedback [7].
Shaza D. Rihan et.al discussed AES and DES performance and the calculation of there encryption algorithms will be presented in terms of processing time, CPU usage and encryption. In this research paper, the presentation of the two encryption algorithms AES [Advanced Encryption Standard], and DES [Data Encryption Standard] are evaluated. In this paper, Advanced Encryption Standard is faster than Data Encryption Standard in the execution time for the double platforms. Data Encryption Standard consumes less CPU usage than AES [Advanced Encryption Standard] for two plate forms [8].
Sombir Singh, et. al, discussed encryption speed and decryption speed for the data encryption algorithm and is concluded quick as that is comparedto Revist Sharmir Adlemen Algorithm [9].
K. Kalaiselvi and Anand Kumar analyzed the parameters, key replace, flexibility, and security concern which concludes the effectiveness of the cryptography system. Srinivas B.L, et. al, showed a new comparative study between the encryption techniques presented with different data type, data size, data density, key size, cipher block modes and encryption time required. Blowfish is the fastest block cipher, but DES appears to be fastest among all the analyzed ciphers.
Pratap Chandra Mandal, concluded that the techniques are useful for real time encryption. The every new encryption technique is fast and secure. Blowfish has the good encryption rate in software. The security level it is offers, and the speed of encryption, which is improved than most of the encryption algorithm is available [12, 13].
Rajender Singh et. al, discussed on selected different types of symmetric algorithms AES, DES, 3DES, RC6, BLOWFISH and RC2. Blowfish presents the best performance among all the algorithms subsequent to that, the best algorithm which get through less power and less time is RC6 [14].
Laxmi Mounika, et al., [15] discussed that an encryption algorithm is used by standards such as IEEE 802.11 through WEP (Wireless Encryption Protocol) using a 40 and 128-bit key. A changeable distance end-to-end key of 1 to 256 bytes (8 to 2048 bits) is used to initialize a 256-byte.
Presently, security is the most essential part of the web and system correspondence framework. So the estimations of the traded information over the web or other media sorts are expanding. Regularly, Cryptography calculation utilized for secure data from undesirable people is changing over it into garbled structure. Thus, security innovation advancement is moderate. Numerous encryptions and decoding calculations are considered to conquer the issue. Keeping in mind the end goal to conquer, security based correspondence and distinctive size of information squares, diverse key sizes and encryption/decoding speed have been depicted in this paper.
Cryptography alluded solely to encryption, which is the way toward changing over standard data (unique message) or information that is sustained into the calculation as information is called plain text.
The encryption calculation performs different substitutions and changes on the plaintext. The plain content is known as the first message.
The mystery key is additionally contributed to the calculation. The precise substitutions and changes performed by the calculation rely upon the key.
A cipher (or cipher) is a couple of calculations that make the encryption and the turning around unscrambling. This is the mixed message created as yield. It relies upon the plaintext and the mystery key. For a given message, two diverse keys will deliver two distinctive figure writings.
This is basically the encryption calculation that keeps running backward. It takes the figure content and the same mystery key and delivers the first plain text.
Confidentiality is the barrier of the transmitted information from latent assaults. From an information transmission, a few levels of guard can be recognized. The broadest administration ensures all client information transmitted between two clients over a phase of time. The other part of classification is the insurance of activity stream from investigation. This requires an assailant not be smart to see the source and destination, recurrence, length, or different qualities of the activity on a correspondences office.
The validation administration is apprehensive with guaranteeing that a correspondence is true. This procedure guarantees that the first of the message is accurately distinguished. Confirmation systems make verification of personalities. Solid validation administration is conceivable among cryptography. Solid verification administration is especially valuable when two PCs are attempting to impart over an uncertain system.
With regards to network security, access control is the capacity to the point of confinement and control the entrance to host frameworks and applications by the utilization of interchanged connections. To accomplish this, every substance that is hard to obtain the entrance should be first distinguished, or confirmed, with the goal that entrance rights can be changed towards the person.
The one who arranges a surge of messages, guarantees that the messages are gotten as sent, with no duplication, insertion, change, reordering, or replays. The decimation of information is likewise secured under this administration. Consequently, the association arranged trustworthiness administration addresses both message stream adjustment and refusal of administration. Then again, a connectionless respectability administration, single that arrangements with individual messages without see to any bigger setting, for the most part gives assurance against message change as it were. A mystery key plan can be utilized to produce a settled length cryptographic checksum connected with a message.
Non disavowal keeps also the sender or recipient from denying a transmitted message. In this way, after a message is sent, the recipient can demonstrate that the alleged sender sends the message as a bitwise data. Likewise, when a message is gotten, the sender can demonstrate the asserted recipient in actuality got the message.
The standard of accessibility expresses that assets ought to is accessible to approved gatherings to everyone. Accessibility administration’s secure frameworks typically get assaulted by interlopers, which may influence their accessibility and sort of administration to their client. An accessibility administration is one that secures a framework to guarantee its accessibility. This administration addresses the security concerns raised by refusal of-administration assaults.
Cryptography have two types - Symmetric key cryptography and Asymmetric key cryptography. Symmetric key cryptography is used for single key both encryption and decryption in the communication system. The symmetric key cryptography algorithms are DES, 3DES, AES, RC4, and RC6. Asymmetric key cryptography is used for one private key and one public key. The asymmetric key algorithm is RSA.
Information encryption standard utilized symmetric encryption calculation issued as a part of 1997. Data Encryption Standard considered by IBM is based on their Lucifer cipher [7]. The plain text is [64 bits] long and 56 bits make up the free key, and the longer plain text sums are prepared to use for 64-bit pieces. Information encryption standard is basically comparable as the encryption procedure. DES has a mind boggling set of tenets and changes that be planned intentionally to concede quick equipment usage and moderate programming executions [1,5]. DES depends on the feistel piece figure. Information encryption standard [DES] structure is the feistel system. DES utilizes a 56-bit key, by utilizing the 8 equality bits for simple mistake recognition. DES additionally called the DEA [Data Encryption Algorithm]. There are fundamentally three methods of operation in information encryption standard [DES]. The primary mode is Electronic Code Book [ECB] in which the plain text is taken care of b bits at once and every square of plain text is encoded utilizing the same key. The second mode is Cipher Block Chaining [CBC] which is the contribution to the encryption calculation is the XOR of the current plaintext square and the former figure content piece.
Figure square content is the same key is utilized for every piece. The third mode is Cipher criticism [CFB] is conceivable to change over any square figure into a stream figure by utilizing the figure input (CFB) mode. A stream Figure disposes the need to cushion a message to be and squares of vital number. It additionally works continuously. In this manner, if a character stream is being transmitted, every character can be encoded and transmitted promptly utilizing a character-situated stream figure. The CFB mode operation is an extremely secure mode [4]. The information encryption standard has moderate encryption velocity [4]. It has a little key size and less security. DES calculation has been a well-known mystery for key encryption calculation and is utilized as a part of more businesses and money related applications [1],[4].
Propelled encryption standard is a symmetric square figure distributed in the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) in December 2001. AES [Advanced Encryption Standard] is otherwise called Rijindael calculation. Rijindeal calculation is the symmetric piece figure. It is utilized by the U.S. Government to secure mystery data and is actualized in programming and equipment. The key length can be autonomously indicated to be AES-128, AES-192, AES-256 [2]. It can be encryption information pieces of 128 bits utilizing variable key length. The default key length is 256 [6,2]. The AES outline utilizes the same three key size options yet confines the piece length to 128 bits. The information square of 128 bits in 10, 12 and 14 round contingent on the key size [6]. AES comprises of four fundamental capacities: one change and three substitutions. They are Substitute bytes, Shift lines, Mix segments, and Add round key. The substitute bytes are the utilizations S-box to play out a byte-by-byte substitution of State. Shift Rows forms the State by consistently moving the last three columns of the State by various counter balances. Blend Columns takes every one of the sections of the State and blends their information, freely of each other, making utilization of number juggling over GF(2^8). AddRoundKey round key is extra to the State utilizing XOR operation. AES ought to have high computational productivity, in order to be usable in rapid applications, for example, broadband connections [5,8]. Advanced Encryption Standard is quick and adaptable, so it can be actualized on different stages specifically little devices. AES have been tried for some security applications. Rijndael has the principle throughput of any of the finalists for input modes and second most astounding for non-criticism modes. For the 192 bits and 256-piece key sizes, throughput course in standard and unrolled usage as a result of the extra number of rounds. The AES is also utilized in different regions, for example, to secure data in savvy cards and online exchanges [6] .
In 1993 Blowfish was composed by Bruce Schneier. It has open area encr yption calculations. Blowfish is fundamentally a symmetric square figure. Its takes variable length key from 32 bits to 448 bits [4]. Blowfish is an extremely secure figure. Its work variations is of 14 rounds or less [2], [5]. Blowfish is supplanted by two fish and rijindaelits, a little 64 bits square size. Blowfish contains two parts; Sub key era and information encryption. Sub key era process changes over the key up to 448 bits in length to sub keys to totalling 4168. Data encryption method include the cycle of a straightforward capacity of 16 times [11]. Blowfish Algorithm is a Feistel Network. Blow fish key size is bigger as it is hard to soften the code up the blowfish calculation [13]. It has a great encryption rate in programming. The key size is bigger as it is hard to soften the code up the blowfish calculation. Also it is presented to every one of the assaults separated from the frail key class assault. Blow fish encryption calculation is pronounced best following of security level that is offer and speed of encryption, which is enhanced than the vast majority of the encryption calculation accessible [11,13].
RC4 is a stream figure planned in 1987 by Ron Rivest. RC4 calculation depends on the utilization of an arbitrary change. It was a variable key size stream figure, which is the byte arranged operation. RC4 is utilized as a part of the Secure Sockets Layer/Transport Layer Security(SSL/TLS) benchmarks that have been characterized for correspondence between Web programs and servers. A variable length key of from 1 to 256 bytes (8 to 2048 bits) is utilized to instate a 256-byte. A variable length key of 1 to 256 bytes (8 to 2048 bits) is utilized to introduce a 256-byte state vector S, with components S[0], S[1], . . ., S[255]. RC4 has an utilization in both cryptography [encryption and decryption]. While the information stream experiences XOR together with a progression of created keys [15] . RC4 calculation is of two sorts; key-booking calculation (KSA) and pseudo-arbitrary number era calculation (PRGA). KSA [key-planning algorithm] is to the finished introduction of RC4 Key. PRGA [pseudo-arbitrary number era algorithm] is to deliver pseudo-irregular number [2],[7].
Rc6 (Rivest Cipher 6) is a symmetric key square cipher. RC6 has an information piece size of 128 bits and a key component which is bolstered by RC6 shifting from 128- 256 bytes. RC6 is most regular key size is 128, 192 and 256 bits [10-14]. RC6 is watch a few techniques for investigating exchange offs amongst vitality and security. The outline of vitality proficient secure correspondence plans for the remote environment later on. RC6 legitimate has a piece size of 128 bits and backings key sizes of 128, 192, and 256 bits. The security convention has the high vitality utilization. The savage power assault has all the earmarks of being infeasible if the key size is huge and the evaluated round of 20 is prescribed. RC6 strategy has the end goal of encryption and decoding. It gives best disarray and dispersion. Disarray is utilized to the cryptographic system that looks to make the association between the insights of the figure content and the estimation of the encryption key as mind boggling as possible [15].
RSA was developed by Ron Rivest in 1997. Revest Shamir Adleman is the public key encryption algorithm. RSA algorithm is the asymmetric key cryptography algorithm. The RSA design is a block cipher in which the plain text and cipher text are integers between 0 and n, 1 for some n. A typical size for n is 1024 bits, or 309 decimal digits [9]. The best security key size is 2048 bit. RSA algorithm is used for secure communication system channel. It is used for mathematical fact that it is easy to find and multiply large prime numbers together, but it is extremely difficult to factor their product [9], [12]. RSA algorithm is based on the private key and public key algorithm [asymmetric key]. There are four possible approaches for attacking the RSA algorithm. Brute force, Mathematical attacks, Timing attacks, and Chosen ciphertext attacks. Brute force involves trying all possible private keys. Mathematical attacks involves in several approaches, all equivalent in an effort to factoring the product of two primes. Timing attacks depend on the running time of the decryption algorithm. Chosen cipher text attacks exploits the properties of the RSA algorithm. The encryption time and buffer usage is also very high [9].
[1] Select P, Q [P and Q both prime, P! = Q].
[2] P, Q is the large prime number.
[3] Compute P X Q=N
[4] Compute φ (p x q) = (p -1)*(q-1)
[5] Select integer k, [g c d (φ (n), k) =1; 1 < k < φ (n)
[6] Calculate d, [d = (k-1mod φ (n))]
[7] Public key[PU={k, n}]
[8] Private key [PR = {d, n}
[9] Calculate encryption process to M < n is the plain text and C=MK mod n is the cipher text process.
[10] To calculate decryption process is cipher text=c and plain text is the target output M=CKmodn [6][12].
Triple Data Encryption Standard is the symmetric key algorithm. 3DES was developed by IBM IN 1978. Three Data Encryption Standard is also known as TDES. The simple DES encryption algorithm is given three times to improve the security of the encrypted text [56 x 3 =168]. The DES key size is 56 bit and also called 3DES key size is 168 bits [5]. The process for encryption is accurately the same as standard DES, but it is repeated three times, therefore the name Triple DES. In this process, The data is encrypted using the first key, decryption using the second key, and finally encryption again with the third key [4] . It is used for multiple length used to 3DES. Triple DES is implemented in both hardware and software. It takes three 64 bit keys with an overall key length of 192 [64 x 3 = 192]. There are three keying option in 3DES. Triple Data Encryption Standard is basically a block cipher. It is used for 48 rounds among triple times data encryption standard. The block size 64 bits used in encryption [5] , [11].
Figure 1 illustrates the 3DES structure.

Figure 1. 3DES Structure
3DES basically has two modes used. They are,
It also has the advantage of proven reliability and a longer key length that eliminates many of the attacks that can be used to reduce the amount of time it takes to break DES.
The comparative analysis for Encryption and Decryption algorithms are listed in Table 1.
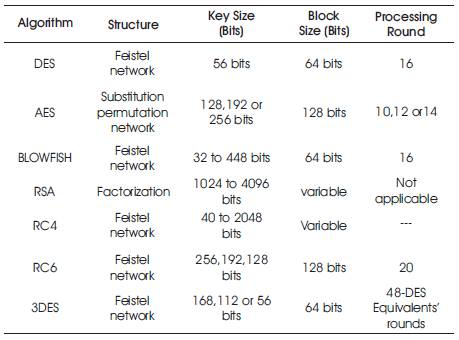
Table 1. Comparitive Analysis Encryption and Decryption Algorithms
Data security is one of the important aspects of communication. Security of data can be achieved using the art of cryptography. There are many algorithms available for cryptography, but the selection of one of the best algorithm is also very important. The algorithm for encryption can be selected based on the type of data being communicated and the type of channel through which data is being communicated. The selected algorithms are AES, DES, and Blowfish, RC4, and RC6 for symmetric, and [RSA] for asymmetric. In this paper, the network security and application areas and also security in networks are discussed. They are used in different types of algorithm for network security. The advantages and disadvantages were also explained in this paper.