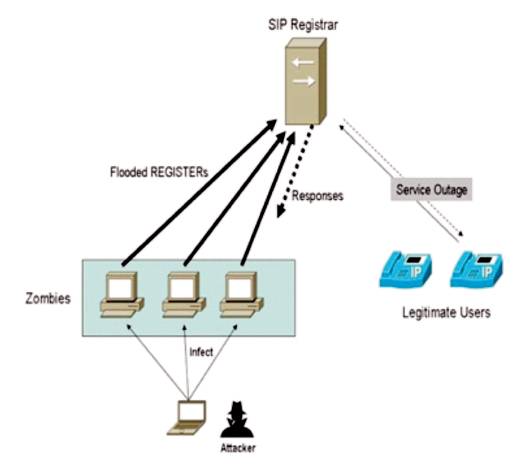
Figure 1. SIP Flooding Attack
Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attack includes by sending large volume of enormous requests to the server or site and it will unable to handle the enormous requests, and the server remains offline for some time depending upon the attack. Flooding attack is one type of the DDoS attack. For the detection of DDoS flooding attack, one of the approaches is used as multi-dimensional sketch design by integrating with Hellinger Distance (HD) analysis. The HD analysis can be used to monitor the network flows. Sketch technique can be used to detect the attack and it is having the capability of selectively discarding the offending messages only, but not the attack resource. Mainly this can be applied to the VOIP networks, but not to all type of attacks. To prevent DDoS attacks, one of the metrics used is the New Cracking Algorithm. This algorithm includes whenever the client enters into the particular web resource exceeding more than the given threshold, then the client's IP address can be added to the blocked list as an attacker, and the security can be applied by using Message Authentication Code (MAC) for the client's IP address. So this algorithm can protect the web resource even for large volumes of DDoS attack traffic.
Denial of Service (DOS) attacks are planned to shut down the servers for a period of time. DOS attacks are usually done by the following methods:
A Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attack is an event in which a legitimate user or organization is rundown by certain services, like network, email or network integration, that they would normally expect to have. DDoS is basically a resource blocking problem, it includes bandwidth, memory, CPU cycles, file descriptors, buffers, etc. Flooding is one type of DDoS attacks it is intended to bring a network or service down by flooding it with enormous amounts of traffic. Flooding attacks occur when a network or service turns into so weighed down with packets initiating imperfect connection requests that it can no longer process legitimate connection requests. By flooding to a server or host with connections that cannot be done, the flood attack eventually fills the target host's memory buffer. Once this buffer is full no further connections are done, and the result is the DoS attack.
Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) flood is one type of flooding attack. It is mainly the bandwidth depletion type of attack. SIP is a signalling protocol used for governing voice and video communications over the Internet Protocol (IP). However SIP is designed with an open-structure and it is susceptible to security attacks as shown in Figure 1. This type of attack is among the most severe attacks since it is easy to initiate and able to quickly exhaust the resources like networks and nodes together. The attack agitates perceived Quality of Service (QoS) and later it leads to DoS. SIP is a transactional protocol and possesses numerous message attributes. The flooding attacks can thus tolerate varied forms and initiate the multi-attribute attack. In order to get a secure VoIP system, an anomaly defense system is desired to detect the flooding attacks, classify their forms, and counter the attacks from bringing damages to the services.

Figure 1. SIP Flooding Attack
Some of the Prevention approaches of DDoS attacks are described as follows.
A defense against the Ad Hoc Flooding Attack in MANETS. The results of this operation will show that FAP can prevent the Ad-Hoc Flooding attack efficiently. The performance of the reliability is tested in an ad-hoc network by implementing Ad-hoc On-demand Distance Vector (AODV) protocol with three parameters throughput, packet delivery ratio and routing overhead.
Security for the data in transmission cannot be given.
A key requirement for ingress or egress filtering understands expected IP addresses at a particular port. It can prevent IP Spoofing [1].
There are applications and open ports in hosts, there is a chance to make use of vulnerabilities by attackers. Therefore, if network services are not required or unexploited, the services should be deactivated to prevent attacks, e.g. UDP echo character generation services [3].
Prevention against attacks that use intermediate propagation nodes. e.g., ICMP flood attacks, Smurf attacks etc. are unbeaten only if host computers and all the neighbouring networks disable IP broadcast [4] .
DDoS attacks cannot be permitted by changing their location or IP address of the active server extremely within a pool of uniform servers or with a pre-specified set of IP address ranges. The victim IP address is invalidated by, altering it with a new IP address. Once the IP addresses change is completed, all internet routers will be knowledgeable and the edge routers will drop the affected packets. Although this action leaves the host system susceptible because the attacker can initiate the attack at the new IP address, which is an alternative practical approach for DDoS attacks that are based on IP addresses. On the opposite side, attackers can make this technique useless by adding a DNS tracing function to the DDoS attack tools [3].
The sketch is a probabilistic data summarization technique. It builds compact and constant-size summaries of high dimensional data streams through random aggregation, by applying a hash function to the data. Specifically, we consider that each data item consists of a key ki and its associated value vi , represented as ai = (ki ,vi ) for constructing a sketch. Using sketch makes the scheme scalable. No matter how many users exist in the VoIP network, the sketch is able to derive a constantsize traffic summary. More importantly, the sketch can construct a probability distribution based on the SIPattribute entries, with no prerequisite to explore the association among different SIP attributes [4].
The HD is used to measure the distance between two probability distributions. To compute HD, suppose that we have two histogram disseminations on the same samplespace, namely, Pi = (p1 , p2 , . . . . ,pn ) and Qi = (q1 , q2 . . . . , qn ). The HD between the given distributions is calculated as follow [1]:
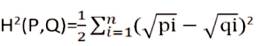
It is not difficult to see that the HD will be up to one, whenever two probability distributions are completely different and down to zero if they are identical. This property offers a good approach to enumerate the coincidence of two data sets in either normal or abnormal situations. Recall that we aim to build an anomaly detection system which desires a statistical model to show the normal traffic condition and indicates alarm when abnormal variations are observed. This property can be shown in HD analysis. A low HD value denotes that there is no significant deviation in the current traffic observations and a high HD is a strong indication that anomalies have appended.
When the HD obtained from a certain element hash-row exceeds, the threshold attack detection is registered. After this, if we continue the update, the threshold will be contaminated by the attack as the attacking traffic will be taken into account in estimating the threshold. To avoid this from happening, we freeze the threshold and keep it as a constant as long as the HD is above it. Also, to prevent the attacking traffic from entering the training set and thus keeps the HD high only during attack. After an attack detection is registered at the (i + 1)th time interval di+1 , we freeze the current training. This process ends when the HD goes below the threshold [1].
Algorithm 1: Estimation Freeze Mechanism

When the clients keep logging on to a particular website often, the web server performance keeps degraded. To avoid this situation, the given algorithm maintains a status table, the fields it includes IP addresses of existing users and its status. If the particular IP address has been signed on for a first time, it makes the status as an authenticated user. For 2, 3, 4 times it marks as an authenticated user. For the 5th time, it marks the current user IP address status as Attacker. All user wishing to increase the time of the server depends up on the application. After that, the user is not allowed to access the service of that particular web resource. The service is denied to that particular IP address.
If an incoming packet validates the packet filter's set of rules, the packet filter drops the incoming packet, or it reject the packet by sending error response to the source.
MAC is a symmetric authentication scheme that allows a user A, which shares a secret key 'k' with sender A, that shares a secret key k with destination B, to authenticate a message 'M' sent to destination B with a signature MAC (M, k) has the possessions that, no one can forge it without knowing the shared secret key k. Next, validate the shared secret key 'k' to obstruct the attackers who are using genuine address or mislead address. Since a legitimate client uses its genuine IP address to connect with the server, it will receive the HTTP forward message (hence the MAC). So, all its upcoming packets will have the calculated MAC with destination IP addresses and thus be protected. The incoming traffic flow with spoofed IP addresses will be filtered because the attackers doesn't receive the MAC sent to the destination. So, this technique effectively distinguishes legitimate traffic from DDoS attack traffic with spoofed IP addresses [2].
Different MAC algorithms are available in cryptographic system, one of the approaches considered is the Secure Hash Algorithm (SHA-1).

When the Cracking algorithm can be applied to the web application, the theoretical calculations are given below.
For Example: Consider the client’s IPs are 10.20.30.1 to 10.20.30.12. Due to the nature of DDoS attack randomly client IP can be selected.
Step 1: User IP: 10.20.30.4. IP can be validated at the history table, whether it is present in the table or not. If it is present and the status of IP can be checked (Blocked/Processing).
Step 2: If the IP arriving into particular web server when it exceeds a given threshold and then further services are not done, the IP can be added to the blocked list as on attacker. In future the requests can be initiated from the blocked IP which cannot be processed.
Step 3: Mean while at the time of response, MAC can be calculated at both server and client side. If it matches the user can get the access, otherwise access will be denied. The following figures show the simulation results. The comparison of various SHA functions are listed in Table 1.
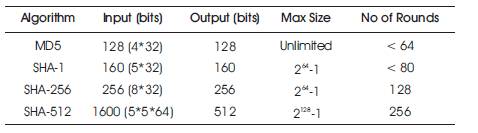
Table 1. Comparison of SHA Functions

Figure 2. Initially Status Table is EMPTY

Figure 3. User Enters into the Website (Number of Times < Threshold)
Figure 4. User Enters Wrong Address to Login into the Website
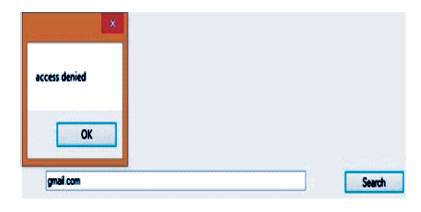
Figure 5. User Enters into the Website (No. of Times > Threshold)
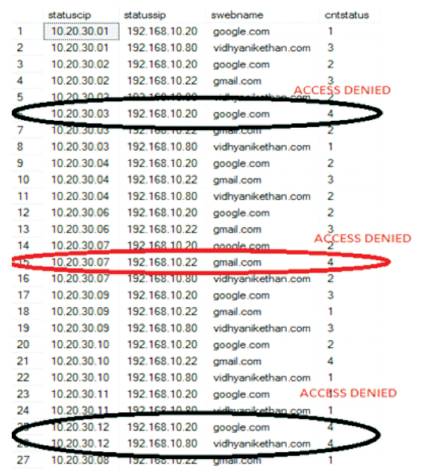
Figure 6. After Some User Logins-Status Table
SIP flooding attack is a major threat to the VOIP networks. For detection, SIP flooding attack can be done by using SKETCH and HD. By the theoretical analysis, threshold value can be preserved and remains constant. With sketch and HD detection of the attack is done, but not the origin of attack. For this, a technique used for both attack detection and prevention is New Cracking Algorithm. In this algorithm, the threshold value can be set, whenever the client enters into the website exceeds the threshold value, it says that an attack has happened, and so further processing cannot be done. Here security can be provided based on the client's IP address by using MAC algorithm. By this procedure, both attack detection and prevention can be done. This technique can be applied to large networks, where it works efficiently.