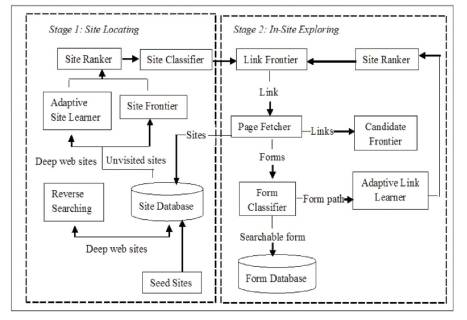
Figure 1. Two Stage Architecture of SmartCrawler
The WWW is an incomprehensible collection of one thousand millions of pages containing tera bytes of information organized in many servers using HTML. The extent of this gathering itself is an imposing snag in recovering fundamental and applicable data. This made web indexes a vital part of our service. The venture expects to make a keen WebCrawler for an idea based semantic based internet searcher. The authors intend to raise the potency of the Concept Based Semantic Search Motor by utilizing the SmartCrawler. They proposed a two phase architecture to be specific SmartCrawler, for smartly collecting incredible web interfaces. On the premier level, SmartCrawler performs site-based crawling for hunting down key pages with the brace of web search tools, abstaining from going by a prodigious amount of pages. To finish more correct answers for a drew in crawl, SmartCrawler position locales to sort out significantly corresponded ones for a devoted topic. In the secondary level, SmartCrawler finishes quick on-site looking by uncovering most relevant associations with associate in nursing versatile association situations. To evacuate incomplete destinations on setting off to some particularly applicable associations in releasing web registries, we plot an association tree data structure to reach a broader degree for a website. The outcomes occur on a game plan of those ranges, which show the adaptability and precision of the proposed crawler structure, which competently recoups significant web interfaces from sizable voluminous-scale neighborhoods and finishes higher rates than other crawler's results.
A WebCrawler is a plan that circumvents the web gathering and putting away information in a database for further investigation and a path of action. The process of web creeping includes gathering pages from the web and organizing them in a fashion that the inquiry motor can recover then proficiently. The basic goal is to perform as such productively and quickly without much obstruction with the working of the remote host. A WebCrawler starts with a URL or a rundown of URLs, called seeds. The crawler visits the URL at the highest priority on the rundown. On the site page, it searches for hyperlinks to other website pages, includes them to the current rundown of URLs in the rundown. This arrangement of the crawler going to URLs rely on upon the principles set for the earthworm. All in all crawlers incrementally slither URLs in the summation. Notwithstanding gathering URLs, the primary capability of the dew worm, is to pull together information from the page. The data gathered is sent back to the home server for capacity what's more, further examination.
It is a troublesome task to find significant net interfaces; as an outcome of they're not recorded by any web seek devices. They now and again every once in a while scatter and keep never-endingly alert. To destroy higher than weakness, past work has organized two styles of crawlers that zone unit tasteless crawlers and concentrated on crawlers. Nonexclusive crawler gets all the searchable structures and don't have some expertise in a specific subject, however revolved around crawlers zone unit, the crawler that spotlights on a specific point. Structure centered crawler (FFC) and obliging crawler concealed net passages (ACHE) courses of action to quickly and mechanically observe elective structures inside a similar space [13], [14]. The expansive segment of the segments of FFC zone outlines unit join, page, sort classifiers and wild director for centered crawl of web-structures [15]. Throb expands the concentrated procedure of FFC with extra parts as sort filtering and obliging association learner. The association classifiers expect a significant part to accomplish higher quality than the first best crawler. The precision of focused crawlers is low with respect to recovering suitable structures. For example, accomplice in nursing test drove for data zones, it's been shown that the billet of Form-Focused Crawler is around sixteen p.c. So it's huge to create exceptional crawler that area unit organized to immediately related substance from the huge net, the most convincing achievable total. A structure for rapid harvest home significant net named SmartCrawler is implied amid this paper. Shrewd Crawler plays out a current level learning of information examination and data isolated from the web. The SmartCrawler is divided into 2 stages: Site finding and insite researching.
Inside the principal stage, SmartCrawler performs webpage based taking a gander at center pages with the assistance of WebCrawlers, staying away from heading off to a bigger than normal assortment of pages. to comprehend an impressive measure of careful results for a concentrated creep SmartCrawler positions the destinations to sort out an incredible degree material, once Site discovering system uses reverse looking strategy and element two-level site situating technique for revealing huge areas and to comprehend a huge amount of learning sources [16]. All through the in-site researching sort out, an association tree is suggested for balanced association arranging, wiping out inclination toward pages in all around adored registries. Pleasing learning algorithmic framework can perform on-line highlight choice and mechanically assembles join rankers. Inside the site discovering stage, an incredible degree related regions area unit has been sorted out in this manner and slither is centered around a given subject may misuse the substance of the reason page of destinations and fulfill a huge amount of right results. All through the in-site researching stage, related joins zone unit framed for smart in-site looking.
Finding profound web content source: The Generic crawlers are fundamentally created for portraying profound web and registry development of profound web information assets, that are not constrained seek on a particular subject, but rather endeavor to get every single searchable structure [1]. Database Crawler first discovers root pages by an IP-based testing [3], and after that performs show slithering to creep pages inside a web server beginning from a given root page [12]. Selecting applicable source: Existing concealed web registries [10], [8], [7] more often than not have low scope for important online databases. This limits their capacity in fulfilling information to the needs. Centered crawler is created to visit connections to pages of interest and maintain a strategic distance from connections to off-theme areas [2], [8].
URL format era: The issue of parsing HTML frames for URL layouts [10]. Moreover, creators in [10,11] examined the issue of doling out extra values to numerous information fields in the inquiry frame with the goal that substance can be recovered from the profound web. The URL layout eras segments, look structures are parsed utilizing systems like that are given as a blueprint in [10]. The investigation demonstrates that producing URL formats by identifying value mix in numerous information fields can prompt in proficiently vast number of layouts and may not scale to the quantity of sites. There are many intrigued information in creeping.
The emphasis on crawler is to choose links to reports of enthusiasm, keeping away from connections that lead to off-subject districts. A few strategies have been to center web creeps (5, 6, 10, and 11). Briefly, it is a best-first hunt centered crawler which utilizes a page classifier to direct the pursuit. They portray pages as a partner with topics in a coherent categorization. This engaged crawler often need connections that is associated with pages named significantly. The alteration to the standard technique in rather than all connections in important pages, the crawler utilized a joining classifier, the disciple, to choose the most connections in a significant page.
Numerous procedures were actualized by scientists to enhance the viability and productivity of SmartCrawler and have been proposed in the writing for the SmartCrawler and a few techniques were aimed to enhance both the exactness and effectiveness of the SmartCrawler [11]. A Hierarchical Approach to Model Web Query Interfaces for Web Source Integration was explained. Applications, for example, Deep Web creeps and Web database combination require a naturally use in these interfaces. Along these lines, an essential publication to be tended is the programmed extraction of question interfaces into a worthy example. Luciano Barbosa and Juliana Freire [5] demonstrated a Versatile crawler for finding shrouded web passage points. This creeping methodology naturally comes up with concealed Web databases, which plans to run through a parity in the midriff of some clashing necessities of this issue: the utilization to pass out comprehensively seek in the meantime keeping up a strategic distance from the utilizations to crawler, an expansive number of unessential pages. Raju Balakrishnan, and Subbarao Kambhampati [7] developed. Source Rank: Relevance and Trust Assessment for Deep Web information Sources based on Inter-Source Agreement. Picking out the generally significant subset of network databases for a critical issue is giving an inquiry in profound web information incorporation.
Kevin Chen-Chuan Chang, et al., explained toward Large scale Integration: Building a Meta Query over Databases on the Web. This research work introduced a strategy to concentrate various leveled pattern trees from Deep web interfaces. This representation is wealthier and less demanding along these lines to be utilized for Deep Web information coordination than high precision values over an extensive variety of interfaces and spaces. Luciano Barbosa and Juliana Freire [4]. scrutinized the searching of Hidden Web Data through Keyword-Based Interfaces. Some volume of data is concealed Web develops, there is expanded enthusiasm for procedures and apparatuses that permit clients and applications to substantial data. In this paper, their location is a significant issue that has been a great extent to disregarded in the writing: how to effectively find the searchable structures that serve as the passage point for the shrouded Web.
The developers have proposed a two-stage structure, a SmartCrawler, for beneficial get-together significant web interfaces and second time splendid crawler is used as a fast as a piece of page chasing. Generally in the central stage, SmartCrawler performs website based chasing down essential pages with the help of web lists. In the second stage, SmartCrawler fulfills fast on-site looking by tunneling most essential associations with a flexible association situating. To take out inclination on passing by some particular material associations in hiding web lists. The designer has laid out, an association tree data structure to finish more broad extension for a site.
For viably finding huge web information sources, Splendid Crawler is made with a two phase building, webpage finding, and in-site page investigating, as appeared in Figure 1. The essential site discovering stage finds the most imperative site for a given point, and a while later in next stage, in-site researches searchable structures from the site. Seeds destination accepts an essential piece of finding applicant locales can be given for the SmartCrawler to start slithering, which begins by different URLs from picked seed regions to examine distinctive pages and territories. Sarry crawler goes with a limit of "speak looking" when the amount of investing URLs in the database is not precisely an edge in the midst of the crawling methodology. Site frontier is expected to bring landing pages of different URLs from the site database, which are situated and composed by SiteRanker on preface of critical districts. The Site Ranker goes with a limit of a Adaptive Site Learner, which adaptively picks up from segments of significant destinations. To fulfill more correct outcomes for an engaged creep, Site Classifier orders URLs into appropriate or insignificant for a given subject in perspective from the point of landing page content.

Figure 1. Two Stage Architecture of SmartCrawler
In the wake of finishing the work of a first stage, i.e., vital site seeking, the second stage makes each essential stride of exploring and uncovering searchable structures. For this circumstance associations of a most significant locales are secured in connection frontier and it's been used to bring the comparing pages. Despite this, connections in the connection pages are being maintained to competitor boondocks to sort out applicant outshirts and after that splendid crawler, positions them with the help of connection ranker. The Link Ranker is adaptively improved by a Adaptive Link Learner, which picks up from the URL inciting important structures. On-site exploring grasps two crawling techniques for high capability and extension. Joins inside a site are sorted out with Link Ranker and Form Classifier portrays searchable structures [17].
Before techniques use to crawl the n number of links, but the SmartCrawler crawls through only those links which has been given more priority as they have been used more number of times. Hence, SmartCrawler reduces the stress of the user by only crawling through limited sites and providing relevant results to the user. This can be implemented by following below algorithm.
Input: Root sites and collected websites
Output: Applicable or useful sites
While # of child sites less than a threshold value Do
Domain = getDeepWebsite (websiteDatabase, rootSites)
Resultant = search (website)
Links = extractLinks (resultant)
For each link in links do
Webpage = downloadPage (link)
Useful = classify (webpage)
If useful then
Useful Sites = yieldUnvisitedSite (webpage)
Output: useful sites
End
End
End
Once the persistent site is found by Site Locating, On-site Exploring starts exploring to find all the inside forms of that website. This can be implemented by one of the crawling strategy, i.e., Stop Early Strategy.
ESC1. The maximum Deep Website is reached.
ESC2. The maximum of all crawling web pages has reached in each of the website.
ESC3. If the crawler has been reached in advance all the web pages without suitable forms in one depth, then it moves directly to the next location.
ESC4. The crawler yields advance number of web pages in absolute.
The authors have implemented SmartCrawler in Java and evaluated the approach [18] over 5 different domains and the experimental results are as described in Table 1.
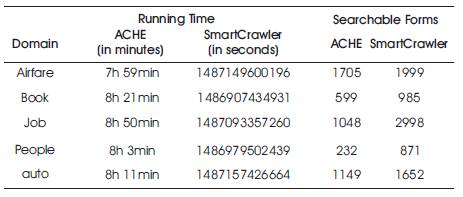
Table 1. Comparison of Running Time and Number of Searchable Forms found for ACHE and SmartCrawler
Figure 2 clearly says that SmartCrawler is more efficient than ACHE. SmartCrawler is very much useful in finding out more deep web pages very fast and accurately.
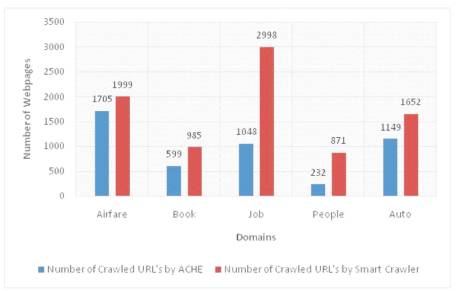
Figure 2. The Number of Applicable Webpages collected by ACHE and SmartCrawler
The authors have built a SmartCrawler to serve the necessities of the Concept Based Semantic Search Engine. The SmartCrawler effectively slithers in an expansive first approach. We could manufacture the crawler and outfit it with information preparing and in addition URL preparing abilities. They classified the data acquired from internet site pages on servers to get content records as required by the Semantic Search motor. We could as well sift through superfluous URLs before getting information from the host.
The researchers additionally arranged metadata from the HTML pages and spurred them to a registry so that the metadata can be employed every bit a part without bounds. They saw at the performance of the existing crawler with that of the SmartCrawler. With the separated content records created by the SmartCrawler, the Semantic Search Engine could recognize ideas from the information rapidly and earn a great deal more productive in fashion. Consequently, we could raise the productivity of the concept based Semantic Search Engine.