Figure 1. Diagram of Multilayer Neural Network (Simon, et al., 2016)
Image compression is an important methodology to compress different types of images. In modern days, as one of the most fascinating machine learning techniques, the authors have applied the idea of Deep Learning in different cases of Neural Networks to prove and justify that it is the most flexible method to analyze and compress the images. Different types of neural networks are available such as Deep Neural Network (DNN), Convolutional Neural Network (CNN), Binarized Neural Networks (BNN), Artificial Neural Networks (ANN) to perform image compression. So, in this review paper the authors have discussed how deep learning concept is applied on different types of Neural Networks in order to achieve image compression of perfect qualities with proper image classifications. In order to obtain that proper image classification, ther is a need for deep learning on DNN, CNN, BNN, ANN and apply the same concept in different types of images in a justified manner with difference of analysis. This is called compression technique based on conceptual analysis of images.
Image compression is a technique where any image can be compressed by using different types of methodologies that have been adopted. Basically, there are two types of image compression techniques (Simon, Deo, Selvam, & Babu, 2016). The 2 techniques include: Lossy: Once the original image is compressed there is a chance to lose some important data and Loss less: Once the original image is compressed there is no chance to lose any data of original image (Kunwar, 2018). There are many types of image compression techniques available in internet, such as Joint Photographic Experts Group (JPEG), Portable Network Graphics (PNG) etc. Out of them JPEG is the most commonly used or accepted in wide range of lossy image compression techniques (Kunwar, 2018). But, the new concept here is to implement a different kind of network that can be used as a classifier of image before image compression. Here, the selected network is Neural Network. A neural network consists of three different stages: input stage, hidden layer and output stage layer (Simon, et al. 2016). Each layer consists of neurons that have learnable weights and biases. Each neuron receives some inputs, performs dot product and optimally follows it with a non-linearity. Here, the authors are using a concept of deep neural network analysis, which is an essential tool for computer vision and the performance can be analyzed in image classification, object detection, semantic segmentation (Patel & Agarwal, 2013). Same concept can be used for low level video signal and image processing. If while studying deeply, it is easy to identify the importance of artificial neural network for image compression analysis. The classical image compression techniques basically depend on Back-Propagation Neural Network (BPNN) techniques. BPNN method signifies back propagation of neural network logic. Here, the authors use three or more fully connected layer of neurons. It is the most commonly used multilayer feed forward ANN technique. BPNN has the simplest architecture like ANN but it has the slowest convergence (Patel, & Agarwal, 2013). In this case, the authors consider the feature of intensity changes and find the number of blocks of the original image. In order to improve Network Convergence, the grey level of the image pixels and their neighbors has to be mapped in such a way that the difference in the grey level of the neighbors within the pixel is minimized.
This paper reviews Deep Learning based Convolution Neural Network Architecture for JPEG image and to train the Deep Neural Network adaptable to any other type of images (Kunwar, 2018).
In this review paper, the authors have used Joint Photographic Extension Group (JPEG), which is universally useful in order to build up global standards such as shading and still picture compressions. In image compression methods, many compression standards are available such as JPEG, JPEG-LS and JPEG-2000 (Li, Zuo,Gu, Zhao, & Zhang, 2018). Before performing image compression by Neural Network based applications, different intelligent denoising techniques has to be applied like SA-DCT, BM3D, which were proposed in late - 2000, but in order to obtain outstanding results different dictionary based sparse recovery algorithms like Dic- TV, RTF, S-D2, D3 and DDCN are used (Kunwar, 2018). They directly address the deficiencies like blocking and ringing, which are very specific to JPEG or JPEG compressions. The image compressions algorithm can be divided into several stages. Input image must be processed through following procedures (Li, et al., 2018):
Apart from this in the encoding stage linear transform can be performed to an image, Quantization and the lossless entropy coding are used to minimize the compression rate. Suppose Discrete Cosine Transform (DST) is used on 8 x 8 image patches, which quantizes the frequency components and compresses the quantized code with variant of Huffman coding. In case of JPEG2000 (Kunwar, 2018), multi scale orthogonal wavelet decomposition has to be used to transform an image and encode the quantized codes. Deep learning method is a fast-growing technology, which helps to generate image compression concept for both loss less and lossy images. In case of lossless compression of images, Deep learning models have achieved the state of the art performance, but in case of lossy image compression it represents a Recurrent Neural Network (RNN) (Li, et al., 2018) to compress 32 x 32 image.
Many deep Learning methods of neural network analysis learn and analyze the compression models by minimizing distortion for a given compression ratio. The work is related to Binarized Neural Network (BNN), where both weight sand activations are binarized to +1 or -1 to save memory storage and run time. In such type of image compression system only the encoder out is binarized to 1 or 0, and a similar proxy function is used in backward propagation (Kunwar, 2018).
It is a new area of machine learning based research, which has the original goal that is to implement the idea of Artificial Intelligence in Neural Network technique.
It was first introduced by a Japanese scientist Kunihiko Fukushima in 1980, it is an interconnected network of processing units emulating the network neurons in the brain (Li, et al., 2018). The idea behind ANN is to develop a learning method modelled by human brain. Deep learning is a method to train multilayer ANN using little data (Simon, et al., 2016). The authors have discussed this with an example, what is the basic difference between Machine Learning and Deep Learning. Machine Learning algorithms learn part of a face like eyes and nose for face detection tasks, but a Deep Learning uses some extra features like the distance between eyes and the length of the noes. In many publications for example Geoffrey Hinton and Ruston Salahutdinov have applied multilayer feed forward neural network effectively retain data time treating each layer unsupervised restricted to Boltzmann's machine using unsupervised back propagation for fine training. Figure 1 shows the multilayer neural network.
A deep neural network is defined as an Artificial Neural Network having at least one hidden layer in between the input and output layers. Extra layers are for enhancing its modeling capacity.
The most popular deep learning methodology is Convolutional Neural Nets or CNN or Conv-Nets which is shown in Figure 2. This type of feed forward Artificial Neural Network is extensively used in Computer vision. Each individual neuron is titled in such a way so that they respond to overlapping regions in the visual fields. In many cases CNN concept is to Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) (Li, et al., 2018).
Figure 2. Illustration of the CNN Architecture for Content-Weighted Image Compression (Li, Zuo, Gu, Zhao, & Zhang, 2018)
Along with CNN and ANN there is another type of neural network which has been recognised in this review that is DNN. It has two major drawbacks: One is over fitting while learning the training data using its hidden layer and other one is computation time. But DNN performs well if same type of training data is used as input (Simon, et al., 2016) and gives low performance when training data is different. After a research of several years a method that is adopted called dropout regularization, which is to remove some units randomly from the hidden layer that can solve the problem.
As mentioned earlier, that Artificial Neural Network has the superiority over other classical methods for image or data compressions because neural network seems to be well suited to this particular function as they have the ability to process input patterns to produce simplest patterns with fewer components. Table 1 describes some of the neural network based image compression techniques.
One of the most successfully implemented algorithms in neural network technology to solve the problem of data compressions is known as back propagation algorithm. In this case, data or image is allowed to pass through the input network. Then subsequently through a small number of hidden neurons. The compressed features of images are stored in the hidden layer (Ahmed & Alone, 2014); so smaller the number of hidden neurons means higher the Compression Ratio (CR). In case of large image compression, it may cause difficulty in training. So, for a large image compression it may be sub-divided to smaller number of sub-images and then each sub-image will be used to train an individual ANN (Simon, et al., 2016). This type of process is implemented successfully for compressed and decompressed images with an impressive Compression Ratio (CR) with little or no loss of data.
The authors have introduced an other new type of network that is known as Kohonen Network when compared with Back Propagation it was observed that Kohonen networks is better in terms of signal to noise ratio but on the other hand training time of Kohonen Network was higher which is indeed a problem (Ahmed, & Alone, 2014). So, for better image compression technique with better signal to noise ratio both the network-based techniques has to be combined, which gives us satisfactory results.
Before showing the best results obtained from different neural network based algorithm, it is necessary to discuss how or in which methods those results are obtained. Figure 3 shows the CNN training flow chart. Different types of training architecture for understanding the binarization of the input to encoder and output at decoder are used. If is binarized the sigmoid output the information is completely lost (Kunwar, 2018). If Gaussian noise is added before sigmoid function, it will start to find the grey code because the symbol encoded with 0 and 1 that can persist noise. That's why in the results and discussions, the authors are showing an example of CNN final training architecture with the addition of noise (Li, et al., 2018).
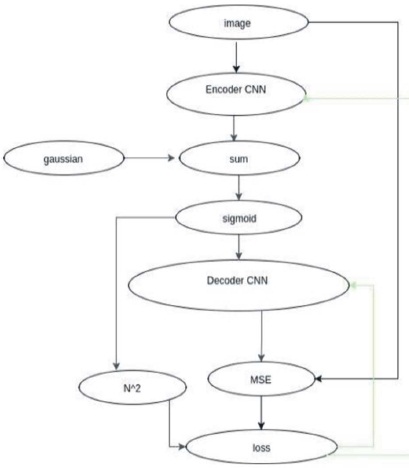
Figure 3. CNN Final Training Flowchart (Kunwar, 2018)
In the case of any of the images, the best compression ratio is obtained with the neural network- based training and with highest PSNR (Kunwar, 2018). That's why some results of original and compressed images are displayed with training state graphs in Figures 4 to 6.

Figure 4. Original Image

Figure 5. Compressed Image
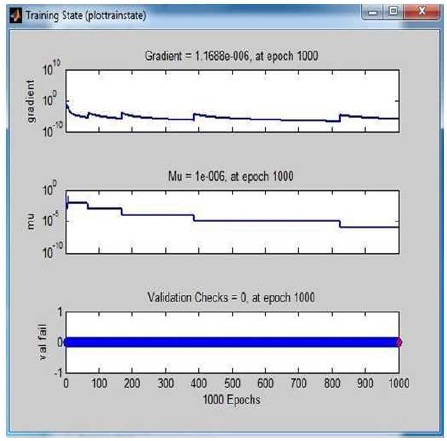
Figure 6. Training State Graph
As mentioned earlier, different applications use Neuro- Wavelet based image compression techniques. Table 2 shows the results obtained using the neural network radial basis algorithm. Figure 7 shows the original medical images. Figure 8 shows the NNBP compression technique's resulted in compressed medical image. Figure 9 shows the comparison between the models with and without importance map (Li, et al., 2018). Those images give us some extra-ordinary idea about how different types of neural-network techniques are adopted for image compression, whereas the table contains a comparison of Compression Ratio, PSNR, Mean Square Error and BPP (Dabass, Vig, & Vashisth, 2018). It will give us some idea about different results obtained from different compression techniques using a combination of neural network Analysis and wavelet based decomposition.
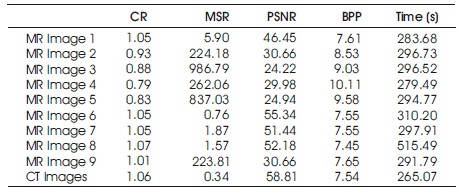
Table 2. Results Obtained using the Neural Network Radial Basis Function Algorithm (Kunwar, 2018)

Figure 7. Original Medical Images
Figure 9. Comparison between the Models with and without Importance Map (Li, et al., 2018)
In the previous mentioned sections, the authors have defined the applications of Deep Learning method related to neural network analysis. A review has been done in order to implement the works for the future purpose. In order to achieve this, three different fields of Deep Learning related to image compressions are chosen. In the future there is a need to extend our works focussing on these three methodologies.
Artificial Intelligence (Simon, et al., 2016) is a new area of research, which is capable of performing a task that a human being can. In modern times it has huge applications in Speech Recognition (Li, et al., 2018), Playing Games, Expert System, Decision Making, Medicine (Dabass, et al., 2018), Aviation and Translation of languages. The work can be extended with the help of Deep learning in Artificial Intelligence in the Gaming Industry (Simon, et al., 2016). The same applications can be implemented in military as well as aviation industry where pilots can avoid air traffic with the help of this technique.
It is another best way to realize Deep Learning by using a different type of algorithm that is GSOM (Ahmed, & Alone, 2014) or Growing Self-Organizing Map algorithm. This concept has been developed in order to identify a suitable map size in self organising map. It starts with a minimal number of nodes and grows new nodes on the boundary of a heuristic. The compressed form of data is obtained from the output nodes of the network, which can be further decompressed by another network (Ahmed, & Alone, 2014). This algorithm can be used as a method of Deep Learning for performing data compressions.
Apart from those two mentioned areas the authors will also try to focus another new area, which is quiet interesting and useful for new dimensions of research that is Wavelet Analysis. Neuro-Wavelet based analysis has been used in different fields of medical image processing in this paper, so it is necessary to know what wavelet analysis is and how it can be implemented in other fields related to image compression (Dabass, Vig, & Vashisth, 2018). Wavelet Transforms (WT) or analysis that replaces conventional Fourier Transform (FT) can be used in Image Compression, Feature Extraction, Image De-noising and another medical image technology. In modern physics Wavelet Transform can be applied rapidly in Astrophysics, Density Matrix Localization, Seismic Geophysics, Optics, Turbulence and Quantum Mechanics. Here, two major applications of Wavelet Transform are discussed, which can be useful for the future scope of research.
5.3.1 Fingerprint Recognition
Fingerprint recognition is another most important area of application where Wavelet transform is playing an important role for the growing world of deep learning. After performing a rigorous research on the application of Fingerprint recognition it is proved that Discrete Wavelet Transformation or DWT based Fingerprint recognition is considered to be one of the best techniques because many new features such as Directional Information, Central Area, Edge Parameters are extracted from DWT. Pokhriyal and Lehri, (2010) proposed an algorithm of fingerprint verification Wavelets and Pseudo Zernike moments where wavelets are used for de-noising and edge extraction.
Image compression and feature extraction is another important field where Wavelet has its major applications, which are increasing in modern days. The main aim of image compression is to exploit redundancies in data, therefore, the data can be 'thrown away' and can be considered after performing reconstruction of original image. By removing redundant data images, it can be represented in smaller number of bits. Grgic, Grgic, and Zovko-Cihlar (2001) presents this comparative study by wavelet transformation analysis in his paper. In this case, it is observed that Discrete Wavelet Transform methodology for both JPEG- 2000 (ISO/IEC 15444-1:2000, n. d) and still image coding. Because of having an inherent features DWT provides multi-resolution
Functionality and better compression performance at a very low bit rate compared with DCT based JPEG standard (ISO/IEC 14496, n. d). This methodology can be implemented in computer vision process for better feature extraction purpose.
So, there are so many fields where Deep Learning concept or method can be applied to achieve better quality of image or data compression for the future extension of the work.
In this paper, the authors have discussed concept of Deep learning methodology along with its implementation on different types Neural Network based on image compression techniques and an overview of wavelet- based analysis on Neural Network Mechanisms (i.e. neuro-wavelet analysis) to describe image compression related problems. In all cases the main goal or objective is to obtain a very clear and better image Compression ratio (CR) with minimum loss of data during compression. Apart from this, in the review methods and analysis of results Signal to Noise Ratio or PSNR is improved by minimizing the effect of noise as much as possible. Noise in images can be removed by different types of filtering like Special Filtering, Motion Filtering, Average Filtering, Median Filtering etc. But the properly justified filtering can increase the Signal to Noise Ratio by improving the quality of signal power. There are many ways to perform this technique but the authors have tried to implement some of the best and universally recognized methods to achieve bettet results.