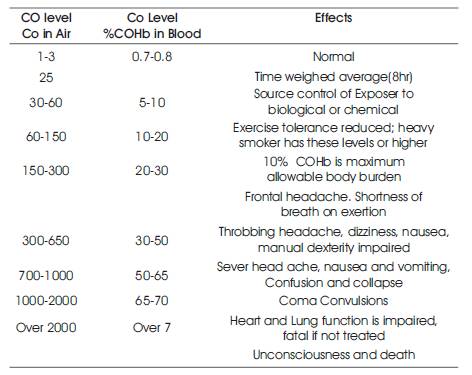
Table 1. Effect of varying levels of Carbon monoxide
Air pollution through fine and ultra-fine particles is a major threat to human health in cities of developed and especially of developing countries. Carbon Monoxide (CO) is the main pollutant in industries, residence and rural areas, CO is commonly referred as the “silent Killer”. CO is extremely toxic and often effects victims in such a manner that they fail to recognize the liability. In certain countries, even higher levels of fine particles occur in the indoor environment due to open stove cooking and heating. The carbon monoxide is mainly released in traffic areas, and Parking garages. There are many sources that are Vehicles’ carbon monoxide sources, Home carbon monoxide sources, Travel carbon monoxide sources, Work carbon monoxide sources etc.,and there are so many effects caused by carbon monoxide. In this present work the detailed description on different types of sensing technologies like Solid state Sensors, Electro Chemical Sensors are used for finding CO and remedial measures to control CO are reviewed.
Environmental pollution is the biggest menace to the human race on this planet today. If people pollute them, then the existence of man and nature will be hampered. Our earth is becoming warmer. If pollution continues, the day is not far when our earth will be a boiling pan and become a desert [1,2]. Impure air causes diseases and impairs the health and causes death. The smoke which is discharged from industries, automobiles and kitchens are the mixture of Carbon Monoxide, Carbon Dioxide, Methane etc which are poisonous gases. These cause lung-cancer, tuberculosis etc. The glaring incident of the Bhopal gas leak in December 1984. Where in thousands of the residents of Bhopal died due to lung problem was caused by methylamine gas from the Union Carbide Plant. The garbage emitting foul smell as well as the decaying plants and animals also cause air pollution. Hence the doctors advise the patients who have lung trouble to settle in some rural places because the air in villages is pure and free from population. The harsh sounds of buses, mopeds etc, affect our power of hearing and cause trouble. The waters of rivers and seas being constantly polluted all over the world by various dangerous chemical and biological wastes. Mills and factories discharge very harmful waste waters into many rivers and sea. There is no doubt that the fish that grow in such waters are poisonous too. Reckless application of chemical fertilizers, insecticides and pesticides pollute the soil. Vegetables and fruits are quite injurious today, because they contain the poison of insecticides and pesticides. If the air to breathe, the water to drink and the soil which produces our crops, vegetables and fruits, all become more and more impure, then our chances of good health and longevity will be very less. Environment pollution is a serious menace to our existence. Impure water from industries can be sent back for purification and then it can be used for irrigation purpose.
Air pollution is introduced due to chemicals, particulates, biological materials, or other harmful materials present in the Earth's atmosphere, and possibly cause disease, death to humans and damage to other living organisms. The atmosphere is a complex natural gaseous system that is essential to support life on planet Earth. Pollutants are classified as primary as well as secondary. Primary pollutants are usually produced from a process, such as ash from a volcanic eruption. Secondary pollutants are not emitted directly. Rather, they are formed in the air when primary pollutants react or interact. Ground level ozone is a prominent example of a secondary pollutant. Some pollutants may be both primary and secondary: which are both emitted directly and formed from other primary pollutants.
Major primary pollutants produced by the human activity are Sulfur oxide (Sox), Nitrogen dioxide(NOx), Carbon Monoxide, Volatile Organic Compounds(VOC), Ammonia (NH3), Odors and Radioactive pollutants.
Particulates are created from gaseous primary pollutants and compounds in photochemical smog. Classic smog results from large amounts of coal burning in an area caused by a mixture of smoke and sulfur dioxide. Modern smog does not usually come from coal but from vehicular and industrial emissions that are acted on in the atmosphere by ultraviolet light from the sun to form secondary pollutants that also combine with the primary emissions to form photochemical smog [3,4].Photochemical and chemical reactions many involve in kinds of chemical processes that occur in the atmosphere by day and night. At abnormally high concentrations, brought by human activities (largely the combustion of fossil fuel) it is a pollutant, and a constituent of smog.
Carbon Monoxide (CO), is also called as carbonous oxide, which is a colourless, odorless, and tasteless gas which is slightly lighter than air. It is highly toxic to humans and animals in higher quantities. In the presence of oxygen, carbon monoxide burns with a blue flame, producing carbon dioxide. Levels normally present in the atmosphere are unlikely to cause ill effects. Inhalation of low levels of carbon monoxide can cause headache, dizziness, light-headedness and fatigue. Exposure to higher concentrations of carbon monoxide can cause sleepiness, hallucinations, convulsions, collapse, loss of consciousness and death. Long term (chronic) health effects can occur from exposure to low levels of carbon monoxide. These effects may produce heart disease and damage to the nervous system. Exposure of pregnant women to carbon monoxide may result in low birth weights and other defects in the offspring. Industry sources generally, exhaust carbon monoxide in air from a combustion process. Examples of industrial plants that produce carbon monoxide are metal manufacturing, electricity supply, mining, food manufacturing, oil and gas extraction, cement lime, and petroleum refining.CO emitted predominantly from petrol vehicles can reach high levels in areas with high traffic density. The CPCB mentions that CO measurement should be conducted near traffic intersections, highways and commercial areas where traffic density is high. Generally areas with a high population density have a large number of vehicles and higher CO levels [8-12].
Carbon monoxide is formed by the incomplete combustion of materials containing carbon and can be produced by virtually anything that burns. It is a common byproduct of fuels that burn such as gasoline, diesel, propane, natural gas, kerosene, wood, coal, charcoal, alcohol, and others. In addition to carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides, sulfur dioxide, particulates, and other toxins are also produced during combustion. Building and house fires produce a significant amounts of carbon monoxide along with a massive number of other air toxins.
Cars, trucks, vans, recreational vehicles, campers, shells, transports, Gasoline/petrol, Diesel, Propane, Natural gas.
Furnace (natural gas, propane, oil, wood) , Stove (gas, wood), Dryer (gas only), Barbeque (gas, charcoal), Gasoline/petrol powered garden tools, Generator (gasoline, diesel, propane), carbon monoxide in cigarettes and tobacco smoke.
Carbon monoxide poisoning is surprisingly common in recreational motor-boating situations, especially for people swimming around swim platforms and boarding ladders located close to the motor exhaust area. Even a mild case of CO poisoning can be made of drowning when the effects of the poisoning take hold of Gasoline/petrol and Diesel.
Carbon monoxide poisoning can easily happen when campers bring a heater into a tent, Heater (propane, kerosene),Generator (gasoline, diesel, propane) ,Camp fire.
Many hotel, motel and dormitory rooms are heated with individual heating units. There could be hundreds of rooms and heating units in a building which increases the risk of sporadic (or unqualified) maintenance. The proximity of heating units to each other also increases the risk that the exhaust venting from one unit could get drawn into the air intake in another unit.
Carbon monoxide is a common industrial hazard resulting from the incomplete burning of natural gas and any other material containing carbon such as gasoline/petrol, kerosene, oil, propane, coal, or wood, Gasoline powered tools such as pressure washers, concrete-cutting saws, power trowels, floor and welders, Propane powered forklifts, forges, blast furnaces, and coke ovens, Paint removers/strippers containing methylene chloride also create carbon monoxide.
Carbon monoxide interferes with the ability of the blood to transport oxygen. Haemoglobin, a protein present in the red blood cells, normally binds oxygen (to form oxy hemoglobin) and transports it to all parts of the body. Carbon monoxide competes with oxygen and binds to haemoglobin (to form carboxy haemoglobin or COHb) much more easily. Carbon monoxide is therefore a chemical asphyxiant. This means that it prevents sufficient oxygen from reaching the tissues of the body. Insufficient oxygen can cause death. The various effects caused by CO are listed below as shown in Table 1.

Table 1. Effect of varying levels of Carbon monoxide
Not all CO sensors are alike. Electrochemical sensing technology provides many advantages over the older semiconductor (“solid state”) sensors or infrared sensors. Electrochemical sensors offer high resolution (≤ 0.5 ppm), a linear signal, long-term stability (≥ 5% over the lifetime of the sensor) and immunity to false alarms caused by “nuisance gases.” The best CO sensing technologies will also alert facility and emergency personnel, via cell phone, in the case of dangerous concentrations of CO [5]. While inadequate ventilation can drastically increase the risks of liability, continuous operation of ventilation systems can be costly. To minimize heat loss in winter, as well as conserve energy used by the ventilation fan motors, some parking garage owners began to operate ventilation systems only during peak traffic times, that is, during the morning and evening rush hours. This, however, failed to take into account instances in which a car was left idling or parking patterns varied from the norm. This explains the growing trend toward installation of CO monitoring and ventilation control systems.
It is also called Metal Oxide Semiconductors (MOS), These types of sensors are based on the principle that metal oxide surfaces will change its conductivity based on their exposure to various types of gases [6].With the appropriate electronics and calibration, the non-linear change in conductivity of the sensor can be then translated into an analog or relay signal, indicating gas concentrations. The accuracy of measurement of these devices can be significantly affected by changes in temperature and humidity. The solid state sensor is shown in Figure 1. There are different ways of making solid state sensors, each arrangement making the sensor's per formance characteristics different. Two typical are the following,
All solid-state sensors have short-term drift(typically ±20%) and long-term drift (varies with manufacturer) that have dictated industry practice of checking calibration on an annual basis when applied in garage applications. Sensors typically have a life of 2 to 10 years depending on the manufacturer. This is the type of sensor most commonly used in residential as CO detectors where the alarm limit typically corresponds to detecting a gas concentration of 100 ppm for over 90 minutes. In contrast, parking garage applications typically need to measure 35 or 50 ppm concentrations that occur within a few minutes. The levels typically measured in parking garages are at the low end of the sensitivity range of solid state sensor. Properly manufactured, solid-state sensors offer a very long life expectancy. It is not unusual to find fully functional sensors that were installed at 30 years ago.

Figure 1. Solid state sensor
Electrochemical sensors are small devices that generate a voltage, based on a reaction between a specific target gas and a chemical mixture as shown in Figure 2. These sensors can be highly specific to the gas measured and highly accurate (better than ± 1 ppm at concentrations under (50 ppm) [7]. Accuracy is not significantly affected by humidity and temperature. Power requirements are also very low, because the chemical reaction of the sensor generates the sensor output, making it ideal for battery powered applications like portable units or wireless devices. The sensor life and calibration is affected by the depletion of the reacting chemical in the sensor and is directly related to the duration and level of exposure to the target gas being measured. Sensor life can vary from 18 months to 5 years depending on gas measured and manufactured. The basic sensors are shown in Figure 3.
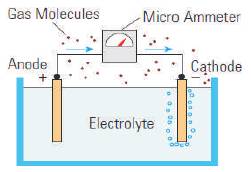
Figure 2. Electrochemical Sensor

Figure 3. Basic Sensor
Air Test offers a unique electrochemical CO sensor. The sensor itself is rated for 5 years of operation and can easily be replaced with a plug-in replacement sensor. The base level model called the TR 2000 is a loop-powered transmitter (current output) that provides a linear signal corresponding to CO concentrations. It is often used when directly connecting to a building control system that will control CO concentrations. Air Test provides a battery powered wireless control system using the TR2000 which is shown in Figure 4 to reduce the high costs related to installing conduit parking garage applications.

Figure 4. TR2000 Transmitter
Until recently, cost was a major factor in deciding which technology to use. Electrochemical has many advantages over solid state technology, but was often two to three times the price. As a result, solid state sensors have often been used where cost and basic functionality is more important than performance. Electrochemical sensors have tended to be installed in high end or owner operated applications where accuracy, specificity of measurement and performance is important. However, the TR2000 sensor’s advanced technology has reduced the cost difference between the solid state and electrochemical sensors to less than 20%. The TR2000 is the first long life, Electrochemical to be offered at a solid state price.
Inhalation of low levels of carbon monoxide can cause headache, dizziness etc.CO emitted predominantly from petrol vehicles can reach high levels in areas with high traffic density. Solid state sensors is the type of sensor most commonly used in residential CO detectors where the alarm limit typically corresponds to detecting a gas concentration of 100 ppm for over 90 minutes. TR 2000 is a loop-powered transmitter which is often used directly connected to a building control system and controls CO concentrations. Electrochemical has many advantages over solid state technology. But those sensors are not enought to control the CO level in air. Hence one of the remedial measures to control pollutants levels is to improve the design of air pollution control devices.