Table 1. Classification of Undergraduate College Teachers Based on the 4G Impact Assessment Scale
The influence of 4th generation broadband cellular network technology on education is explored in this paper. With the widespread use of smartphones and tablets, students are increasingly using mobile devices to access learning resources, communicate with peers, and complete assignments. The advent of 4G technology has had a revolutionary impact on undergraduate education, transforming the way students access information and interact with course materials. With 4G, students can now quickly and easily access online resources, download and stream multimedia content, collaborate with classmates in real-time, and participate in remote learning. This technology has had a profound influence on the way education is managed today, providing faster and more efficient access to educational resources and a personalized learning experience while streamlining administrative processes and assisting teachers in instruction. 4G technology has completely revolutionized the way education is thought of and experienced, creating an open environment, interactivity, and increasingly specialized training for students and professionals alike.
The world has seen tremendous advances in mobile communication technology, ranging from 4G to 5G and beyond. With 4G networks, people all over the world have access to the internet, allowing them to explore the world of knowledge at unprecedented speeds. This has naturally had a major impact on the world of education as well.
At the most basic level, 4G enables students to have easy, unrestricted access to educational resources that are otherwise difficult or time-consuming to find. The abundance of educational materials available online due to the spread of 4G networks allow learners of all ages to access essential learning materials. This abundance of materials makes it easier for teachers to create class assignments and find resources to supplement their instruction, leading to improved educational outcomes for students. 4G networks also make it possible for students to connect to lectures and courses from anywhere in the world. With 4G, knowledge is no longer restricted to physical classrooms. Students can now interact with teachers and experts remotely, allowing them to learn with greater ease and flexibility (Agarwal & Agarwal, 2014).
Traditionally, education has been centered on sources such as schools, teachers, and print media. People accessed this information by enrolling in school, seeking out teachers, and visiting libraries. Before the digital era, information was not readily available to the majority of people, and even those who did have access were unable to obtain up-to-date information relevant to the current context (Händel et al., 2020).
Now, modern society demands to know information as soon as it happens, and the world is transitioning from an information society to a knowledge society. As such, education is given the highest priority, and brainpower is becoming the most valuable asset of any organization. Technology has made information accessible and transmittable from anywhere to all groups of people (Zawacki-Richter et al., 2015a). Education has spread to most parts of the world, and Information and Communication Technology (ICT) has become an integral part of everyday life.
The utilization of ICT facilities in education has increased significantly due to advancements in the telecommunications sector. In India, progress in this area has been slow to start, largely due to a lack of competition. Although the first telecommunications services in India were established by the Oriental Telephone Company Limited of England in 1881, these services were limited to the elite members of society and could not be considered a proper telecommunications service (Aithal & Prasad, 2016). However, in recent years, the landscape has changed drastically with the emergence of new generations of telecommunications.
Efforts to control the spread of the COVID-19 virus have affected all sectors worldwide, including the higher education system, which switched to digital higher education (Hodges & Fowler, 2020). Despite the already established digital learning platforms and the usually good technical equipment of students, it would be misleading to assume a general ability of the digital natives to use technology in academic contexts (Lei, 2009; Zawacki-Richter et al., 2015b). The same is true regarding the acceptance of technology. Hence, even after the pandemic ends, the use of technology in education will only increase as it makes education simpler and more efficient (Stephan et al., 2020).
The year 2016 was a landmark for the Indian telecom industry as it saw the long-awaited sector consolidation. This was driven by a number of factors, such as increasing pressure on profitability, hyper-competition, spectrum trading and sharing guidelines, and a favorable Merger and Acquisition (M&A) policy. These changes facilitated the implementation of new educational strategies during the pandemic and beyond. This has enabled India to make significant strides in the field of education and has helped to ensure that students are able to continue their studies despite the challenges posed by the pandemic.
The introduction of technological tools into the education system has been a game-changer for teachers, students, and everyone involved in the educational process. Since the early 20th century, technological tools have been used in the field of education, but the lack of proper telecommunication technologies was a major barrier to their efficient use. This changed with the arrival of Jio, a subsidiary of Reliance Industries Limited, in the highly competitive telecommunications industry. With its cutting-edge technology, comprehensive services and competitive rates, it has been established leading in the market. Other operators have followed suit, and the telecom sector in India has experienced an unprecedented rate of growth. This growth has been instrumental in transforming the educational landscape in India, providing students with access to a wealth of resources and opportunities that were previously unavailable. As such, Jio 4G has been a major contributor to the advancement of the Indian education system.
Despite the availability of low-cost technological facilities in Indian educational institutions, teachers and students had been reluctant to use them until the COVID-19 pandemic struck the nation. The virus has had a devastating effect in many aspects, and the education sector is no exception. Schools, universities, and other educational institutions have had to close their doors in order to contain the spread of the virus, leaving students and teachers in need of alternative methods of learning to ensure that students can still gain the knowledge needed to succeed.
In response to the COVID-19 pandemic, many schools changed an online learning format, allowing students to continue their studies without having to be in a physical classroom. This new format of learning has its advantages, such as having access to a variety of materials through different websites, not having to adhere to a traditional classroom schedule, and be able to participate in virtual field trips. However, students had less contact with their teachers, they may find it difficult to maintain a steady pace of learning, and they have to become familiar with different technologies in order to access the information they need. Despite these challenges, online learning opened up a world of possibilities for students, provided them with the opportunity to explore new topics to gain valuable skills.
Schools and universities responded to these changes by transitioning to an online format or hybrid system, while various financial aids were available to alleviate the burden. Even after the pandemic subsided many people are continuing to embrace the use of new technological facilities in their educational process due to the convenience it provides. This would not have been possible without the introduction of 4G technology in India. Therefore, it is crucial to assess the influence of 4G on the education system and its transformative effects on the learning experience.
Miller (2006) conducted a study of a selection of elementary school classrooms during their normal instructional routines to observe, analyze, and describe the impact of educational technology on learner interactions. As a study grounded in the concepts of the qualitative research tradition, the research methods employed included observations, personal interviews with teachers, group interviews with students, and document review. The purposeful selection of teachers, who were disposed to distinctly different pedagogical practices and uses of educational technology, provided a wide variety of experiences for the data collection process as a participant and interacted with the classroom occupants. The study was conducted by the school's principal. The findings of the study support the conclusion that, integrating technology can positively impact the interactions of learners in elementary classrooms when used as a tool to support constructivist pedagogy.
Young (2008) conducted a study to determine the effect of computer technology use in the classroom on students' grades, motivation, attitude, and attendance. The study used teacher or student technology surveys to measure teacher use, student use, and overall use of technology in the classroom. The results of the study indicated that teachers' technology use, students' technology use, and overall technology use depended on how well the teacher used technology in the classroom. While the use of technology was motivating for students, it had no significant positive effect on their grades or attendance. Additionally, the study found that the continued use of technology was low among the teachers in the sample. These results suggest that if technology has to be effective in making changes in students' grades, motivation, attitude, and attendance, schools must be adequately prepared for technology use in the classroom.
Cederholm (2010) addressed the issue of developmental education, which is being discussed at the national level and was discussed in the Alabama post-secondary arena. Committees and symposiums were formed to discuss this topic, and this issue is important, as developmental education is an essential function for most community colleges. This study adds to the current data on the success of students who took developmental courses. Most studies on the topic of developmental education focused on the comparison between students who had remediation and those who did not. There is not much data that compared the type of instruction given in remedial courses and the different types of instruction affected student learning outcomes. This study compared two different methods of instructional delivery in a developmental English classroom. Straight lecturebased classrooms and classes where some type of technology was used to deliver course material were compared, and the learning outcomes for each class were evaluated.
Loveland (2012) observed that technology education is an academic subject area that teaches students the ways in which human beings change their environments to be better suited to their needs and wants, thereby using various types of knowledge. Technology education has its roots in the industrial arts and crafts movements and centers around the products and systems created by humans (Vries, 2009). Wright and Wilton (2012) describes technology as the use of objects such as tools, machines, systems, and materials to change the natural and human-made environments.
Sulehria (2019) found that evolution is the essence of the impact left behind by every being and every technology. Advancements in the field of computer networks have progressed from a simple telegraph invented in the 18th century to the 5G communication technology on the verge of being implemented in South Korea. The needs of human beings never cease to exist, but they surely result in the invention of new technologies to pacify them. In this study, Sulehria (2019) provided an overview of the generations of networks along with a brief introspection on 5G technology that will provide access to a wide range of telecommunication services in accordance with service demands in a multi-user environment.
Keenan (2020) mentioned that since the launch of the first 5G services by Verizon and AT&T in the USA, 5G networks have been rolled out in a further 17 countries, with South Korea, the United Kingdom, Germany, and the United States leading the charge. Analysts are forecasting 2.7 billion 5G connections by 2025, and the uptake of 5G is expected to be faster than any previous cellular generation. Expectations are high for its future impact on the global economy. In this review of the evolution of cellular networking, previous generations of networks are briefly examined before exploring why 5G is different and how it is expected to deliver many anticipated economic benefits.
Pilatso and Chukwuere (2022) observed that fourthgeneration (4G) wireless communications and technologies have improved various aspects of daily life, including health, communications, and education. The focus of this study was to explore the impact of 4G mobile technologies on university students' academic performance. The research utilized a quantitative approach and a closed-ended questionnaire to determine the impact of 4G technologies on students' academic performance at a Higher Education Institution (HEI). The study examined the impact of 4G mobile technology on students' academic performance through research questions that concentrated on the effects of the technology. Results showed that 4G mobile technologies improve students' mobility, internet quality, faster internet connections, and access to online resources compared to visiting a physical library.
Sun and Jin (2022) explored the scope of 5G in the context of online music education. With the formation of a scale and pattern for online music education in the 4G network era, its necessity and educational achievements have emerged. However, the upcoming 5G network era presents new challenges for online music education, and necessary changes must be made. This paper aims to address these changes by exploring the characteristics of online music education in colleges and universities and summarizing and analyzing the current work status and problems faced. The goal is to improve the level of work and take online music education to new heights.
In recent years, the influence of 4G and technological progress on education has been undeniable. Mobile technology, interactive classroom tools, and cloud computing have opened up a variety of dynamic, multidimensional learning opportunities for students that would not otherwise be available on traditional platforms. This has enabled teachers worldwide to enhance the quality of teaching and learning experiences with multimedia-based activities and real-time interactions while also reducing teaching costs by streamlining administrative processes. Furthermore, these advancements have enabled learners to access educational material from anywhere at any time for selfdirected study. Undoubtedly, 4G and other digital advancements are revolutionizing education. In general, the importance of 4G and its technological progression in education is inevitable. Technology has revolutionized the field of education, making it easier and more efficient for students to learn and for teachers to teach. With the help of technology, teachers can better engage their students and ensure that everyone understands the material, while students can access information quickly and collaborate with one another more effectively. Thus, the present study aims to investigate the major influences of 4G in the undergraduate education sector.
The present study utilized primary data obtained through the normative survey method. Stratified random sampling was used to obtain an adequate, representative, and randomized sample. The arts and science colleges in Kerala have been categorized into North, Central, and South strata, which comprise five, five, and four districts, respectively. The data was collected using a 5-point scale from undergraduate teachers in Kerala. The tool used in this study to analyze the impact of 4G in undergraduate education was the "4G Impact Assessment Scale," consisting of 35 items, 33 of which were part of the 5-point scale, and 2 items were ranking questions. Appropriate statistical techniques such as mean, standard deviation, and t-tests were used to analyze the scores and test the hypotheses. The t-test was used to determine the significance of the difference between the means for different groups based on gender, locality, and age group.
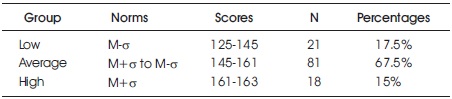
The distribution of 4G influence assessment scores had a mean of 153.36 and a standard deviation of 8.003. As a result, undergraduate college teachers with 4G influence assessment scores of 161 or higher were classified as the "High - 4G influenced group," those with scores less than 145 were classified as the "Low - 4G influenced group," and those falling between these scores were classified as the "Average - 4G influenced group." Table 1 shows the classification of undergraduate college teachers in each group based on their scores on the 4G impact assessment scale.

Table 1. Classification of Undergraduate College Teachers Based on the 4G Impact Assessment Scale
The arithmetic mean and standard deviation of the male group are 152.53 and 8.26, respectively, and those of the female group are 154.03 and 7.79, respectively. The tvalue obtained is 1.012901896, which is less than the table value of 1.98 at the 0.05 level. This indicates that there is no significant difference in the mean scores for the influence of 4G among male and female teachers. Table 2 shows the data and the result of the significance test of the difference between the mean values of the 4G impact assessment scores based on gender.
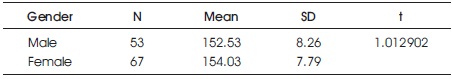
Table 2. Significance Test of the Difference between the Mean Values of the 4G Impact Assessment Scores Based on Gender
The arithmetic mean and standard deviation of the rural group are 150.72 and 8.61, respectively, and the urban group are 156.94 and 5.39, respectively. The t-value obtained is 4.321845, which is greater than the table value of 1.98 at the 0.05 level. This indicates that there is a significant difference in the mean scores for the influence of 4G among rural and urban teachers. Table 3 shows the data and the result of the significance test of the difference between the mean values of the 4G impact assessment scores based on locality.
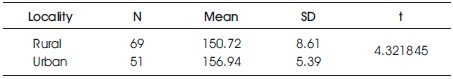
Table 3. Significance Test of the Difference between the Mean Values of the 4G Impact Assessment Scores Based on Locality
The arithmetic mean and standard deviation of the younger group are 154.89 and 6.85, respectively, and those of the older group are 151.36 and 8.97, respectively. The t-value obtained is 2.444324, which is greater than the table value of 1.98 at the 0.05 level. This indicates that there is a significant difference in the mean scores of the influences of 4G among younger and older undergraduate college teachers. Table 4 shows the data and the results of the test of significance for the difference between the mean values of the 4G impact assessment scores based on age group.
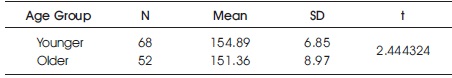
Table 4. Test of Significance for the Difference between the Mean Values of the 4G Impact Assessment Scores Based on Age Group
The calculated F value is 3.71. The table value of F for degrees of freedom (2, 117) is 5.30 at the 0.05 level and 4.61 at the 0.01 level. From this, it is clear that the computed F value is less than the table value (F = 3.71 with df (2, 117), p > 0.01). It indicates that there is no significant difference between the mean values of 4G impact assessment scores based on North Kerala, Central Kerala, and South Kerala among undergraduate college teachers. Table 5 shows the summary of ANOVA of the scores of regions.
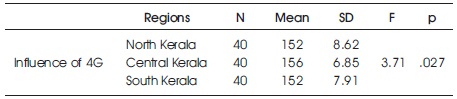
Table 5. Summary of ANOVA of the Scores of Regions
The influence of 4G on undergraduate education is examined by exploring its effects on learning outcomes, student engagement, and access to educational resources. The findings of this study shed light on the potential benefits and challenges of 4G technology in undergraduate education and provide insights on how much 4G influenced the teaching and learning process.
The study found that there is no significant difference in the influence of 4G among undergraduate college teachers based on gender. This indicates that both male and female teachers have equal access to and benefit from the technology. However, there is a marked disparity in the influence of 4G technology among college professors in urban and rural areas, which can affect how educators in both settings utilize communication and information technology. Significant differences in the influence of 4G among undergraduate college teachers were observed based on age group, with younger teachers being more tech-savvy and embracing the technology to a greater extent than their older counterparts.
Therefore, this highlights the need for continuous training and development programs to ensure that all teachers are equipped with the necessary skills to effectively integrate technology into their teaching practices. However, no noteworthy disparities in the impact of 4G among undergraduate college teachers based on their geographic region in Kerala were observed. This indicates that the implementation of 4G technology is having a uniform effect on college professors, regardless of their region. Nevertheless, as observed in the study, there are still notable differences in the impact of 4G technology among college professors in urban and rural areas and among different age groups. Therefore, it is crucial to address these disparities through continuous training and development programs to ensure that all educators possess the necessary skills to effectively integrate technology into their teaching practices.
The advent of improved 4G facilities has brought significant changes in the field of education. One of the major benefits is increased access to online learning resources. With faster and easier access to e-books, online courses, videos, and other educational content, students and teachers can benefit from a wealth of information. Improved 4G facilities have also enabled better communication and collaboration among students and teachers, fostering virtual classrooms, online discussions, and video conferences. This can enhance learning outcomes by facilitating greater interaction and participation. Additionally, improved 4G facilities have enabled greater flexibility in learning, enabling students to access learning materials and resources from anywhere at any time. Furthermore, the use of technology in education has been enhanced, with mobile learning, gamification, and virtual reality providing a more engaging and interactive learning experience. Finally, improved 4G facilities have increased access to education for marginalized communities, bridging the digital divide and ensuring that all students have access to quality education. Overall, improved 4G facilities have the potential to transform the education system and provide new opportunities for students and teachers to learn and collaborate.
The rapid advancement of technology has brought about a revolutionary change in the education system. With the introduction of 4G technology, it has become even more accessible and convenient for students to access educational resources at any time and from any location. This study aims to provide recommendations based on the findings of the research conducted on the influence of 4G technology on undergraduate education. The recommendations are aimed at enhancing the learning experience and improving academic performance for undergraduate students.
The education system needs to adapt to the rapidly changing demands of the 21st century by providing students and teachers with adequate infrastructure. This includes high-speed internet connectivity, reliable servers, and hardware capable of running multimedia educational materials. Institutions should develop multimedia content that can be accessed on mobile devices and ensure that 4G telecommunication facilities are available to all students, even to those who may not have access at home. Additionally, teachers and education professionals must be trained in the effective use of these facilities, and data security and privacy must be a top priority. By using 4G telecommunication facilities, students and teachers can collaborate more effectively, and institutions should encourage the use of collaborative tools to promote active learning and enhance student engagement. It is also important to collect data on student performance, engagement, and satisfaction to assess the impact of 4G facilities on learning outcomes. Finally, governments and educational institutions should collaborate with telecom companies to make these facilities more affordable and bridge the digital divide, allowing all citizens to benefit from technological advances and innovative educational solutions.
The influence of 4G technology in the field of education has been far-reaching and profound. Its implementation has allowed more expedient connectivity between teachers, students, and educational institutions, allowing better access to resources and a greater capacity to share ideas in a global context so that learning can take place anywhere at any time. It has also enabled teachers to respond more quickly to students' queries, enhancing their ability to gauge perceptions and engage in instructive dialogue. Furthermore, 4G technology has enabled new workspaces where collaborative efforts are nurtured and innovation is encouraged. Ultimately, the widespread adoption of 4G technology in the educational sector has been fundamental in ushering to a new era of innovative teaching practices and providing unprecedented access to knowledge regardless of geographic or financial restraints.
The emergence of 4G networks has had both positive and negative ramifications for education. Also, high-speed internet and broadband-enabled applications, such as video streaming, are transforming educational experiences by making it much easier to access a wide variety of resources, such as online courses. This enables greater flexibility for distance learning, which can be an invaluable asset for those who are unable to attend physical institutions due to geographic or financial constraints. Additionally, 4G networks have allowed teachers to leverage exciting new technologies, such as virtual reality and augmented reality, in the classroom setting.
On the other hand, however, 4G networks have introduced new distractions into classrooms, with students increasingly relying on their phones instead of paying attention in class. Social networking addiction and game addiction are some of the negative outcomes of 4G facilities. The students should be aware of the potential risks of 4G technology and take steps to mitigate its negative effects.