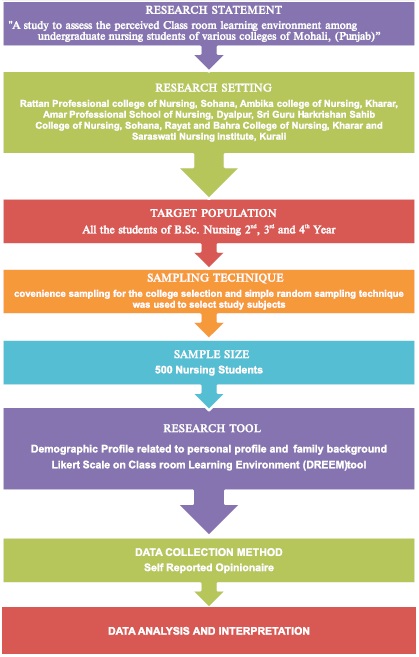
Figure 1. Schematic Representation of Research Methodology
The learning environment has a strong impact on students' learning experiences and outcomes; it dictates what, how, when and why students will learn. Also, it affects students' level of enthusiasm, encouragement and degree of learning effectiveness. A non experimental, descriptive research design was used to assess the perception regarding class room learning environment among undergraduate nursing students. DREEM (Dundee Ready Educational Environment Measure) by Mcleer and Roff was used to determine class room learning environment. Five Nursing institutions were selected conveniently to select 500 randomly selected students. The findings of the study revealed that majority (81.2%) of the study subjects were having good perception of their class room learning environment followed by 16.2% with very good perception score. Only 2% of them were having average perception whereas none of them were having poor perception of their class room learning environment. Perceived classroom learning environment score was found out to be significant with the mother's occupation at 0.01 level of significance and gender and type of family at 0.05 level of significance respectively.
In the era of globalization and technological revolution, education is considered as the basis for every human activity. The quality of student performance remains at top most priority for educators. It is going to make a difference locally, regionally, nationally and globally (Farooq et al., 2011).
Nurses form an integral part of the healthcare system and play an important role in that country's national development. The primary, secondary and tertiary healthcare services, that are a part the healthcare delivery system, are delivered by nurses who must be scientifically and clinically prepared to assess the healthcare needs of the people around the globe. Student nurses enter the clinical area as new and inexperienced and have little understanding of contextual meaning of theories in textbooks and practical learning. As per the Benner's theory from “Novice to Expert”, published in 1982, the student nurses need rules to help monitor their performance and opportunities to develop skills that can only be acquired in any clinical situations (Parks et al., 2013).
Some researchers stated that learning environment has been defined as everything that is happening across the classroom or department, faculty, or university. It also refers to the diverse physical locations, contexts, and cultures in which students are supposed to learn. The term describes the culture of a school or class and its presiding ethos and characteristics, including how students interact with each other and treat one another, as well as the ways in which teachers manage the educational setting to facilitate learning. The qualities and characteristics of a learning environment are determined by a wide range of factors comprising of school policies, governance structures, physical facilities and other features may also be considered important elements of a “learning environment”. (Bakhshialiabad et al., 2015).
According to Dunn and Burnett (1995), the student learning environment consists of all the conditions and forces within an educational setting that affect learning. Shuell (1996) quoted the student educational environment as a rich psychological soup consisting of cognitive, social, cultural, affective, emotional, motivational and curricular factors, in which teachers and students are motivated toward effective learning. Without the appropriate environmental ingredients, it is very difficult to achieve a satisfactory learning product. (Sand-Jecklin, 2009).
The World Federation for Medical Education emphasized the learning environment as one of the objectives for the evaluation of medical education programmes. The quality of the learning environment has been identified to be very important for effective learning (Ugusman et al., 2015).
Martha (2009) stated that “the academic performance of higher education depends on performance of graduate students”. Kujan (2015) observed that “the measurement of student's previous educational outcomes are the most important indicators of student's future achievement; this refers that the higher the previous performance, the better will be the student's academic performance in future endeavors (Alos et al., 2015).
The evaluation of the student's perception of learning environment at the nursing institutions help educators and staff in measuring the quality of learning that occurs within the vital place. Nursing profession is compelled to address the challenges posed by globalization. Institutions of higher education should measure the educational quality in order to function effectively and efficiently in a highly competitive environment. (El-Gilany & EL-sherbeny, 2017).
Organizing a good learning arena is crucial for bachelor students in nursing because a major part of their studies and training take place in that context. The quality of the clinical studies has a great impact on the quality of the research studies on the undergraduate nursing students as a whole. The students' experiences and their perception of the quality of their class room studies vary a lot. So, the present study was conducted to assess the perception of the undergraduate nursing students regarding their class room learning environment.
A study to assess the perceived class room learning environment among undergraduate nursing students of various colleges of Mohali (Punjab).
To assess the perceived class room learning environment among undergraduate nursing students.
To associate the perceived class room learning environment of undergraduate nursing students with the selected demographic variables.
Figure 1 shows the schematic representation of the Research Methodology.

Figure 1. Schematic Representation of Research Methodology
Quantitative research approach was used for this study.
Descriptive approach and (Non - experimental design) was used for this study.
The data was collected from undergraduate nursing students of six selected nursing colleges of Mohali.
This study was conducted in SAS Nagar Mohali, which comes under Punjab. Mohali is twin city adjoining Chandigarh. It is a gate-way connecting Punjab with union territory of Chandigarh which is the joint capital of Punjab and Haryana. It is a well-planned modern city of Punjab having the best infrastructure. There are many private reputed nursing colleges in the city which provide quality education to the nursing students at affordable cost. The study was conducted in various nursing colleges of Mohali that provide knowledge and skills to nursing students in Basic B.Sc Nursing.
Population for the study comprises of nursing students who were studying in various nursing colleges of Mohali, Punjab.
Power analysis was used to estimate in advance how big a sample is needed for study. Findings of the pilot study were used to calculate the sample size based on precision and confidence interval formula. The sample of the study consisted of 500 nursing students from selected Nursing colleges in SAS Nagar Mohali.
In the present study non probability (convenience) sampling technique was used to first select the various nursing colleges.
From the selected nursing colleges the students were selected from each class with the help of simple random sampling (lottery method without replacement) to recruit the study subjects. 133, 177 and 190 undergraduate nursing students were selected from B.Sc Nursing 2nd year, 3rd year and 4th year respectively.
5.2.1 Inclusion Criteria
Both male and female nursing students were included in the study.
Students of 2nd, 3rd and 4th year of Basic B.Sc. Nursing.
Nursing students who were studying in selected colleges of Mohali.
Nursing students who were willing to participate.
Nursing students who were not willing to participate in the study.
Nursing students who were not present during the time of the study.
Students of 1st year were excluded as they were the beginners in the degree program and will not be aware of learning environment.
Section A: Socio-Demographic Profile of the study subjects.
The first part of the tool consists of 2 items describing the demographic variables of the study subjects related to personal profile and family background.
The variables included in the personal profile were Age, Gender, Habitat, Marital status, Type of family, Place of stay during study and financing during study.
The variables included in the profile related to family were Annual income of parents, education level of mother, Education level of father, Mother's occupation, Father's occupation, number of siblings.
Section B: This part includes the assessment of the Class room learning environment based on DREEM (Dundee Ready Education Environment Measure) tool.
It consists of total 50 items with five subscales that are as follows:
The items were scored on 5-point Likert scale (strongly disagree to strongly agree).
The total score for all subscales is 200.
Items were scored as follows:
Positive Items: Strongly agree 4, Agree 3, Uncertain 2, Disagree 1 and Strongly disagree 0.
Negative Items: Strongly agree 0, Agree 1, Uncertain 2, Disagree 3 and Strongly disagree 4.
(Items 8,12,15,16,21,23,34,39,45,46) were negative whereas all the other items are positive.
Table 1 shows the Scoring criteria for Assessment of Class room Learning Environment, and Table 2 gives the Domain wise representation of the scores.
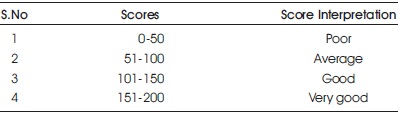
Table 1. Scoring Criteria for Assessment of Class Room Learning Environment
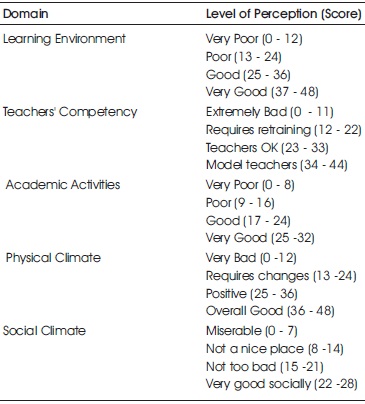
Table 2. Domain Wise Interpretation of the Scores
Table 3 shows the percentage distribution of study subjects as per their personal profile.
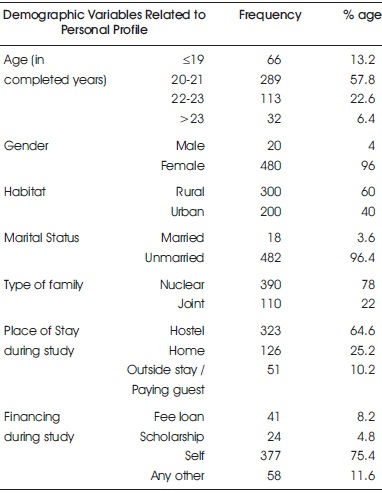
Table 3. Frequency and Percentage Distribution of Undergraduate Nursing Students as Per their Demographic Variables Related to Personal Profile
Age: Majority (57.8%) of the study subjects were in the age group 20-21 years followed by 22.6% in the age group 22- 23 years whereas 13.2% were less than or equal to 19 years of age followed by few (6.4%) with age more than 23 years.
Gender: Majority (96%) of the study subjects were females followed by 4% who were males.
Habitat: Majority of the study subjects (60%) were from rural area followed by 40% from the urban area.
Marital Status: Major portion of the study subjects 96.4% were unmarried followed by only 3.6% who were married.
Type of Family: 78% of the study subjects belonged to nuclear family followed by only 22% who were from joint family.
Place of Stay during Study: Majority (64.6%) were staying in the hostel followed by 25.2% who were staying in the home whereas only 10.2% were staying as paying guest.
Financing during Study: Majority 75.4% were paying fees by self followed by 11.6% who were using any other method of financing. Few of the study participants (8.2%) were paying fee through loan and only 4.8% used scholarship for their financing.
Table 4 shows the distribution of the study subjects as per their demographic variables related to family.
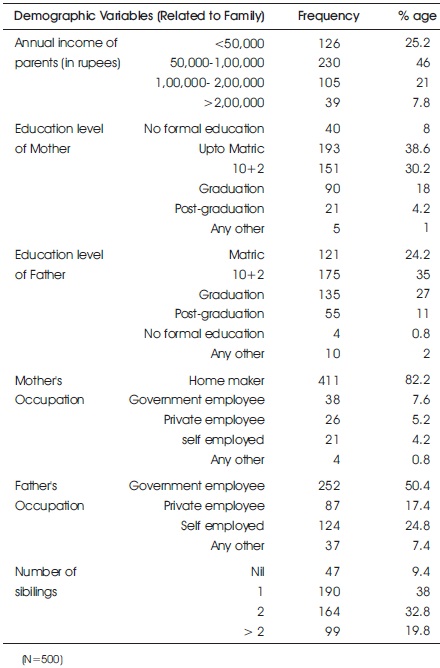
Table 4. Frequency and Percentage Distribution of Undergraduate Nursing Students as per their Selected Demographic Variables Related to Family Background
Annual Income of Parents: Majority (46%) of the study subjects were having income between 50,000-1, 00,000 followed by 25.2% with less than 50,000. Parents with annual income between 1,00,000 – 2,00,000 were 21% followed by only 7.8% with income more than 2,00,000.
Education Level of the Mother: Majority (38.6%) were matric pass followed by 30.2% who were 10+2 pass whereas only 18% were graduate and 8% of them were not formally educated. 4.2% of them have completed post graduation whereas only 1% have undergone some other education not mentioned in Table 4.
Education Level of the Father: 24.2%of the study subjects were matric pass, 35% were10+2 pass whereas only 27% were graduate and only 0.8% of them were not formally educated. 11% of them have completed post graduation whereas only 2% have undergone some other education not mentioned in Table 4.
Mother's Occupation: Majority (82.2%) were home makers followed by only 7.6% who were government employees. Few of them were private employee (5.2%), self employed (4.2%) and doing any other occupation (0.8%).
Father's Occupation: Majority (50.4%) were government employee, followed by 24.8% who were self employed whereas only 17.4% were private employee. Few (7.4%) of them were doing any other occupation that is not mentioned in the categories.
Number of Siblings: As per the number of siblings, majority (38%) were having 1 sibling followed by (32.8%) of the study subjects having 2 siblings, whereas 19.8% were having more than 2 siblings. Only 9.4% were having no siblings.
Table 5 depicts the frequency and percentage distribution of study subjects as per their class room perception score. Majority (81.2%) of the study subjects were having good perception of their class room learning environment followed by 16.2% with very good perception score. Only 2% of them were having average perception whereas none of them were having poor perception of their class room learning environment.
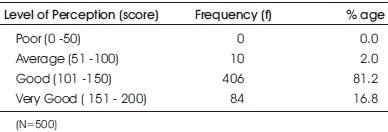
Table 5. Frequency and Percentage Distribution of Undergraduate Nursing Students as per their Perceived Classroom Learning Environment
Table 6 and Figure 2 depicts the domain wise frequency and % age of perceived Classroom Learning Environment among undergraduate nursing students. As per the learning environment majority (72.8%) of the study subjects perceived good learning environment followed by 24.2% who perceived it very good whereas only 3% perceived poor learning environment. As per the teacher's competency, Major portion of study subjects (80.4%) perceived teachers ok followed by 11.6% who felt that teachers require training. Only 8% perceived teachers as model teachers.
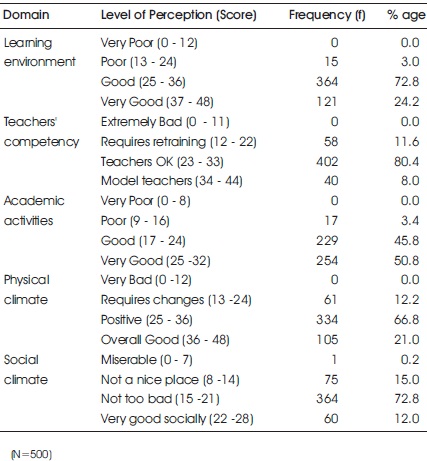
Table 6. Domain wise Frequency and Percentage Distribution of Undergraduate Nursing Students as per their Perceived Classroom Learning Environment
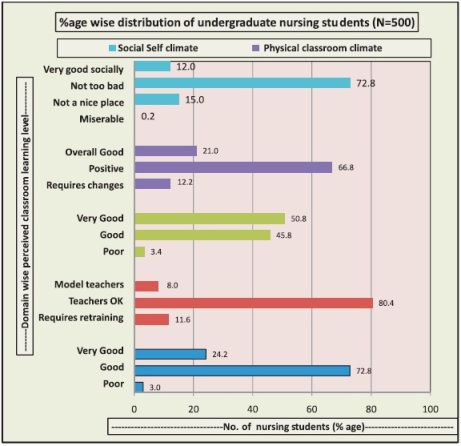
Figure 2. Domain wise frequency and Percentage distribution of undergraduate nursing students as per their perceived Classroom Learning Environment (N=500)
Majority (50.8%) of the study subjects perceived the academic activities as very good followed by 45.8% as good and only 3.4% felt poor perception regarding their academic activities. 66.8% of the study subjects felt their physical climate positive followed by 21% who felt it overall good whereas only 12.2% felt that physical climate require changes. 72.8% of the study subjects felt their social climate not too bad followed by 15% who felt that it is not a nice place whereas 12% found themselves very good socially. Only 0.25% found their social climate miserable.
Table 7 and Figure 3 depicts the score data of perceived Classroom Learning Environment among undergraduate nursing students. The overall mean score and standard deviation for the class room learning environment was found out to be 135.4 and 15.6 whereas for the domains like learning environment, it was 33.6 and 4.01 followed by 27.5 and 4.33 for teacher's competency. The mean and SD for physical climate was 32 and 6.04 whereas for academic activities it was found out to be 24.6 and 3.60 followed by social climate with mean 17.8 and SD 3.26.
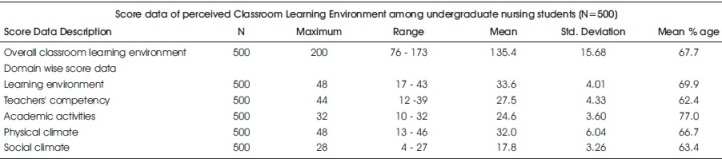
Table 7. Score Data of Undergraduate Nursing Students as per their Perceived Classroom Learning Environment (N=500)
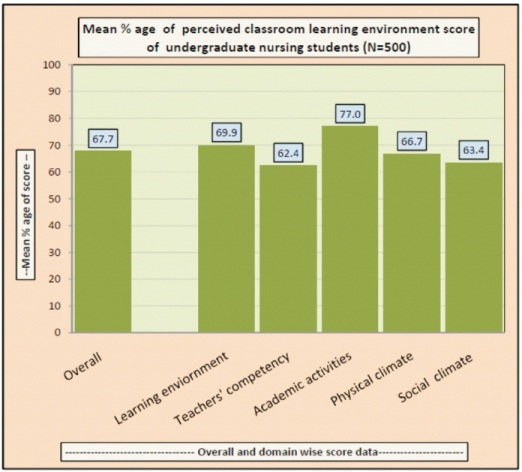
Figure 3. Mean Percentage of Undergraduate Nursing Students as per their Perceived Classroom Learning Environment (N=500)
Table 8 shows the association of perceived classroom learning environment score with selected demographic variables of undergraduate nursing students related to personal profile. The association was found out to be significant with the gender and type of family at 0.05 level of significance.
Table 8. Association of Perceived Classroom Learning Environment Score with Selected Demographic Variables Related to Personal Profile of Undergraduate Nursing Students (N=500)
Table 9 shows perceived classroom learning environment score to be significant with the mother's occupation at 0.01 level of significance whereas it was found to be non significant with the annual income of parents, education level of father, education level of mother, father's occupation and no.of siblings.
Table 9. Association of Perceived Classroom Learning Environment Score with Selected Demographic to Family Background of Undergraduate Nursing Students (N=500) Variables Related
The findings of the present study concluded that the mean score of the study subjects per their perception of the classroom learning environment was 135.4 with standard deviation 15.68 and mean percentage 67.7% as depicted in Table 7. The findings of the study are similar to the study conducted by (Riquelme et al., 2009) in which they stated that students perceived their class room environment more positive than negative.
Another study conducted by (Sayed et al., 2012) supported the findings of the present study in which they reported that the mean score of study subjects was 143.9/200 which reveals the positive perception of students regarding class room learning environment.
A study conducted by (Abusaad et al., 2015) also supported the findings of the present study that the students perceived their class room learning environment positively whereas the study conducted by (Mustapha et al., 2010) disagreed the current study findings as they indicated a relatively low satisfaction regarding learning environment among medical students with the mean score of 111.5/200.
A similar study conducted by (Farooq et al., 2011) concluded that students aged 20 years and less had more positive perception than the students over the age of 20 years which is not supported by the findings of the present study as there was no significant association found out with age and the class room learning environment.
The findings of the present study were similar to the findings of the study which revealed that gender is highly associated with the perception of the nursing students regarding class room learning environment.
Another study conducted by (El-Gilany & EL-sherbeny, 2017) concluded that the mean score of student's perception of learning, teachers, academic self perception and social self were 28.9, 28, 21.2 and 16.8 respectively which is almost similar to the findings of present study.
The findings of the study can be used while conducting in service education programs for enhancing the knowledge of nursing teachers related to learning environment of the undergraduate nursing students. Findings can be used to upgrade the skills of teaching faculty regarding the advancement in the teaching and learning environment to enhance the academic performance of the students.
The findings of the present study can improve the learning environment of the undergraduate nursing students as the administrators will come to know the strengths and weaknesses of the environment and will also improve the factor that affects the academic performance of the students negatively. They can also upgrade the teaching skills of the teachers, evaluation of the students and periodic assessment of the learning environment that will improve the quality of education in nursing institutions.
Findings of the study can be used to improve the standards of nursing services so as to minimize the errors on the part of students. The findings will also help the clinical instructors and staff nurses communication, interaction and positive reinforcement among nursing students.
The findings of the present study will help the other researchers to conduct further researches on the similar topics in various Indian settings as much has been done in other countries. The findings of the present study will serve as the basis for assessing the learning environment and help in improving the standards of nursing education in various settings by teaching teachers about the importance of learning environment for students academic outcomes.
The study was limited only to selected colleges of Mohali as few college authorities refused to take the data from the students.
The study was limited to Basic B.Sc. Nursing students.
The study was limited to self reported rating scale tool that was used in the study.
The study was limited in terms of time as limited time was given to the researcher from the concerned authorities of the selected colleges to get information from the respondents.
Based on the results of the study following recommendations can be made.
The study can be replicated on a larger sample to generalize the findings.
The comparative study can be conducted to assess the learning environment of undergraduate and post graduate students.
Similar study can be conducted in private and government institutions to see the difference in the perceptions of the students.
The findings of the study concluded that majority (81.2%) of the study subjects were having good perception of their class room learning environment followed by 16.2% with very good perception score. Only 2% of them were having average perception whereas none of them were having poor perception of their class room learning environment. The overall mean score and standard deviation for the class room learning environment was found out to be 135.4 and 15.6 respectively. Perceived classroom learning environment score was found out to be significant with the mother's occupation at 0.01 level of significance and gender and type of family at 0.05 level of significance respectively.
Authors would like to acknowledge the study subjects for providing them their responses. Our sincere thanks to all those who assisted us directly or indirectly in the successful completion of this study.
The study entitled “Perception Regarding class room learning environment among undergraduate nursing students” is self funded research work of Mrs. Shaveta Sharma.