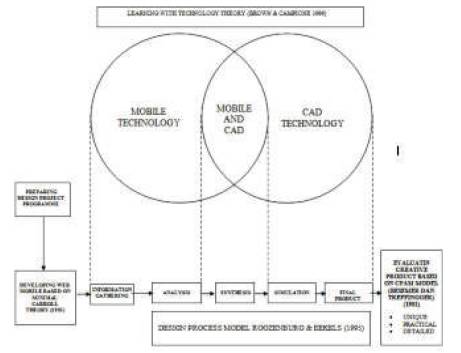
Figure 1. Conceptual Framework
The purpose of this research is to examine the effect of integrating the mobile and CAD technology on teaching architectural design process for Malaysian polytechnic architectural students in producing a creative product. The website is set up based on Caroll's minimal theory, while mobile and CAD technology integration is based on Brown and Campione's technology of learning theory. This study utilized a quasi-experimental method. Final semester students from four (4) polytechnics were used as research samples where sixty (60) students are in the treatment group and another sixty (60) students are in the control group. The final products being evaluated by the experts in architectural field using an instrument based on Creative Product Analysis Model (CPAM). The inferential statistics namely T-Test and Pearson Correlation Analysis with a significant level p = 0.01 were utilized. Research outcome shows that there is a significant difference between the treatment group product (M=79.1) and control group product (M=70.5). It also shows that there is a significance correlation between CPAM creative model details and the final product designed using mobile and CAD technology integration where r (unique) = 0.905, r (practical) = 0.857 and r (details) = 0.758. This research contributes to the use of real case in the development of an architectural website, in the use of mobile technology as media information sources, the use of CAD technology in designing process and in the construction of validated instrument which is used to evaluate creative architectural products.
Architectural design is a complex and open process. Designing process starts from abstract which had a problem to be developed stage by stage until a level where it can be produced as a product. Designing activities is a repetitive problem solving process (Demirkan 1998). According to French (1998), architecture design is a response to human special needs which is refuge and comfort. Lawson (1997) states that architectural design is a process where an architect produces space, place and building which has a big amount of effects on human life quality. According to Mortbitzer (et al2010) architectural design process has moved from a 'craft based approach' to a process that involved technology and inherits endless difficulties. Most architects agreed with Sanders (1996) whom stated that architectural design is a repetitive process where the process scheme can be recognized, valued, repeated, explored and repaired until the best solution is achieved. In the context of this research, architectural design is a systematic process through a few stages in producing a new product that can be valued from physical aspect and providing benefits to human life and environment. Decision making activities in architectural design process happens at sketching stage, schematic design stage and final design stage. At the details stage, design process is focused on producing drawings documents and planned building construction activity. This research concentrates on schematic stage of design process which involves sketching and schematic design. As a conclusion, the beginning stage of design process involves collecting the information needs in the design process and producing new ideas. Technological development nowadays, has given chances for mobile and CAD technology to be integrated in design process. Mobile technology gives chances for students to have access to the information without time and place limits. Websites referring to real cases provide opportunity to gather quick information for design process purpose. Media variety in design process also can give more choices to designer in creating new ideas. According to Dong & Gibson (1998), CAD technological development in three dimensional drawings, three dimensional digital model and computer simulation can provide new methods for designers to find more solution in schematic design process.
The basis of this study is to explain how architectural design process can be intensified by using information technology and how this would be possible in practice. The objective of this research is to improve architectural design from the creative problem-solving viewpoint. The main goal is to intensify architectural design by using information technology. These had been divided into two partial objectives, which focused on how mobile technology will help students to acquire the information needed in the design process and how CAD technology will help students in creating creative solutions at the different stage in the design process. This research also wants to see the effect of integrating CAD technology at the different stages in the design process. This research also identified the effect of integrating CAD technology at the synthesis stage and the simulation stage in the design process. As a conclusion this research would like to study the effect of integrating mobile technology and CAD technology to produce creative product in the design process.
The conceptual framework for this research was built based on Carroll's minimal theory (1995), Brown's and Campione's learning with technology theory (1996) and creative product analysis matrix model (CPAM), Besemer dan Treffingger (1981). This conceptual frame consists of two independent variables and one independent variable. Two independent variables are the use of web mobile in obtaining design's information and the use of CAD technology in creating new ideas activities whereas the independent variable is the creative product from the design process. For this research the design project programme was prepared by the researcher. The web mobile for gathering information activity had been developed by the researcher based on Carroll's minimal theory (1995). The intergration of CAD technology in the design process occurred at the synthesis stage, the simulation stage and before producing final creative product. Evaluation instruments created by the researcher being used to evaluate product from analysis stage, synthesis stage and simulation stage. The final products had been evaluated using the instrument that built by researcher based on CPAM model.
The products from each stage compared by researcher to study the effect of integrating mobile technology and CAD technology in design process. Graphically the research processes is shown as conceptual framework in Figure 1.

Figure 1. Conceptual Framework
With architecture being a much more complex career, real case study as a lecturing method starts to be an effective method amongst the lecturers. According to (Vijayalakshmi 1997)., real architecture cases involve construction and designing process of a completed building. Oren (1990) says that information usages based on real project will helps student to analyze, make comparison and validate important aspects from studied buildings. With the use of real case method, researcher will develop a website which is related to the same buildings type that designed by students. Important links from this website will be connected to additional informations for students. According to Oren (1990), links from a website can increase students' knowledge towards issues that being studied. For this research, the use of real case in the development of the website is expected to make the student information searching ease and focus to the project needs. Focused information searching is suitable to be used in a website based on a mobile technology with regards to the proven ability of the mobile technology today.
There were different opinions in defining mobile knowledge. Lehner and Nosekabel (2002) describe mobile knowledge as a service that provides electronic information generally and educational content which helps information searching without time and place limits. Vavoula and Sharples (2002) explains that there are three ways where learning can be mobile which are learning is mobile in a space, learning is mobile in different aspect of life and learning is mobile without time and places limits. According to Anna et al. (2003) education based on mobile technology is a learning method using small device, mobile and become convenience in every aspect of life. From definition above, a conclusion can be made that education based on mobile technology is an educational approach that are capable of conveying information at every time and place based on student needs. Learning activities can be achieved even when students and lecturer are in mobile position. Referring to Chen and Kinshuk (2005), educational service based on mobile technology is a movable learning sources and can be access by students without time and places constraints. In order to make a dynamic mobile technology based learning atmosphere, learning system has to be made ready in providing information without time and place constraints Chen and Kinshuk (2005). Learning system also has to be designed, where the information provided can be chosen by students according to their needs. The system also has to be able to change the information based on student needs Chen and Kinshuk (2005). Educational system design based on mobile technology has to be dynamic, can be changed easily and can be used at any time and any place. As a conclusion, educational system design based on mobile technology has to be adapted by users at every time and situations. According to Bottentuitista et al. (2007), website usage through mobile technology can attracts more students to use the internet. In conclusion, if interactive multimedia website that refers to real case is developed using mobile's technology, information searching process will be easier where information can be reached by students without time and place constraints. The effective use of web site based on mobile device in developing information has been supported by the studies of Catangay (2009) which showed on how students in selected schools in Philiphine acquire more new informations for science subject when web site based on mobile device being integrated in the learning process. Through faster information reaching process, students creativity can be generate with sufficient amount of information and it can also fasten the students' skill in creating new ideas in the design process.
CAD technology enables people who involves in architectural design industry to sketch and develop their work on computer screen, it can be saved and printed for future use in making changes and editing. According to Husain (2007), nowadays CAD is recognized as computer aided design not as computer aided drafting anymore. This is because of the facts that CAD technology can actually do more than drawings. A close relationship has existed between CAD software developer and architect, in order to build a user friendly CAD software for architectural design (Vijayalakshmi 1997). CAD technology also enables the producing of high visual impact digital model and gives freedom to the architect to think about object, space and shape in the same screen. Referring to Salman (2004), rapid development for CAD technology has changed the stages in concept shaping from two dimensional to three dimensional. CAD technology development nowadays has proved that the real strength on today's technology is not towards drawings process but in creating new ideas using visual CAD technological impact (Dong & Gibson 1998). CAD technology existence in architecture has two primary objectives which are to be applied in human cognitive design process through the computing smart technology and to become an idea representative media in architectural design process (Koutamanis 2003).
Three dimensional digital models is the another representation media that can be developed using CAD technology. According to Wei Dong and Gibson (1998), digital model gives chances for architect to think, pictures, communicate and making assumptions in designing process. At concept development stage, digital model design can be used to analyze overall shape, space planning and to decide space height. In schematic stage, digital model can be used to study the suitable type of construction material, color and lighting for the designed buildings. At the final stage of schematic, digital model can be used to produce a high visual impact design representation. Digital model with the use of CAD technology can produce a visual impact similar to real environment in construction sites. According to Jiangyin (2003), digital model has the ability to represent photo realistic situation with regards to environment details. As a conclusion, compared to conventional model, digital model give chances for architectural students to study about the designed building component in details, suitable finishing materials for each space designed and lighting condition for building's interior. With the CAD technology capabilities, designing process will be simpler, faster and it will give more chances for student to develop their ideas in designing process.
Simulation is a popular teaching technical amongst educators. According to Micheal (2000), simulation helps student to understand a situation, a process and the replication of real situation activities. Gokhale (1996) believes that virtual experience can give chances for students to study while doing practical activities and not only depending on lectures in lecture room only. Menn (1993) says that 90% of the students learned by doing the activities himself even with the help of simulation methods. In architectural context, computer simulation brings in the real situation in building design. With the capability of CAD technology nowadays, student can use software such as 3D Studio Viz to observe building detailed effect, lighting and movement in a space through animation just like in a real situation. Computer simulation helps students to choose suitable building details, lighting and space arrangement for the designed building. The advantages of computer simulation in designing process is that it can boost designers visual capabilities towards space and helps designers to quickly evaluate the quality of designed space. If computer simulation is integrated in learning design process at polytechnic, it is predicted that students can produce a much more creative space design. There were not many empirical researches which can proves that computer simulation can increase students' creativity. However, there are several researchers such as Gokhale (1996), Micheal (2000) and Lawson (2007) whom has made an assumption that computer simulation can increase student creativity. Through this research, researcher hopes that it can strengthens previous research outcomes on computer simulation capabilities via three dimensional digital models which can produce a creative architectural design product.
This research consists of two main activities in the design process which is designs' information development activity and creating new ideas activity. Information searching for design purposes on web site based on real case is provided by researcher using mobile device while for creating new ideas activity, CAD technology is used. The web site used in this research developed by the researcher using Caroll's minimal theory. In applying Carroll's Minimalist theory when developing the web site the researcher follows the recommendations by Kearsley (1994) which are to allow learners to start immediately on meaningful tasks to minimize the amount of reading and other passive forms of training by allowing users to fill in the gaps themselves and to make all learning activities self-contained and independent of sequence. The web site that had been developed for this research can be referred at http://www.kajian_senireka.param.mobi. The integration of the web mobile and CAD technology in the design process for this research is based on Brown and Campione (1996) learning with technology theory. With this theory the integration should be done with the latest equipments required to get the accurate results.
Through this study, researcher wants to see the differences in final product designed using mobile and CAD technology integration with the final product build using conventional method. Researcher also wants to see upon how is the effect of integrating web site based on mobile device in the design information development activity. This is a quantitative research to study the effects of mobile and CAD technology integration in the design process to produce architectural creative product. Quasi experimental method is used to study mobile and CAD technology integration effects in design process.
Research has been made on final semester students of diploma architecture from four (4) polytechnics in Malaysia. All the students selected have the same basic understanding of the design process. The students also have the basic skill for using ACAD 2007 and 3D Studio viz software. Both skills have been learned from previous semester. Research duration is for six weeks involving one hundred twenty students (120) students as research samples. In this research, research samples have been asked to design a kindergarten building. Sixty (60) students from POLIPD and PMM were selected to design with the integration of mobile and CAD technology and they are used as treatment group while the other half of the students are from PUO and POLISAS perform the design process using conventional method and they are used as control group. All the four polytechnics selected are using the same curriculum for diploma in architecture which being developed by the Malaysian ministry of higher education. This research has been conducted by two lecturers from each polytechnic selected. Design process for treatment group and control group has been conducted simultaneously. Products for every activity from both of the design processes have been evaluated by selected lecturers using the research instruments provided.
To evaluate the product for each activity in the design process three instruments have been developed by the researcher. For information analysis product instrument for analysis activity being developed based on requirements being put by [1]Laseau (2001) and Ching (1979), while for product from synthesis activity instrument being developed based on requirements being put by Laseau (2001) and Koberg & Bagnall (1981) and for product from simulation activity instrument being developed based on requirements being put by Laseau (2001) and Mills (2005). The evaluation instrument for the final product is developed by researcher based on Creative Product Analysis Matric (CPAM) model (Besemer and Treffingger 1981). Researcher has been using CPAM model as a guide to evaluate the creative architectural design product. Based on CPAM model the creativity of the design product is based on three main criteria which are uniqueness, practicality and product's detail.
A pilot test was carried out from 27th October 2008 to 8th December 2008 with 30 students from POLIPD. The reliabilities coefficients of the instrument are shown in Table 1. Data from this pilot test not being used for the final analysis. All the instruments used have high reliabilities coefficients.
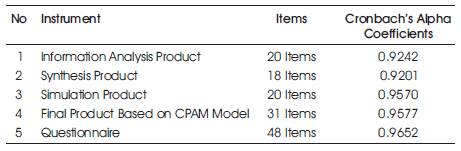
Table 1. Reliability Coefficients of Research' Instruments
The main data analysis based on the instruments evaluation forms using inferential statistics (Independent t-tests) and being supported by the data from questionnaire being analyzed using descriptive statistics (Means, Standard Deviations, and Frequencies). Raw data from lecturers was used and analyzed via computer. The analysis is done using Statistical Package for Social Sciences (SPSS) version 11.5.
The findings for this research being divided into five categories which are identifying students interest in finding design information, inferential data to compare design information created through analysis activity, inferential data to compare design product from synthesis and simulation activity and inferential data to compare final design product through conventional method compare to integrated method.
In identifying student interest to find information needed in designing process whether it is via mobile technology based website or via conventional method, research outcomes are shown in Table 2.
Research outcomes shows that the total number of student searches in treatment group is 392 (M=6.53) and total searches in control group is 178 (M=2.97). This outcome clearly shows that student searching activities increased with web site integration related to real case based on mobile technology.
This outcome comparing the quality of designs' information being created from analysis activity consists of two methods which are design information created through conventional method and design information created through integrated method. Research outcomes are shown in Table 3.
In analysis stage, inferential data shows that there is a significant difference between the mobile technology integrated data (M=81.2) and conventional method (M=65.5), t (118) = 18.369, significant.
The significant different on the product being produced in analysis activity proves that the integration of web site based on mobile technology helps the students to produce quality design information in analysis activity.
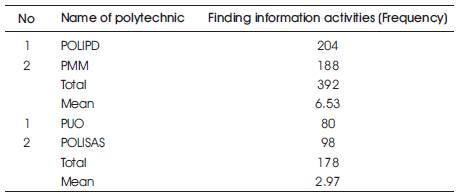
Table 2. Descriptive Statistics in Finding Information Activity
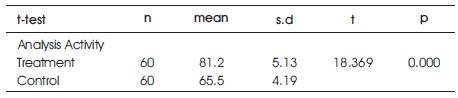
Table 3. Finding on Comparing Design Information Produced in Analysis Activity
In determining student skills at synthesis stage in design process with CAD integration, research has been made to decide whether students using CAD technology integration in synthesis stage has made more idea changes from two dimensional to three dimensional compared to students using conventional method in synthesis stage. The research outcomes of the synthesis activity in the design process are shown in Table 4.
Research outcomes shows that conceptual diagram produced for treatment group is 229 (M=3.82) while conceptual diagram produced by control group is 150 (M=2.50). Research outcomes also show that sketching changes from 2D to 3D for treatment group is 235 (M=3.92) while total number of sketching changes from 2D to 3D for control group is 127 (M=2.12). It shows that treatment group is actively involved in synthesis activity compared to control group.
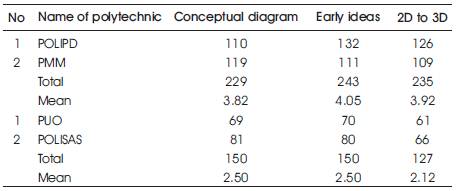
Table 4. Finding on Ideas Produced in Synthesis Activity
The inferential finding data for synthesis activity are shown in Table 5. This inferential data will determine whether there is a significant different between the product being produced by treatment group at the synthesis stage compare to the product being produced by control group at the synthesis stage.
Inferential data shows significant difference between initial idea created in synthesis activity using CAD technology integration (M=80.6) compared to initial idea created in synthesis activity using conventional method (M=67.1), t (118) = 17.184, significant. This proves that the initial ideas being produced from integrated method better than the initial ideas being produced from conventional method.
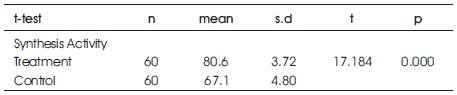
Table 5. T-test Finding to Compare Mean Between Treatment Group and Control Group Product for Synthesis Activity in Design Process
The inferential finding data for simulation activity are shown in Table 6. This inferential data will determine whether there is a significant different between the product being produced by treatment group at the simulation stage compare to the product being produced by control group at the simulation stage. The creative and quality product being produced at the simulation stage helps the students to produce a quality final design product.
Inferential data shows there is a significant difference between final design idea produced in simulation activity using CAD technology integration (M=80.5) compared to final design idea produced in simulation activity using conventional method (M=66.9), t (118) = 12.267, significant. This proves that the design idea being produced from integrated method is better than the design idea being produced from conventional method.
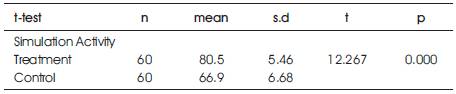
Table 6. T-test Finding to Compare Mean Between Treatment Group and Control Group Product for Simulation Activity in Design Process
In this research the creativity of the design product being determined based on CPAM model which are unique, practicality and detail. This inferential data will determine whether there is a significant different between the final product being produced by treatment group in the design process compared to the final product being produced by control group in the design process. The inferential finding data for comparing design product between treatment group and control group are shown in Table 7. This finding can prove positive effects on the integration of mobile and CAD technology in the design process for producing creative product.
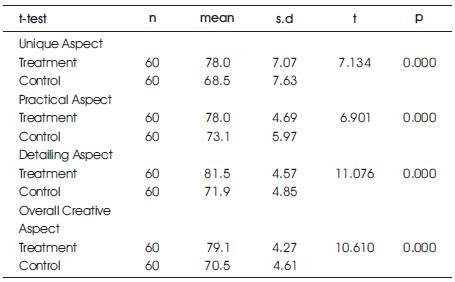
Table 7. T-test Finding to Compare Mean Between Treatment Group Product and Control Group Product Based on CPAM Model
Inferential data shows that there is a significant difference between design process integrated with mobile and CAD technology (M=78.0) compared to conventional method (M=68.5) in producing unique design product, t (118) = 7.134 significant.
Inferential data also shows that there is a significant difference between design process integrated with mobile and CAD technology (M=78.0) compared to conventional design process (M=73.1) in producing a practical design product, t (118) = 6.901 significant. Inferential data also shows that there is a significant difference between design process integrated with mobile and CAD technology (M=81.5) compared to conventional design process (M=71.9) in producing high details architectural product, t (118) = 11.076, significant. As a conclusion, final product comparison from creativity aspect between treatment and control group show significant differences.
Research outcomes also show that there is a significant difference between final product produced through the design process that being integrated with mobile and CAD technology (M=79.1) compared to final product produced using conventional method (M=70.5) from creativity aspect, t (118) = 10.610 significant. Overall, inferential outcomes show that there is a concrete effect on mobile and CAD technology integration in producing a creative architectural design.
This research shows on how the integration of web site being built using the real case approach based on the mobile device help the students to get more design information at anytime and any place. The integration of mobile technology in the design process generates students' interests to be more active in searching design information during the design process. More design information being gathered by the students makes it easy to produce creative products. The integration of CAD technology makes it easy for the students to change their designs' ideas from two dimensional to three dimensional. Three dimensional models in the form of digital model make it easy for the students to get the overall view of the building they want to design at the early stage of the design process. CAD technology also allows the students simulate the real situation in their design process. This simulation activity makes it easy for the students to generate ideas in creating their final design products to solve the problem being given to them.
From this research, the integration of mobile technology and CAD technology help the students to produce quality product of architectural works. The final students' products from the treatment groups had its own identities. The products from the treatment group also show qualities of creative products based on CPAM model. Some samples from the students' products are shown in the Figures 2,3 and 4.

Figure 2. Product a

Figure 3. Product b

Figure 4. Product c
In this research of creative architectural design, the design process and opportunities of information technology in intensifying architectural design are studied. In this paper also, positive results for mobile technology based on website shows that learning approach using mobile technology can be a good replacement for computer based learning approach. Students and lecturer can gain benefits from easier and faster access of information sources. When it is easier for the students to get the design informations it will create interest to them to involve actively in the searching designs' informations activity. Web site being built by a real case approach also will make the students activity to search for design information become focus and easier. As a conclusion the integration of web site built on a real case based on mobile device will make the searching information activity in the design process become focus and occur at anytime and any place. Rapid development in mobile technology has contribute in growth of faster and higher memory mobile equipment, so that these mobile equipments can be used to download data faster than before and it can also save a lot of informations in the memory. Mobile technology offers a practical educational approach in providing a unique learning community based on technology for the betterment of future polytechnic. Still, there has to be a lot more qualitative and quantitative research to obtain suitable guidance for mobile technology integration in learning process. Mobile technology offers an ideal educational approach in providing a unique learning community based on technology. Today graphic resolution and screen size for mobile equipment is suitable for graphic and images presentation. Furthermore, if internet surfing cost can be cut to a lower price, this mobile technology will definitely be useful for higher education students or out-campus students.
From CAD technology design aspects, it is proven that CAD technology able to help students in producing three dimensional digital models and also increases students understanding of space through good visual effect. This is because CAD technology enhances student creativity and it also encourage student to appreciate interior space when student are doing simulation using different details and lighting into the same space. Student also get excited with produced space via simulation increment with different details and lighting towards their three dimensional digital model. Student understanding toward space is increased with the ability to run a simple interior animation. With the animation, student can look at the space from a different perspective. Student gives good response towards three dimensional digital model usage to produce good quality interior space design.
Overall, CAD technology via three dimensional digital models helps student to produce a creative final product design. Digital model effects can be strengthened with the research done towards NBBJ firm by Mark Von Wrote (2000) which shows that three dimensional digital models can give good design idea and it also helps designer to validate the space, building shape and details of designed buildings. This research outcomes being supported by Mortbitzer et al (2010) which mentioned that building simulation is now considered the integrated element of the design process due to the advanced technology of the design process. This research outcomes is also strengthened by Lawson (2007) research outcomes which states that architect Ian Ritchie has produced a creative gallery space in London Museum with the help of CAD technology integrated design. Lawson (2007) also says that the kindergarten design produced by kindergarten teachers with the help of CAD technology has higher esthetic value than the one produced by an architect using conventional method. From this research, it is concluded that CAD technology are able to help architectural student to produce a much more creative product design. CAD technology, specifically via three dimensional digital models can boost student understandings towards space while they are in designing process through the use of good visual impact.
Final answers to details in intensifying and developing design have not been produced, but the profound understanding of the design process shows clearly where these opportunities are and where they can be found. Although CAD has had, and will have, some evolutionary influences on the design process of architects as an entity, the future CAD user interface should adopt its features from the architect's practical and creative design process, and not vice versa.
Based on the synthesis of this research some significant findings about the applicability of digital technology to architectural design can be presented. Present mobile technology can help architecture students to obtain informations easily to help them in the design process. Present CAD technology suits architectural design quite well in routine tasks and the final phases of design. Present CAD technology applies fairly to architectural design in the early phases of design in sketching. Overall, mobile and CAD technology integration in design process is proven to have increase the quality of the final product designed by architectural students which has been achieved in the learning process via design module.