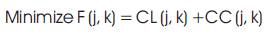
It is very important to determine the loading of distribution network because it helps in distribution system planning and network reconfiguration etc. In this paper enhancement of maximum loading of radial distribution feeders using genetic algorithm is proposed. The enhancement is done by the optimal conductor selection of radial distribution system. The effect of load models on the enhancement of maximum loading is also investigated. The load growth period is also considered in the investigation. With the proposed method optimal set of conductors are selected by maintaining acceptable voltage limits and current carrying capacity of the feeders. The effectiveness of the proposed method is illustrated with 32-node practical radial distribution system. The proposed method will reduce the real and reactive power losses and also improves the voltage profile.
The power losses in distribution systems are significantly high because of lower voltages and higher currents compared to high voltage transmission system. If a conductor is loaded near to its thermal rating, losses will be increased. Hence, line conductors are loaded under their thermal limit. Reduction of total loss in distribution systems is very essential to improve the overall efficiency of power delivery. The pressure of improving the overall efficiency of power delivery has forced the power utilities to reduce the loss, especially at distribution level.
It is important to select proper size of conductor of distribution system because it increases the loading of the system. In [1] an algorithm is proposed for selecting the optimal size of conductor of feeder segments of radial distribution networks based on analytical approach. The approach discussed by Wang et al. [2] included an economical current density based method and a heuristic method, which together enabled a satisfactory solution that could be easily achieved. Miu and Chiang [3] proposed a solution algorithm to determine distribution loading capability. A solution algorithm suitable for large-scale unbalanced distribution networks with capacitor control actions was developed and tested. However, their model was suitable only for constant current load and for radial main feeder only. Das [4] presented a simple algorithm for determining the maximum loading of the feeders without violating the maximum current capacity of branch conductor. A predetermined annual load growth was also considered to determine allowable load growth period without violating the minimum voltage limit of the feeder. A dynamic model for the development of primary and secondary circuits supplying a residential area had been proposed by Kirn and Adler[5]. S. Ghosh et al [6] presented an analytical method for enhancement of loading of radial distribution system. S. Sivanagaraju et al[7] presented a heuristic method for improving the maximum loading by optimal conductor selection of radial distribution systems. J.S. Savier et.al [10] discussed an exact method for loss allocation in radial distribution systems. The important feature of this method is that no assumptions are made in the allocation of real power losses. In ref. [11], the authors dealt another method of loss reduction in radial distribution systems, i.e capacitor placement method. In this method they have explained the direct search method for capacitor placement. L.D.Ar ya et. Al[12] described an algorithm for rescheduling reactive power control variables so as to have an adequate loadability margin for current operating point. Co-ordinated Aggregation based PSO (CAPSO) has been used as optimization technique. Two objective functions have been selected for load margin enhancement. One is minimization of total reactive power loss and other considers minimization of incremental reactive power loss. But this method was applied power systems rather than distribution systems. In ref. [13] authors discusses the impact of covered overhead lines on distribution reliability and safety. They have used monte carlo simulation for evaluating the reliability index of the system.
In this paper a method is proposed for enhancing the maximum loading of radial distribution system using genetic algorithm. The effect of load models on conductor selection of radial distribution system is also investigated.
The problem of choice of the optimal type of conductor for each feeder segment is presented as an optimization problem using branch wise minimization technique. The detailed algorithm of the technique is given in [8]. Nevertheless, the salient features of the algorithm are explained in this section.
The objective function for optimal selection of conductor for branch j with k type conductor is
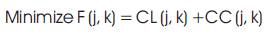
I) Cost of energy losses (CL): The annual cost for the loss in branch j with k type conductor is,

Where
Ke = annual cost of energy loss (Rs/KWh)
Lsf = loss factor
Peak Loss (j, k) = real power loss of branch j under peak load conditions with k type conductor.
ii) Depreciation on capital investment (CC): the annual capital cost for branch j with k type conductor is,
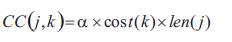
Where
α = interest and depreciation factor
Cost (k) = cost of k type conductor (Rs/km)
Len (j) = length of branch j (km)
The loss factor is expressed in terms of the load factor as
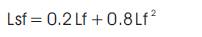
i) Feeder voltage: the feeder voltage at every node in the feeder must be above the acceptable voltage level, i.e.

ii) Maximum current carrying capacity: current flowing through branch j with k type conductor should be less than the maximum current carrying capacity of k type conductor, Imax (k), i.e.
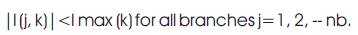
The detailed algorithm to determine optimal size of the conductor is given below
| Step 1: | Read the system data |
| Step 2: | Perform load flow |
| Step 3: | Initialize population. |
| Step 4: | Set the iteration count to '1'. |
| Step 5: | Calculate the objective function using eqn. (1). |
| Step 6: | Calculate the fitness value using 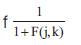 |
| Step 7: | Sort data in the ascending order of fitness. |
| Step 8: | Now copy the best string of chromosomes of old population to new population. |
| Step 9: | Now perform crossover and mutation operations respectively for generating remaining chromosomes. |
| Step 10: | Now, replace old population with new population. |
| Step 11: | Increment iteration count. If iteration count < max.count, go to step 4. Else go to step 12. |
| Step 12: | Print the total real power loss, reactive power loss, and voltages. |
 must be computed using
must be computed using 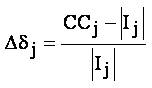 The minimum of all the values of
The minimum of all the values of 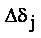 must be selected.
must be selected.
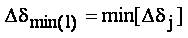
Update the values of loading factor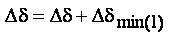
The real and reactive power loads of all the nodes beyond the branch l must be increased by a factor 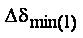 and the rest of the loads remain unchanged.
and the rest of the loads remain unchanged.
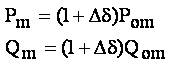
To calculate the effectiveness of various load models on loading of conductor practical voltage dependent load models are considered. Practical voltage dependent load models i.e residential, industrial and commercial given in [9] have been adopted for investigation. The load models mathematically expressed as
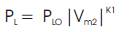

Where PLO , QLO are the active and reactive load powers respectively, at the nominal voltage of 1.0 p.u. and |Vm2 | is the actual voltage magnitude of node in p.u. In a constant power load model, conventionally used in power flow studies k1=k2=0. The values of the real and reactive exponents used in the present work for residential, industrial and commercial loads are given in Table 1[9]
The growth in feeder load may be due to addition of new loads to the feeder or due to the incremental addition to the existing loads. Once, the load exceeds the feeder capacity, limited by voltage regulation or thermal constraints, new facilities such as substations or additional feeders need to be created. Till such time, the substation feed area and the configuration of the feeders may be assumed to remain unchanged. It is further assumed that the feeder load grows at a predetermined annual rate, in proportion to the connected loads.
Real and reactive power load at any year 'h' is given by
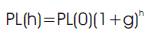
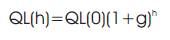
Where
g=Annual load growth rate
PL(0)=Real power loads in the base year(0th year)
QL(0)=Reactive power loads in the base year(0th year)
PL(h)=Real power loads in the year 'h'
QL(h)=Reactive power loads in the year 'h'
The eqn. (11) and (12) can be used to determine the maximum allowable load growth in a period of 'h' years. It is assumed that the annual load growth rate g=8%.
The effectiveness of the proposed method is illustrated with a practical 32-node system existing in Anantapur town, India. The line and load data of the system is given in [1] .
The system cannot be overloaded before conductor modification as the current in some of the feeder segments is violating the current constraint. Hence, the conductors selected based on genetic algorithm optimization technique are tabulated in Table 2.
With the new set of conductors, the system can be overloaded and Table 3 shows the values of loading factor and maximum allowable load.
From these Tables 3 & 4, it is observed that the maximum loading condition is improved after optimal branch conductor selection. Eqn. 11 & 12 is used to determine the maximum allowable load growth period. From Table 3, for constant power load, TPL(N=Nmax) = 1844.64 kW and as mentioned earlier real power load at the base year, TPL(0) = 1680 kW. Therefore, using Eqn. (11), Nmax can be obtained as:
1844.64 = 1680 (1+0.08)Nmax
Or Nmax = 1.2 years
Similarly for Industrial, residential and commercial loads Nmax are obtained as 2.4, 3.6, and 3.8 years for before conductor modification respectively. The Nmax values after conductor modification are given in Table 4 for constant power, industrial, residential and commercial loads as 5.4, 6.8, 8.1 and 8.4 years respectively. The load growth of the feeder is allowed as long as the voltage limit is not violated. The summary of load flow results of 32- node system is given in Table 5. From Table 5 it is observed that minimum voltage is improved from 0.9825 to 0.9906 and total losses are also reduced from 25.37 to 10.17 kW.

Table 1. Load Types and Exponent Values
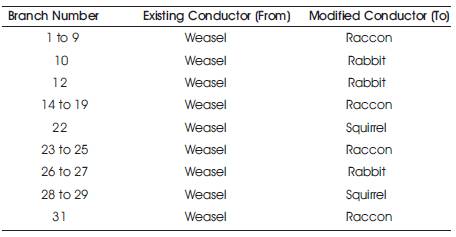
Table 2. Modifications in the feeder conductor type after conductor selection of 32-node radial distribution system
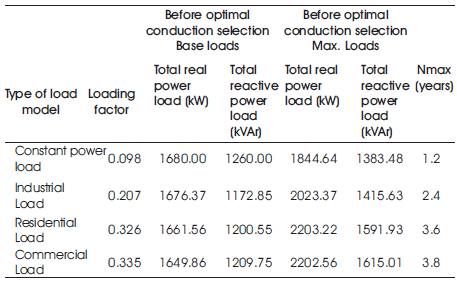
Table 3. Loading factor and maximum load before conductor selection
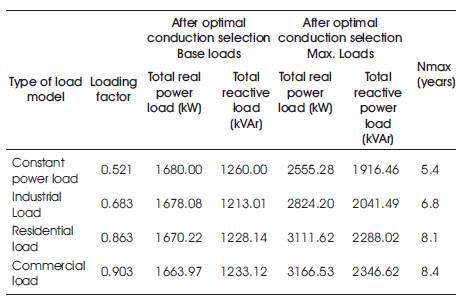
Table 4. Loading factor and maximum load after conductor selection
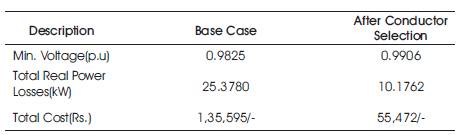
Table 5. Summary of results of 32-node system
A simple genetic algorithm method has been proposed for improving the maximum loading of the radial distribution feeder by using optimal conductor selection algorithm for different types of practical load models by considering the maximum current carrying capacity of branch conductors. Voltage and current constraints have also been satisfied by allowing the feeders to take the load growth up to a specified period of time. The effectiveness of the proposed method is demonstrated with practical 32-node system in India. It is found that loading capability is highest for commercial loads, lowest for constant power loads and lie in between for residential and industrial loads.