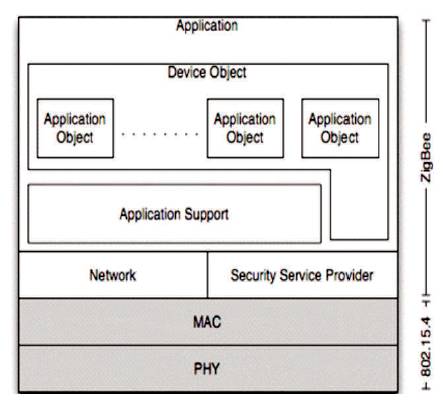
Figure 1. ZigBee and IEEE 802.15.4 (Obaid et al., 2014)
ZigBee is an IEEE 802.15.4-based specification for a suite of high-level protocols applied to create personal area networks with little, low-power radios, for instance of house automation, and different low-power, low-bandwidth that perform small range jobs require instant connection. The main focus of this paper is on measuring the performance of ZigBee network. For this purpose, various protocols, such as DSR, AODV, OLSR, and ZRP have been used along with NetSim Simulator. The performance is analyzed by taking various parameters, such as Throughput (Mbps), Delay (Microseconds), and Packet Transmitted with the help of routing protocols like DSR, OLSR, AODV, and ZRP to improve the routing protocols’ performance and reliability.
Technologists have never faced any difficulty while discovering possible applications of wireless sensors. The wireless devices are much easier to install as compared to the wired devices. Moreover, sensor installment is very costly in the case of wired sensors. Wireless sensors also bear many drawbacks. High power consumption is one of them. To tackle with this problem, a new wireless technology came into existence which is called as ZigBee. (Singh et al., 2012). ZigBee is low-power, minimal information charge and shut proximity (i.e., personal area) wireless ad-hoc network system. ZigBee and IEEE 802.15.4 have reduced information charge wireless network requirements that could eliminate the expensive and damage susceptible wiring in industrial applications (Zigbee, n.d). Flow or method control equipments may be positioned anywhere and they however communicate within the rest of the system. It can be transferred, considering that the network does not worry about the physical area of a sensor, pump, or valve (Singh and Kapoor, 2017).
Figure 1 represents the ZigBee architecture which involves the six layers, i.e. Application, ZigBee Device Object (ZBO), Application Support (APS), Network, Security Service Provider, MAC, PHY. The main task of ZigBee Device Object (ZBO) sub layer is to determine the type and nature of the device used in the network. While building a secured network between two devices, this layer is responsible for replying the binding requests. The Application Support (APS) is another sub layer, which performs the task of maintaining tables. The information included in the tables is useful for creating an association among the devices. Further its application is to verify all the other devices which work in the operating field during the discovery phase.

Figure 1. ZigBee and IEEE 802.15.4 (Obaid et al., 2014)
The main objectives of this paper are as follows,
Dynamic Source Routing (DSR) is a routing protocol used for wireless mesh networks. It uses source routing rather than depending on the routing table at each intermediate device Dynamic Source Routing (n.d). The DSR protocol is a reactive routing protocol, but the concept applied is specific resource routing. In this routing protocol, data packets which are delivered contains the entire, sequenced range of all the nodes via which each data packet has to proceed through to achieve the destination. DSR enables the network to be entirely self-organizing and self-configuring without the need for almost any preexisting network infrastructure. DSR consists of two systems which are Route Finding and Route Maintenance
AODV is just a current routing protocol that adopts a purely reactive approach and effective at both unicast and multicast routing. It creates a route on-demand in the beginning of communication session and uses it till it breaks, after which a fresh route setup is initiated. AODV adopts a very different mechanism to keep up routing information. It uses traditional routing tables, one entry per destination. In this protocol, nodes have control to decide the way in which of the routing protocol is to be used between computer device and mobile ad hoc network. Every node learns about other nearby nodes and how to reach them (Paulus et al., 2013).
OLSR is a proactive and table driven routing protocol. It uses periodic messages to update the topological information of the network among the nodes. The nodes exchange this data to establish a route to the destination node in the network. The benefit of this scheme is that routes are immediately available at each node to the destination node (Optimized Link State Routing Protocol, n.d). It reduces the possible overhead in the network protocol and it is used to MultiPoint Relays (MPR). Reducing the time interval for the control messages transmission brings more reactivity to the topological changes. OLSR protocol is suitable for large and dense area of networks (Paul and Sarkar, 2013).
Zone Routing Protocol is a hybrid wireless networking routing protocol that uses equally proactive and reactive routing protocols when sending the data within network. ZRP is used to speed up delivery and minimize control overhead by selecting the most effective form of protocol to use throughput the route (Zone Routing Protocol, n.d). The Zone Routing Project (ZRP) includes equally reactive routing and pro-active routing methods into a hybrid routing protocol. ZRP is a routing protocol, which is used to decrease the control overhead of proactive routing protocol and decrease the latency in reactive routing protocol. It is really a reactive process and the way finding process is only started when required or on demand.
NetSim is a system simulation instrument that lets you build system situations, model traffic, and study efficiency metrics. Network simulation is just a strategy where a program designs the conduct of a network possibly by calculating the connection between different network entities (hosts/routers, data links, packages, etc.) using mathematical formulae or really catching and playing straight back observations from a generation network.
A Network model is just an non-constant means of addressing products and their relationships among devices. Network mode is established with the help of networking devices like hubs, switches, modems, nodes, joining cables, etc. (NetSim, n.d).
A network scenario is just a narrative explaining expected interconnection sending data and their particular receiving data in the system.
Network performance is used to measure the performance evaluation of a protocol network and performance metrics is established using Network Statistics.
Figure 2 shows the scenario diagram of 6 nodes of ZigBee with central PAN coordinator. The data is transmitted and received through PAN coordinator by using source and destination nodes. In this scenario, node 1 and node 6 are taken as source node and destination node, respectively. The performance evaluation of effort in the work is examined by NETSIM simulation software. The main network for this software containing randomly placed ZigBee nodes is build up within an area of 100*100 (in meters). The system's performance can be assessed by various ZigBee protocols named as DSR, AODV, OLSR, and ZRP.
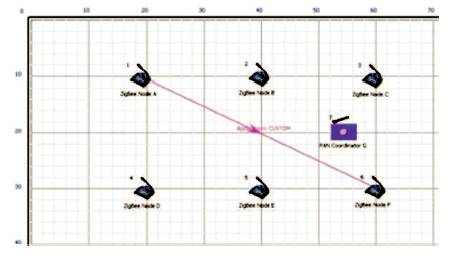
Figure 2. Scenario of Network with 6 Nodes
The simulation parameters are given in Table 1. The screenshot of the scenario with ZigBee Technology is given in Figure 2.
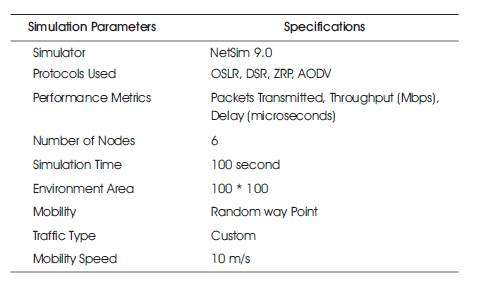
Table 1. Simulation Parameters
Throughput is the main metric to check the efficiency of routing protocols. Throughput refers to how much data can be transferred from one location to other location in a given amount of time. Thus, throughput is the rate of successful message delivery over a communication channel. Figure 3 shows the results of throughput containing 6 nodes by taking ZigBee routing protocols, such as OLSR, DSR, AODV, and ZRP. Results of OLSR, DSR, and ZRP are analyzed from this figure. Data is calibrated into Mbps. AODV is better than ZRP, DSR, and OLSR in performance. Throughput of DSR, AODV, OLSR, and ZRP are 0.099945, 0.103072, 0.08908, and 0.099319, respectively.
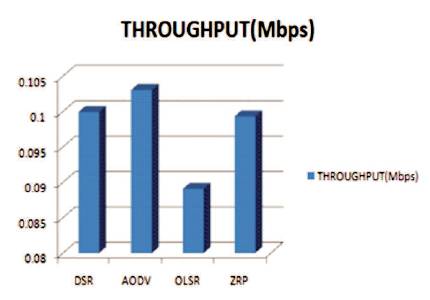
Figure 3. Performance Evaluation of Throughput (Mbps) in terms of DSR, AODV, OLSR and ZRP
A packet is the unit of data that is routed between an origin and a destination on the internet and it is send from one place to another on the internet. Packet transmission is done for a small pack of data sent across a network. Figure 4 describes that the performance of OLSR is maximum that is 56018. The least performance can be witnessed in terms of AODV (3943). There is difference of 5867 ZRP and DSR with performance being 41861 and 35994 respectively.
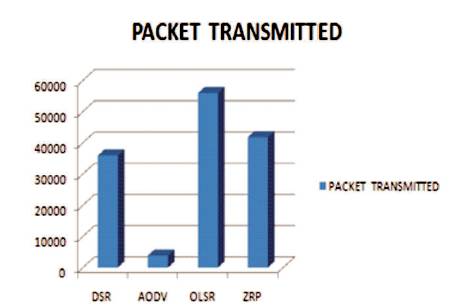
Figure 4. Performance Evaluation of Packets Transmitted in terms of DSR, AODV, OLSR and ZRP
Delay is the important metric which is used in the network for checking the performance of the network and this is basically measured in fraction of seconds. It specifies that how long data is travelled from one node to another. Figure 5 shows that AODV has the least delay time that is 4121212.986 and DSR, OLSR; ZRP has long delay time that are 41458859.06, 40054676.62, and 40463207.92 orderly.
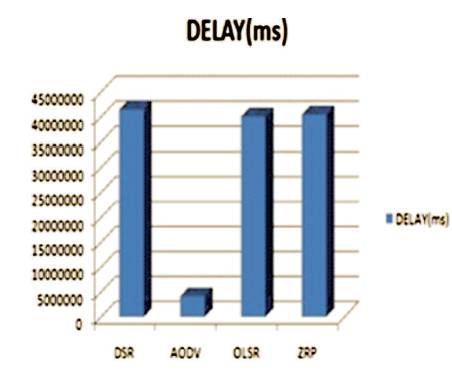
Figure 5. Performance Evaluation of Delay (Microseconds) in terms of DSR, AODV, OLSR and ZRP
Table 2 shows observations of performance metrics such as packet transmitted, throughput, and delay, which are concluded for various ZigBee routing protocols by taking 6 nodes in the scenario of network.
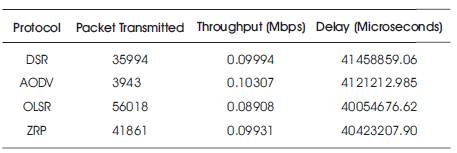
Table 2. Observations of Performance Metrics
In this paper, the main characteristics of ZigBee technology have been demonstrated. ZigBee is definitely a start, global, packet-based routing protocol technology, which makes easy to use the procedure for secure, trusted, reduced energy wireless networks. The authors have discussed the performance metrics comparison of DSR, OLSR, ZRP, and AODV routing protocols for ZigBee technology with packets transmitted, throughput, and delay. The performance evaluation on ZigBee routing protocol by taking 6 nodes scenario was represented in this paper. The simulation results showed that AODV performs well in terms of throughput and delay as compared to DSR, OLSR, and ZRP. OLSR shows increased ratio in packet transmitted as compared to DSR, ZRP, and AODV routing protocols using the Netsim simulator.