Figure 1. Personal Digital Assistance which students use in Classroom
This paper presents the survey of mobile learning in education environment. Technology and trends rapidly increase day by day and the evolution of 4G system is being implemented. Currently users of PDA and Smartphones are using whatsapp's applications to save cost and time. The methodology of the paper is based on survey of earlier research and latest research. The investigation of Mobile learning in Universities and Education Institutions has been discussed. Mobile learning provides lot of benefits to the student at the moment. Students can easily learn through mobile, Smartphone and PDA using internet connection. The objective this paper is to present the analysis of mobile learning and education.
Online education has lot of benefits, and students can submit or retrieve data, and upload and download their assignments and paper. Online learning management system is mostly provided by the National and International universities and most of the universities provide online education program. Mobile education is that particular education in which student can enhance their skills online, asking question to the teacher and to colleagues. Mobile computing integrated into e-learning make courses in the universities more accessible and portable. The students can read the lectures and listen to video lecture also. With the arrival of mobile learning, universities are aware of learning tools e.g. IPOD and Tablet, which play a major role in learning education through mobile. Most of the organizations and learning centers deliver information and even lecture online, and through video conferencing.
The arrival of cell phones, PDA, MP3 players, portable game devices, handhelds, tablets and laptop have changed the way we learn and, these devices are connected and communicating to each other in ways that would have been impossible a few years ago. Through mobile computing we can view E-Books of every type, and electronic magazines and Journals are part of online learning. Before 8 years, mobile apps were not so mature and sufficient to fulfill the desired requirement of the user. ELearning has been taken far away from class room and mobile learning is in class as well as on class room and far away.
This paper is structured as follows Section 1 describes the common mobile computing devices and its usage in university campus, Section 2 shows some details of educational proposition of mobile learning. Section 3 details on the survey done by other researchers. Section 4 presents challenges of mobile learning and education and finally the paper is concluded. [1]
PDA stands for Personal Digital Assistance. It works like a cell phone and has large LCD display. It is shown in Figure 1. Laptop and PDA support mobile learning education. Merit: student can send email to the teacher and view their lectures. Blue tooth, and Wi-Fi are connected with PDA. Demerit: the cost of the PDA matters, because users increase their call limits and internet connection limit that increases its cost.

Figure 1. Personal Digital Assistance which students use in Classroom
Smartphone contains internet connection to facilitate student for downloading lectures and tutorials. Smartphone is considered as a complete phone as shown in Figure 2 and it has a smart battery and strong signaling capacity with internet connection. Merit: user can view and edit their document. Demerit: Smartphone is changing the trend of younger generation.

Figure 2. Smartphone student is using in classroom and outside the university
Laptop is known as portable computer and it is used like a mobile phone. Laptop contains Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, internet connection and smart storage space for storing digital data. The main goal of laptop is to create digital document and project using time constraint. Merit: smart working in smart time. Demerit: laptop has limited battery.
Tablet PC works like a mini computer and is enriched with mobile features. It has a touch screen and student can integrate his voice and body movement with the intelligent tablet sensing. Merit: Tablet computer is low weight and easy to carry Demerit: sensitive touch screen. [2]
Peer2Peer Network enables developers to create collaborative application for mobile phones using network technology such as Bluetooth & What's Apps. The architecture of mobile, support Personal area network. Technologies for P2P networking include fixed and wireless network technologies e.g. Bluetooth, WLAN, WiMax, GPRS (General Packet Radio Service) and UMTS (Universal Mobile Telecommunications System), allowing devices both to be ”mobile” and to ”interconnect” with mobile or fixed P2P infrastructures. [15]
Mobile wireless is a WI-FI technology in which student connects with Wi-FI router to connect with the internet. Most of the students depend on internet bandwidth and its usability. WLAN has advantages and benefits. Student can easily watch video lectures online and listen to audio lectures as well. Figure 3 shows the Mobile Learning Apps used in different scenario.
Figure 3. Mobile Learning Apps used in different scenario
Teachers are using internet connection for uploading their lectures and class notes on the web. Most of the students carry smartphone and tablet for their personal usage. Students have limited time for study, and mobile plays a significant role for developing a study framework. Private sector and public sector universities have begun online learning management system on their web site, which is a very remarkable effort to enhance the skills and knowledge level of the students.
Bluetooth is a technology which is used for data transfer from mobile to mobile communication. University students carry cell phone and they have lot of education material, and knowledge is transfered from person to person using Bluetooth technology.
Most of the mobile phone companies offer GPRS package for internet connection, and it is very affordable and usable for everyone. GPRS connectivity is based on mobile generation, 3rd generation and 4th generation mobile network, and have lot of capabilities to send and receive heavy data. [3]
In this paper, the author has proposed the architecture of mobile learning in university environment as shown in Figure 4. The terminal connected with the infrastructure inside the university Local Area Network (LAN) is also connected with the external network environment. The university offers server platform for course management system for educational resources and it is connected on the university LAN. A student might access the platform directly from the university LAN or through the internet in order to collect the learning materials. The student can access the data center of the university from WLAN as well as from Local LAN network.
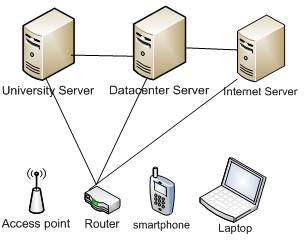
Figure 4. University Mobile Learning Architecture
The advantage of this architecture is that it offers services to the teacher and student in the university premises. The author suggests electronic learning using mobile devices, and mobile device contain lot of online apps and building block apps which students can download easily using internet service. E.g. Teacher agent and word editor for learning and writing assignment. The university classroom frequently should have the following equipment e.g. PC or laptop, microphone, speakers, tablet, webcam, projector and a monitor or screen. At the university classroom, the lecturer and professor will present and deliver the content of the learning material to the students in a classical manner, or via the internet to the student that are at home, at work, or mobile. Mostly the student and the teacher when they are at home, usually use their own personal computer or laptop using high speed internet connection. Students use their mobile devices e.g. smartphone and tablet, they usually connect with GPRS, UMTS, LTE for learning. According to this paper, the technology development and trend has increased, speed and density of integrated circuits, enhanced transmission capacities on the optic Fiber network and networking flexibility, distributed and open platform-based communication software capacities. Figure 5 shows a detailed Architecture of Mobile Learning & Education.
Figure 5. Detailed Architecture of Mobile Learning & Education
The university server provides facilities to host the digital educational resources, which can be accessed by the lecturer and all students either locally, or throughout the internet connection. Entire student and faculty of the university can access the server platform to collect or download the data from the server using cloud computing environment.
3.1.2 Disadvantages of Mobile LearningThe main drawback of using Smartphone is students misusing mobile apps and mobile services e.g. socializing their data and project to the entire student member using internet apps. [4]
Zhang et al. has developed a reference framework for partitioning a single application into elastic components with dynamic configuration of execution. The components, called weblets, are platform independent and can be executed transparently on different computing infrastructures including mobile devices or IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service) on cloud providers such as Amazon EC2 and S3[8]. The application is split down to a UI component, weblets, and a manifest describing the application. Weblets are autonomous functional software entities that run on the device or cloud, performing computing, storing and network tasks. An elasticity manager component decides on migration, instantiation and migration of the weblets. These processes are transparent to the running application.
3.2.1 Ad-hoc Mobile CloudsAn ad-hoc computing cloud represents a group of mobile devices that serve as a cloud computing provider by exposing their computing resources to other mobile devices. This type of mobile cloud computing becomes more interesting in situations with no or weak connections to the Internet and large cloud providers. Offloading to nearby mobile devices save monetary cost, because data charging is avoided, especially favored in roaming situations. Moreover, it allows creating computing communities in which users can collaboratively execute shared tasks. [16]
According to this paper, the user will access the cloud space using his/her qualifications so that the required data will be shared from the cloud based client request only for the real user. Figure 6 shows the present data storage and management system.
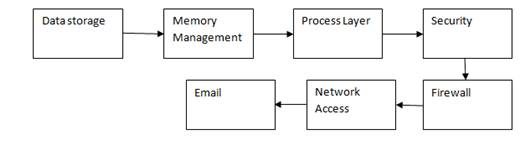
Figure 6. Present data storage and management scenario
The student who wants to make use of mobile learning has to register and get recommendation to use it via web service. Students can also download mobile apps which will be installed in mobile phone through the GPRS and WIFI connectivity. The student can read the documents, look at the video tutorials, listen to lectures or seminars and finally they can take up self assessment. They will be given results and analysis so that they can evaluate their strengths & weaknesses on their own. The mobile system helps to learn while you roam and also education for all at any time any where globally. Professionals can also share their valid tutorials into the cloud for development of education community. Figure 7 represents the process flow of mobile learning cloud computing.
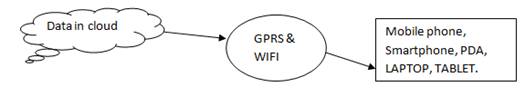
Figure 7. Process flow of mobile learning cloud computing
In client mode, user has to download this application and install in their personal digital assistance device and their Smartphone. The student has to connect to the GPRS/Bluetooth/ WI-FI and connect to the cloud network and get the required topics and based on the selected topic, materials will be downloaded to the mobile for the reading process. Figure 8 represents the Process flow of mobile learning.
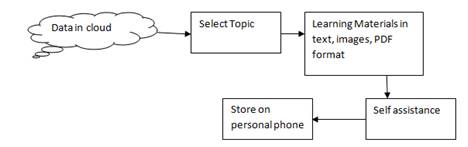
Figure 8. Process Flow of Mobile Learning
Mobile cloud plays an essential role in student life, because the data sharing is very important for learning system. Most of the cloud services provide security services to secure mobile cloud data within a cloud. Student and teacher data have lot of importance because its usability and needs are increasing day by day. Today there are lot of direct applications for teaching and learning as opposed to simple platform independent tools and scalable data storage. [2]
According to Lave & Wenger (1990) Mobile devices and Smartphones also allowed for interaction with the course content and other classmates in a highly situated and contextualized way. Author suggests that the situated learning takes place in the same situation in which it is applied. Situated learning serves the individual's understanding and the legitimacy of the situation. The learning can happen in the situation of the actual university grounds environment, where the explanation of group of people was being inspected and was individualized to the student group. [5]
3.4.1 Variety of way of LearningAccording to Joanne Gikas &. Michael M Grant (2013) students used mobile computing devices, to interact with each other and share their knowledge and skills. This included recording of videos or voice note to be uploaded to the course site and then discussed by the entire class. Students were able to communicate and work together about course content by using mobile computing devices for text message and email. Students also sense that they have chance for strengthening of the course material when using their mobile devices. Students also participate in online programming competition and online quiz segments. Students also participate on projects as a group or a team. Students also view their results and statistics on course site, and if they found any gap and problem, then they improve their skills and knowledge. Students and teachers use their twitter account to share their knowledge and information and also tweet on a specific topic and research. [5]
3.4.2 CommunicationThe main advantage of the mobile device is that students can communicate with fellow classmates and the instructor. According to Lakeshore university students, they felt that the constant communication made available through the mobile device was key in the success of the instruction and allowed them to be fully productive. Learning happens casually from small group teamwork, while students gather information around campus. Students interacted with each other through applications, e.g. Skype, team viewer and Face book. [5]
3.4.3 Group MeetingAccording to Joanne Gikas (2013) “Students at the University of Northbrook and Coastal College spoke positively about accessing course content e.g. discussion board of learning management system, course reading, and video clips they needed to watch for class on their mobile device. Furthermore to accessing content they used their devices to upload and post content to their course sites” [5]. Figure 9 shows Cloud Computing with various component.
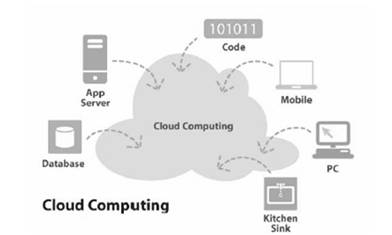
Figure 9. Cloud Computing with various component
According to Ryann K. Ellis (2009) LMS (Learning Management System) is a software application that automates the administration, tracking and reporting of training events. The system is working on multiuser environment where designer can create, store, reuse, manage and deliver digital learning contents from a database. [6]
In recent times a growing number of institutions and business organization have squeezed the concept of elearning and m-learning. They use web based learning systems to fulfill their educational needs. The education system with many users has been increasing day by day, and so they require web based learning management system to fulfill their desired requirement and targets.
3.5.1 Mobile AgentAccording to Seng Wai Loke (1999) Mobile agents can be regarded as software components which can move from host to host to perform computations. Mobile technology is required to enable efficient data sharing and distance learning with up-to-date data, and to allow distributed and mobile workers access information on demand. Mobile agents have been working within an organization to organized data [7]. Mobile agents replaced client server model because mobile agents are based on internet application e.g. applet.
3.5.2 Synchronization in LMSAccording to Joe Sirott Sun et al, in their research paper, Content synchronization in LMS is new area which involves the transfer of data from one machine to another. Many researchers have conducted their researches concerning synchronization in different applications on data transfer e.g. synchronization of data between accounts, website mirroring, content distribution, storage networks and web search for information [8].
Semantic web is an internet technology that simplifies the process of most appropriate content delivery to the learner. The most appropriate use of XML (Extensible markup language) Meta data, is delivery of learning content that meets the needs of learner. In this way, the learner can receive learning content that will enhance their practical skills and knowledge.
3.6.2 Grid TechnologiesEssential reason of Grid technologies to permit handling of vast quantity of information is that so with addition of Grid in education management, thousands of existing learning resources become an easier task. By mixture of computational ability of grid networks and advantages of semantic web, there is better description of existing resources, and delivery of learning content is fast, easy, successful and very useful [9].
There are lot of challenges in mobile learning, since mobile screen is limited and limited text is displayed on mobile screen. Mobile communication technology can support the learner to read the content and explore the content in guiding learners to be involved in active learning process without support of rich multiple external representations for providing the complete functions. Web learning supports accurately and provides individual learner with higher satisfaction. The main issue is location and response time of the learner. Location means where the learner use their computers to access web learning [10].
Prensky (2001) and several other authors have explained the changes in learners in terms of generational differences, measuring such differences by the ease with which they take on and become accustomed to new technologies. [11] Oblinger (2003) Considers the key character of today's learners as being digitally literate, always on mobile experimental, and group of people oriented. There is a new focus on mobile technology of generation focus on developing capacities in the form of creative, collaborative, critical and communicative responses. [12] According to Thomas (2005) it is the potential for institution to have pervasive learning, where learner and author himself are in a location that the learner finds meaningful and relevant. The development of such pervasive learning models cannot be an end in itself, but is itself a response to learner's new ways of being [13] .
The technological changes in wireless and mobile technology have extensive factor for the learner and the teacher. The literature review considered the following option for mobile learning e.g. Tablet PC and PDA & Smartphone, laptop which play a significant role in mobile learning. But the factor of the price of laptop computer for the learner, is crucial where they can reach a serious group of learner. The extensive availability of technology is fundamental to itself, if it is insufficient for the effective learning environments. [14]
According to Rachel Cobcroft (2005) Universities and other education organizations felt that the main factors of responding to external factors are competition, market trends and government policy imperatives, and internal factors are student preferences, staff capabilities and educational approaches. The changing cost of technology purchase and maintenance also mean that the rider of mobile and wireless access compares it to being increasingly favorable with the maintenance of oncampus computer facilities, even if students are provided with the support financially or free hardware when they first enroll. Bates and Poole (2003) propose a similar model for determining technology choices for effective learning and teaching in higher education; their criteria include appropriateness and access, ease of use and reliability, costs, teaching and learning approaches, interactivity, organizational issues, innovation, and speed. Whatever the list of criteria employed, an examination of whether the right technology has been selected is debatably a key feature of a complete evaluation of mobile learning.
Universities need to manage implementation of self-determining of specific models and types to preserve resources and minimize change exhaustion. There should be option for selecting the appropriate technology infrastructure, which requires an assessment of the appropriateness, quality, compatibility and cost of the devices. The main factor is learning management system in addition to maintaining device-independent need to deliver facade important problem to mobile learning implementation. Teacher will need to establish the background in which the use of mobile technologies is relevant. For example significant social, economic, ethical and educational factors will influence the effective and efficient form of mobile technologies [14].
Cloud computing and mobile computing have completely changed the world. Students and faculty data exist in cloud and are updated day by day. Mobile learning and education has rapidly increased these days. The majority of the universities provide online education program. Mobile learning evolves in the entire educational institutions and it has lot of business and educational application. Students feel that they are very busy in their lives and have no time to stay in front of desktop computer to write assignment and projects. With the increasing usage of Smartphone, tablet, IPAD and PDA, that have built in online education apps e.g. online learning management system, that is diminishing. Mobile agent play a significant role in mobile education. There are lots of challenges which are existing in mobile education e.g. the future of Smartphone and PDA, whether they will exist or not is a challenging question for upcoming generation of 5G and later. The future research direction relating to mobile education might contain mobile online apps and their usability in mobile education and what would be the role of public sector and private sector universities to promote online education.
The author is thankful to his teacher Rana Ajmal who has assisted him a lot and provided him much help to complete this paper.