Introduction
Telecommunication as known is transmission of waves over a distance for the purpose of communication; modern telecommunication Medias include telephone, television, radio and computer. Mobile telephony is the provision of telephone services to phones which may move around freely rather than stay fixed in one location. Mobile phones connect to a terrestrial cellular network of base stations (cell sites), whereas satellite phones connect to orbiting satellites. Both networks are interconnected to the Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN) to allow any phone in the world to be dialed.
The evolution of the telecommunication industry, over the years in the world, has seen several inventions in the computer age. It has provided a lot of changes in the Information Communication Technology (ICT) world where at a click of a button, one can envisage the whole world. Communication is one of the key frameworks to economic growth and sustainability for a developing nation such as Ghana. Since access to most cities, towns and villages across the country are most of the times not accessible by vehicles; one will require communication gadgets such as telephones and mobile phones to reach business partners, families and friends located at these remote places. This can be done through a phone call, text messaging, voice mailing, E-mailing or internet browsing.
The research covers areas of analysis of user preference or choice of network in the mobile telecommunication industry in Ghana. Over the years, Ghana's telecommunication industry has been monopolized by a state owned company by name Ghana Post and Telecommunication. In the early 1990's, the economy saw some deregulation of the National Communication Policy. By 1994, it brought about a split of the state owned Post and Telecommunication Company into two exclusive individual entities with each having its own budget allocation as well as management.
The telecommunications industry in Ghana has been on a very progressive journey and it has covered a great distance in a very short period of time. Not long ago very few people had private telephones that worked. As in 1996, the telephone density of Ghana was 0.26% meaning that there were 2.6 telephone lines for every 1,000 people including 35 payphones in the entire country out of which 32 were located in Accra. This was one of the lowest in Africa. Today there is one phone for every four Ghanaians This tremendous increase in the tele-density has been a result of the establishment of the National Communications Authority (NCA) in 1997 and the subsequent deregulation of the telecom industry, which brought about the growth of wireless telephony as a result of significant investment by operators. For the consumer, being in touch simply means being able to purchase a mobile handset and subscribing to a wireless service. Deregulation also meant opportunities for ambitious entrepreneurs and large telecom companies to establish operations in Ghana and participate in what was to become the biggest boom in Ghana's recent economic history. (Http://www.ghanaweb.com).
This saw Ghana Telecommunication come under the brand name Ghana Telecom (GT) to operate with a management Lease out agreement with Telekom Malaysia (TM), an Asian telecommunication giant. Currently, it is trading under the brand name Vodafone Ghana. They provided both telephone and mobile communication across the entire country, as they had the necessary infrastructures to do so.
This saw the private sector come into active participation in the Telecommunication industry of Ghana as the industry welcomed Millicom Ghana (now trading under the brand name Tigo) as the first investor. It also saw Scancom Ghana (now trading under the brand name MTN); CellTel Ghana (now trading under the brand name Expresso) and Westel Ghana (now trading under the brand name Airtel) come on board with the referee being the National Communication Authority (NCA).
After fiercely contesting a bid to operate a cellular network in Ghana, Globacom came up with the license to operate in the country. Over two years, they faced problems with the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) of Ghana in putting up cell sites across the length and breadth of the country until recently when they were cleared to erect radio masts in the country by EPA. Globacom trading under the brand name Glo is a powerful brand in its mother country, Nigeria and among the market leaders after they modernized the industry.
The emergence of these telecommunication networks meant, the ever growing competitive nature of the industry, and user or subscriber preference for these telcos is influenced by the services they provide.
1. Problem Statement
A number of users or subscribers select telecommunication networks without taking into consideration the quality of services and the value for money. Once allegiance or loyalty to a particular network are influenced by several factors, but recently users opt for networks without an in-depth scrutiny and evaluation of services rendered by these telcos, and the cost of patronizing and staying on a particular network.
New subscribers who want to use a mobile device for the first time are sometimes faced with the puzzle of selecting a network provider and if possible would prefer to use two or more networks after some time; all are based on services received from these telcos. The question is what these services are and what caught the eye of the subscriber.
1.1 Main Objective Of Study
This research is to critically analyze the factor(s) that influence subscriber or user preference for the mobile telecommunication networks in Ghana and whether services rendered by these networks have an influence in user choice.
1.2 Other Objectives
This research is to find out services rendered by the six telecommunication networks.
The study hopes to seek whether income levels, educational status, and age are factors for the choice of a network.
1.3 Methodology
Data needed for this research will be gathered through questionnaires, interviews and internet. The questionnaire was administered in the ten (10) regions in Ghana. The data was analysed using the chi-square test as follows:
And compared with the critical value,
χ2[(r-1)(c-1), α] = The table value with degree of freedom given as,
DF=(r-1) (c-1)
Where,
Oij Is the observed value on the ijth observation
Eij Is the expected value of the ijth observation
R is the row.
C is the column
α Is the level of significance and is given as 0.05 in this study.
The expected value 
1.4 Hypothesis Statement
This research work is aimed at testing the significance of the below stated hypothesis at 0.05 significance level.
Ho: there exist no association between age, education and income level on the selection of a preferred network.
H1: there exist an association between age, education and income level on the selection of a preferred network.
1.5 Scope Of The Study
The study focused mainly on Ghana with a time horizon of (13) thirteen years; thus from 2000 to 2013. These formed a cross sectional data collected from the NCA website and through phone calls as a secondary data for analysis of the market shares of operators.
1.6 Significance Of The Study
For the government or the National Communication Authority (NCA), to critically analyze the impact of competition among the mobile communication networks and the effects on their clients. The study will be of great benefit to the stakeholders of the mobile telecommunication service providers, as this will encourage the market leaders to move ahead and explore the untapped resources, increase their investments in those areas within the telecommunication Industry of Ghana. To the general public, the study will help them get value for their money as well as quality services.
2. Literature Review
The Ghanaian Mobile Telecommunications industry over the years has seen telecommunication firms such as Ghana Telecom (GT) now Vodafone Ghana, as the incumbent and the sole provider of telecommunication access to both its colleagues in the industry and the general public. NCA, (1997). Vodafone Ghana provides operations in both fixed telephone and mobile communication across the entire country. They had the necessary infrastructure to function as a network operator and a service provider. It also saw the private sector come into active participation in the Telecommunication industry of Ghana in the year 1992. Millicom Ghana limited (now trading under the brand name Tigo) was the first mobile company. Followed by Scancom Ghana (now trading under the brand name MTN); CellTel Ghana (now trading under the brand name Expresso), Westel Ghana (now trading under the brand name Airtel) and new entry Globacom (trading under the name Glo) were established under the approval of NCA who supervised and controlled the activities of all these operators.
The National Communication Authority (NCA) was set up with consumer responsibility among its top level objectives by Act 524 of 1996. As already noted among the main objectives for establishing the regulatory body, the NCA has the following responsibilities;
- To ensure that communication system operators achieve the highest level of efficeincy in the provision of communication services and are responsive to customer and community needs.
- To protect operators and consumers from unfair conduct of other operators (with regards to the quality of service provided and tariffs to be paid)
- To facilitate the availability of equipment to consumers and operators.
- To promote competition among companies engaged in the provision of communication services.
- To promote growth of the industry by promoting research and development of technologies and the adoption of new innovations in the industry.
To achieve these and other objectives, the NCA is mandated by the Act which established it, to grant authorizations and issue licenses as well as regulate tariffs. ( National Communications Authority Act 524, 1996)
All these operators were providing telecommunication services to the entire nation, hence the rivalry in the market and the struggle for market shares and customer penetration levels. This study hopes to seek the user's singular or multiple reason(s) for choosing a particular service provider over the other.
Consumer or user preference primarily means an option that has the greatest anticipated value among a number of options. This is an economic definition and does not tap into wishes or dreams but for all practical purposes is an appropriate definition. Preference and acceptance can in certain circumstances mean the same thing but it is useful to keep the distinction in mind with preference tending to indicate choices among neutral or more valued options with acceptance indicating a willingness to tolerate the status quo or some less desirable option. (TECHNEAU- Consumer Preferences “An Overview”)
2.1 History of GSM/Mobile Telecommunication
Reginald Fessenden's Radiophones invention during the World War II marked the significant step to having an improved technology for the mobile phone industry. His Shore-to-Ship communication helped have this brilliant cordless telephone that could make and receive telephone calls provided one was hooked up to a cellular network operator.
The whole idea was first mainly for the use of the military in the 1950's to help them supply troops with logistics and arms as a more advanced form of communication that was used by the United States. This saw the emergence of different forms of broadcasting technologies that came up from 1947 to 1979.
This advanced Mobile Phone service networks came into being by first starting with mobile phones that were only glued to vehicles due to power and weight constraints. The mobile phones first emerged with the first-generation analogue systems before transforming into the GSM in April of 1991 known as the second-generation.
This saw Ghana having a mix of commercial mobile services till date but the First generation mobile technology is gradually facing out. Hence, the acceptance of the GSM network as the new generation of mobile phones across the world today. It comes in a handy and light form for easy usage. Ghana as a country had its fair share of the GSM with Scancom Ghana trading under the brand name Spacefon. This saw a total evolution of the industry as it was the first to launch the service in Ghana in the late 1995. By the year 2001 the number of telecom providers providing mobile services in Ghana had risen to 4 namely OneTouch (Ghana Telecom), Scancom Ltd, Kasapa, and Mobitel, with Ghana Telecom and Westel providing fixed line services. This was a major achievement in the young telecom reform history of Ghana. And by the end of 2009 it has increased the number of mobile network providers to 6 providing competitive pricing to their customers, with a significant increase in the number of mobile service subscribers from meagre 2000 in 1994 to 15,504,612 in February 2010. However, this success story would not have been possible without the telecom regulator – National Communication Authority. (Fink et al, 2002) in their analysis of 86 developing countries across Africa, the Middle East, Latin America and the Caribbean observed that improvement in performance of the telecom sector is maximised when privatization and competition is supported by an independent regulator. (Tobbin P. “Understanding the Ghanaian Telecom Reform, 2010).
World brands like Nokia did not start its operations as an electronics manufacturer but as a raw material company. It grew up into becoming a conglomerate. It was then active in paper, rubber and chemical but the evolution took place in the 1980's into the 1990's, when the activities were diversified from the chemical into an electronics manufacturer. Their strategy had paid off with the Nokia brand emerging as the world's vendor in the mobile handsets business since the late 1998 till date. (Cowhey, et al.,1990b).
Through innovation and market segmentation, Nokia saw the need for different products for different lifestyles. With the level of penetration of the mobile telecommunication industry, one will argue that they are nearly at the right place at the right time. This technological and mobile handset innovation was introduced into Ghana as well.
2.1.1 Customer Satisfaction And Market Share
The relationship between customer satisfaction and market share is an emerging issue in need of greater understanding. Achieving success in one may lower performance in the other. Market share can be gained by attracting customers with preference more distant from the target market. Service capabilities also can be overextended as volume grows. Clearly, there can be situations in which increasing one or the other is not profitable for the firm. For example, an extreme approach for maximizing customer satisfaction would be to eliminate all but one customer and direct all resources to that individual. Obviously, it would be a rare set of circumstances under which it would be profitable to do so. Conversely, a high market share is likely to be profitable only if enough customers have similar preferences. A firm that manages both to provide high customer satisfaction by customizing its offering to each customer and maintain a large market share would have to enjoy very high economies of scope and scale. Another way to think about this issue is to consider what the small niche firm has to do to be successful. Providing superior customer satisfaction is critical for its survival. (Anderson et al.1994)
2.2 The Mobile Telecommunication Industry's Strategies And Services
The mobile telecommunication industry in Ghana has adopted series of strategies that have reflected into their market shares and strategic positioning on the Ghanaian market. The most successful strategist is the operator on top with the greatest share of customers in the market, as we understudy the various cases in this section whether they were using promotions or any special advertising and marketing tool that they were privileged to at the expense of their competitors.
2.2.1 The Case of MTN
The Company started its operation in 1995 under the brand name Spacefon, then to Areeba and now MTN. With its introduction of the GSM technology, it attracted many people unto their platform when they came into Ghana. Being the first digital cellular network in Ghana, the high quality service offered by their GSM technology attracted more customers to them. Scancom Ghana Limited had always stood out with their wide network coverage and numerous value-added services to be the market leader. Due to their innovation and entrepreneurial drive, it saw them as the number one on the Ghana Club One-hundred lists from the year 2003 to 2005. Scancom remains one of the biggest companies in Ghana and their cellular network has the most subscribers.
MTN, has variety of services tailored to suit customers' specific needs, lifestyle and economic situations. Their services are specially designed to enhance mobile experience and add value to subscription. With their 3.5G coverage, you not only get closer to more people in more places but you can also connect in real time to family and friends with MTN Video Calling, download more instantly with MTN Loaded and explore more with the fastest internet connection from MTN Mobile Broadband.
MTN, as part of customer retention, currently runs the ―Dream Big Mega Promotion‖, with daily and monthly winnings and a final prize of a three-bedroom house. Over the next 100 days MTN customers have the chance of winning fantastic prizes including daily cash prizes of GH¢10,000, an Android Tablet and MTN airtime vouchers. Subscribers can participate in the promotion by texting WIN to 2020, at premium rate of 75Gp per SMS.
Services
MTN, provides several services which are categorized, internet services which includes; a 3.5G F@stlink router, data services, MTN video cam, MTN play, MTN broadband, blackberry, and MTN data vouchers. Value added services includes; e-selfcare, MTN sim swap kit, MTN toll free services, MTN voice SMS.
―Staying in Touch is one other service rendered by MTN, these are; MTNpay4me, Me2u, MTN video calling, MTN zone, MTN phone backup, and MTN family and friends.
MTN Roaming service provides you with; PayAsYouGo (PAYG), Pay monthly roaming, MTN seamless roaming etc. MTN were the first to introduce the ―Mobile TV service in collaboration with DSTV and their ―Mobile Money transfer with banks in Ghana puts them on top of the market in Ghana.
Coverage in Ghana
2.2.2 The Case of Vodafone
Vodafone in Ghana is an operating company of Vodafone Group Plc, the world's leading mobile telecommunications company, with a significant presence in Europe, the Middle East, Africa, Asia Pacific and the United States.
Vodafone is the only total communications solutions provider - mobile, fixed lines, internet, voice and data - and is currently unmatched in providing fixed line and internet services. They are the second ranked operator in mobile with a huge potential to take over the market.
Vodafone, a household brand in the world today made its roots into the Ghanaian market with the purchase of the then Ghana Telecom and its subsidiary OneTouch. They use to have the largest telecommunication infrastructure in Ghana until the reforms and deregulation of the industry. But due to their bad management practices in the mobile network industry, the then telecommunication giant Areeba totally took over the competition to now have the largest market share. Figure 1 shows Regions marked green represent areas of coverage nationwide. (MTN, Ghana 2012).
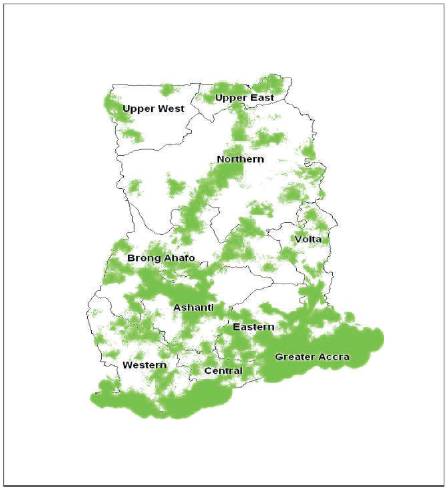
Figure 1. Regions marked green represent areas of coverage nationwide. (MTN, Ghana 2012)
But with the takeover by Vodafone Ghana of both mobile and fixed phone networks in the last quarter of 2008 saw another powerful launch of the network.
With a 3G network, Vodafone prides itself on the 10 reasons why you should choose the brand;
Trusted brand, Superior network quality, Double bonus, Free weekends, Value bundles, Internet everywhere, Roaming, Loyalty rewards, Amazing call rates, Hassle-free switching.
Some strategies have been adopted by Vodafone to lure more customers and retain existing ones; these include the ―Cool Chop Promotion. A three bedroom house from Lakeside Estates is up for grabs in the 90-day promotion as well as three fully serviced plots of land, a brand new Hyundai Santa Fe and over GHC 1 million worth of other prizes. By texting ‗WIN' to 4141, over 10,000 customers will be rewarded in the 90 day promotion. Over 90 days, the highest texters will be rewarded daily, weekly and monthly, with prizes ranging from airtime, smartphones and tablets, thousands of Ghana cedis, 40 LED TVs, serviced plots of land, a car, culminating in the grand prize.
2.2.3 The Case of Tigo
Millicom Ghana was the first cellular network to start its operation in Ghana as a private investor under the brand name Mobitel. It came into being right after the deregulation. It started its operation with the analogue mobile system but was not innovative on the market until Spacefon now MTN came onto the market with the GSM technology. This shifted their taste from Mobitel to the then Spacefon network. Mobitel then grew to become Buzz mobile telecommunication and now Tigo.
With their vigorous advertisement on the air waves over the years has seen them with the slogan ―express yourself with promotions to encourage their old subscribers to come back onto the network. Still in pursuance of more customers, Tigo runs a service aimed at bringing more users, the ―Free Bonto service. With Tigo Free Bonto, customers can do a lot with just a little, customers get double or triple bonus anytime they top up Tigo credit, bonus credit can be used to call or text any network in Ghana, make international calls and browse the internet.
Tigo has a 3.5G network with great service plans which includes, Tigo Postpaid, Tigo Prepaid, Tigo Cash, Tigo Phones, Tigo Scratch Cards, International Roaming, Tigo Credit Transfer and MyControl.
2.2.4 The Case of Airtel
A complicated network was introduced into Ghana during the last quarter of the year 2008 with so much media attention. It was a takeover from the then Westel communication by Zain. They were the first to launch some unique products like a 3.5G network that carried one of the very fastest internet connectivity and video calling.
Their only limitation was their coverage area as the network was only limited to the capital city Accra, Tema and Kumasi.
Now a 3.75G network, it has unique services and a broader nationwide coverage.
Smart Zone, Family and Friends, Free Night Calls, Me2u, Web2SMS, CallerTunes, Voicemail, Call Barring, Call Forwarding, Call line ID, Call Waiting, Conference Call, International Dailing, Loyalty Programs, Move to Airtel, SMS, Airtel Money, are just but a few services rendered by Airtel.
Airtel, came up with a promotion dubbed, ―Airtel Deedew Promotion, by simply making calls, SMS or browse the internet, top up using scratch cards, airtel money or electronic transfer, acquiring a new SIM or airtel bundled Samsung phone, users build up points, customers with the highest built up points for daily, weekly and monthly points win. Customers stand the chance of winning; a Honda CRV car, Two Honda City Saloon Cars, GHC5000 and GHC2000 cash, all expense paid trips to the UK to watch an Arsenal Game, Samsung handsets and devices such as the S3, Tab 10.1 and Galaxy Pocket, plus other amazing prizes.
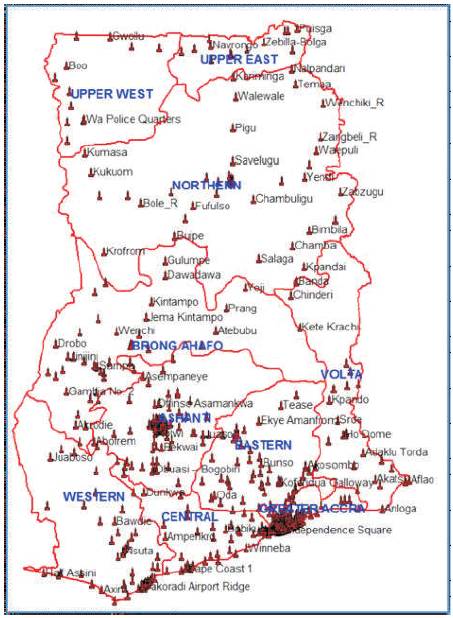
Figure 2. Nationwide coverage of Airtel. (Airtelghana 2012).
2.2.5 The Case of Expresso
Expresso has been in existence since 1995, operating under the name of Celltel; it was the second mobile operator in the country at the time. In 1998, Hutchison Telecom then acquired 80% of the company, improving the analogue infrastructure that was in place at that time.
In January 2003, the company was re-branded to Kasapa Telecom, the only locally branded telecoms operator in the country, with 9,000 subscribers.
Kasapa experienced significant growth and in September 2005, the company made a switch from an analogue network to a CDMA network to further strengthen its market position.
In July 2008, Expresso Telecom acquired 100% of the company. After the acquisition, the company has been working on many strategic initiatives and, more recently, an operational transformation project and network expansion programme has seen the company increase its coverage from 40% to nationwide coverage.
Following on from the network expansion and upgrade, in November 2010 the company successfully re-branded into Expresso, now providing unrivalled high-quality voice and data services to customers across various market segments.
Expresso offers a wide range of services ranging from, mobile internet, provision of handsets, using your handset abroad, and connecting people. Expresso operates high-speed networks over 3G and is building and extending networks across all their markets as they know that demand for internet and data access will increase. In addition it's supporting HSPA to meet this growing demand, to give customers a true mobile broadband experience.
In the last quarter of 2012, expresso launched an innovative service to keep existing customers and attract more users, the service gives subscribers the chance to enjoy up to 100% discount day and night on calls they make to other Expresso subscribers. For one to enjoy the free weekend calls, one must be an Expresso customer and expected to spend a minimum of GH¢ 1 on calls within the week.
2.2.6 The Case of Globacom
After fiercely contesting a bid to operate a cellular network in Ghana, Globacom come up with the license to operate in the country. Over two (2) years, they faced problems with the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) of Ghana in putting up cell sites across the length and breadth of the country until recently when they were cleared to erect radio masts in the country by EPA. Globacom trading under the brand name Glo is a powerful brand in its mother country, Nigeria and among the market leaders after they modernized the industry.
In July 2008, Glo was granted the Operating License to conduct business in Ghana, this saw the arrival of Glo1 sub-marine fiber optic cables in Ghana to start operations a year after. This submarine cable will link Ghana to the West African sub-region, to UK and the world as it promises a gargantuan Internet Bandwidth for its clients. April 2011 saw Glo1 officially commencing operations in Ghana.
Glo Mobile Ghana Limited launched a number reservation campaign to kick-start activities marking the launch of its commercial services in Ghana.
The campaign dubbed ‗Reserve Your Number' gives one million minus one (999,999) Ghanaians the chance to reserve their special 023-3 numbers on the Glo Mobile Network by texting their preferred number to the Glo SMS code 0230010100.
A new brand on the markets with services such as: Glo Biiiiig 5, Glo gista, and Good Day Ghana. High Speed Internet (HSI), Glo WAP, Caller Data Exchange, Glo Back-up and Magic Plus are some wide range Value Added Services (VAS).
2.3 Cellular/mobile Voice Market Share (December 2012)
The total cellular/mobile voice subscriber base in Ghana as at December 2012 stood at 25,618,427.
MTN had a marginal increase and maintained its position as the market leader with a subscriber base of 11,734,500 representing 46% of total market share.
Vodafone increased in subscriber base to 5,259,487 which represents 21% of total market share. Tigo had a marginal subscriber base increase, closing at 3,698,409 which represent 14% of the market while Airtel increased its subscriber base to 3,192,154 representing 12% of the total market share. GLO decreased its subscriber base; its current subscriber base of 1,568,014 represents 6% of the total market share.
Expresso though, decreased its subscriber base to 165,863.The 165,863 represents 1 % of the total market share. (NCA 2012)
2.4 Tariffs of Mobile Telephony Operators (prepaid) –(September, 2012)
All rates are quoted in Ghana Cedis and the billing rate is per minute (Table 1).
Please Note:
- ** MTN, Zain and Tigo have different SMS-IDD rates for various destinations.
- All the international destination rates are calls to Mobile Networks.
- All calls are charged per second except calls to international destinations on MTN and Vodafone.
- Calls to international destinations on MTN are charged in 5 second blocks.
- Calls to international destinations on Vodafone are charged per minute.
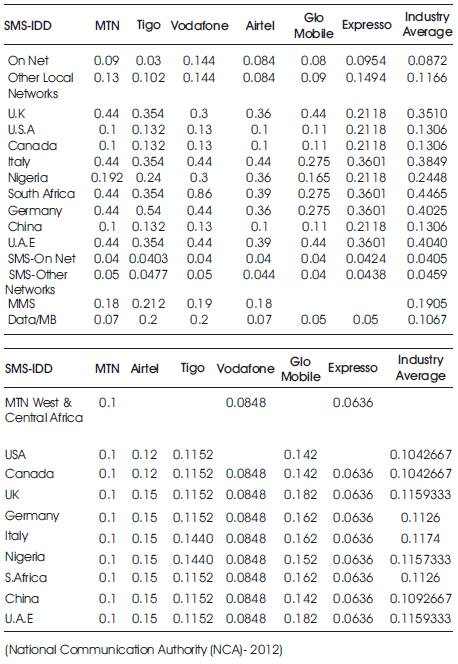
Table 1. Tariffs of mobile Telephony Operators (Prepaid)
3. Data Analysis and Interpretation
This section discusses the analysis of data collected. It made use of descriptive statistics and empirical finding of industry data collected from NCA Ghana and a field survey.
3.1 Age Distribution of Respondents
Age is an important variable in a socio-demographic analysis. It helps to ascertain whether age has any association or influence in a particular choice of network.
From Table 2, age of respondents ranged between 18yrs to 60yrs and above. Majority of respondents fell within the range of 18- 30yrs representing 50% of total respondents whereas 2% formed the minority of 60yrs and above.
3.2 Income Level of Respondents
Income plays a significant role in the choice and usage of a particular network, in that a subscriber must be able to patronize and afford the services and charges by these telecommunication network companies.
From Table 3, the income range 101 – 500 has the highest frequency of 46 respondents representing 49.5%.
3.3 Educational Status of Respondents
The knowledge for having value for money and a proper scrutiny of various telecom networks can be easily assessed for choice when one is educated; hence educational level is prone in analyzing a user's preference to a particular network.
From Table 4, tertiary recorded the highest with 64 followed by Secondary, JHS and Basic with frequencies 55, 26 and 6 respectively.
The Table 4 also showed that all the 150 respondents have a certain level of education.
3.4 Subscriber Base Of Respondents
Figure 3 below shows the subscriber base of respondents from the field survey to the various telecommunication networks in Ghana. Out of a total of 150 respondents, 68 users representing 45% were subscribed to MTN, 45 users of Vodafone representing 30%, Tigo users summed up to 16 representing 11% of total respondents. Airtel, Expresso and Glo pulled 14, 1, and 6 respectively representing 9%, 1% and 4% of total respondents.
3.5 Ranking The Factors That Influence The Choice Of A Network
Figure 4 demonstrates the ranking of factors perceived to be influencing user choice of network in the mobile telecommunication industry in Ghana. Out of the listed factors as: Low Voice Call/SMS Charges, Good and Quality Service, Family and Friends, Easy Internet Access, and Good Advertisement and Customer Centered Products, Family and Friends ranked the highest with 32%, Low Voice Call/SMS Charges followed with 30%, Good and Quality Service, Easy Internet Access and Good Advertisement and Customer Centered Product rated 20%, 11% and 7% respectively.
3.6 Tests For Association
The researcher seeks to find out whether there is an association between the age, education and income level in the selection of a service provider of all the 150 respondents. The chi-square test for association was used to measure the correlation or association between the three (3) variables, age, education and income level with network selection.
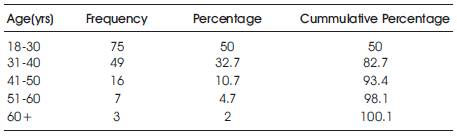
Table 2. Age distribution of respondents
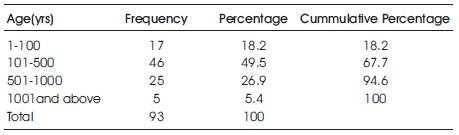
Table 3. Income Distribution of Respondents
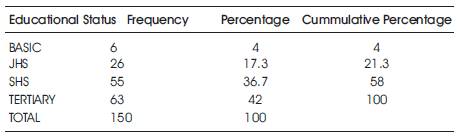
Table 4. Educational Distribution of Respondents
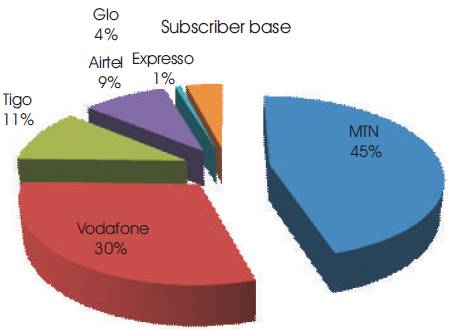
Figure 3. Subcriber base of respondents
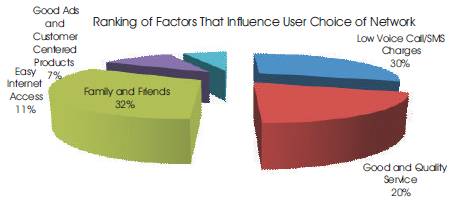
Figure 4. Ranking of Factors That Influence User Choice of Network
Hypothesis Statement
Ho: there exist no association between age, education and income level on the selection of a preferred network.
H1: there exist an association between age, education and income level on the selection of a preferred network.
3.6.1 Test for Association between Age and Network
Chi-square probability value, χ²= 0.3298, the level of significance is given as 0.05 in this study.
Since χ² value = 0.3298 >= 0.05, we fail to reject H0, therefore we conclude there is no association between age and choice of network (Table 5).
3.6.2 Test for Association between Educational Status and Network
- Chi-square probability value χ² = 0.0627, 1.the level of significance is given as 0.05 in this study.
- Since χ² value = 0.0627 > 0.05, we fail to reject H0, hence we conclude there is no association between educational status and network selection (Table 6).
3.6.3 Test for Association between Income level and Network
Chi-square probability value χ² = 0.0154, the level of significance is given as 0.05 in this study.
Since χ² value = 0.0154 < 0.05, we reject H0 in favor of H1and conclude there is an association between income level and the selection of a network (Table 7).
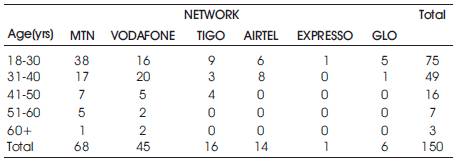
Table 5. Tabular Analysis of Age and Network
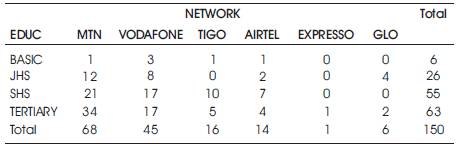
Table 6. Tabular Analysis of Educational status and Network
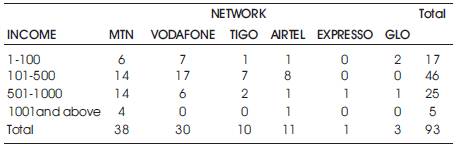
Table 7. Tabular Analysis of Income Level and Network
3.7 Satisfaction
This is a measure of how products and services supplied by a network provider meet or surpass customer expectation. A simple 'yes or no' question of whether users were satisfied with the products and services rendered by various telecommunication networks during survey provides the basis for this results. Figure 5 shows a maximum satisfaction towards users subscribed network.
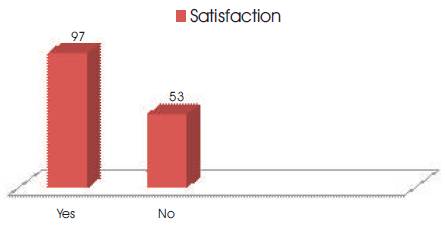
Figure 5. Satisfaction of users
Conclusion and Recommendation
Conclusion
This study analyzed the user preference in the mobile telecommunication industry in Ghana. The study used both primary and secondary data sources. The research examined the factors that influence users to opt for a service provider within the mobile telecommunication industry of Ghana and can only be concluded based on the various results from the analyzed data.
The current market structure shows that, the industry is experiencing an intense competition; this competition brings an immense difficulty in selecting a service provider for the first time since most of the industry players provide almost the same services and products.
Analysis of results showed a similar trend of subscriber base market share with the subscriber base in Ghana. Out of 150 respondent, MTN had 45%, Vodafone stood at 30%, followed by Tigo with 11%. Airtel, Expresso and Glo stood at 9%, 1% and 4% respectively. The findings also revealed that, from the shortlisted factors that influence users choice of network, Family and Friends was a major reason for network selection, whereas Low Voice/SMS Charges followed suit as a reason for choice of a network. Good and Quality service, Easy Internet Access and Good Advertisement and customer centered products were all reasons for user preference in the telecommunication industry.
The research revealed, there was no association between age, educational status and the selection of preferred network but rather a stronger correlation or association existed between the income level and the choice of network.
The research findings concluded that 35% of respondents were not satisfied with their service providers because of High Voice Call/SMS Charges of some telcos. Again respondents that subscribe to two or more service providers do so because of dissatisfaction.
Recommendation
It is recommended that, companies operating in the industry especially those with the greater market share must not relent on their effort but rather find innovative ways of providing services that will meet the demands of customers in order to keep their market share.
It is also recommended that service providers, especially MTN should make it charges a little affordable in order to maintain its customers. Further improvement in the speed of network access is also suggested to all service providers.
It is further recommended to the network users to fully scrutinize the product and services, find value for money and seek good and quality services from network providers.