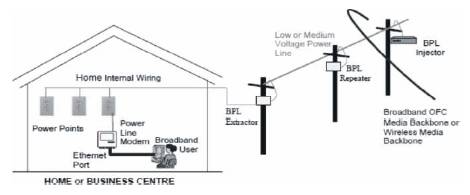
Figure1. Architecture of Broadband over Power line Technology
Broadband over power line technology provides high speed broadband Internet access over conventional electrical power lines. Broadband over power line is a recently commercialized technology that allows broadband Internet (using Internet Protocol - IP) to be communicated over the power grid at speeds ranging from 4Mbps to 145Mbps for delivery of data traffic and applications to homes and businesses on a shared basis. It is gaining attention due to ease of deployment, cost effectiveness and high speed reliable services. BPL is already deployed in many countries like U.S, Africa, Europe and Middle East. In India, IIIT Allahabad has undertaken a project in collaboration with Corinex Communications Canada to implement a prototype of BPL for University campus and nearby villages. This paper shows the critical analysis of Broadband over power line technology deployment in Indian context.
Broadband over power line is a technology to provide broadband digital data transmission over the public electric power distribution system. It provides high speed data transmission over long distances. The term Broadband refers to a telecommunications signal or device of higher bandwidth than another standard or signal or device. In telecommunications, a broadband signaling method handles a relatively wide range (or band) of frequencies. The broader the bandwidth of a channel, the more the information-carrying capacity, for the same channel quality.
This technology offers high speed internet access to customer premises through the commonly accessible electrical paths, thus eliminating the need of transmission of data over last mile through copper cable, short haul satellite systems, optical fiber cable and wireless technologies. Broadband over power line technology combines the principles of Radio Communication, Wireless modems and networking. We can get high speed Internet access by using one plug in device. This technology is economically advantageous as it eliminates the need of separate infrastructure for Internet access. Electrical grid is everywhere available and even the remote areas can be provided with the privilege of Internet access.
The architecture of Broadband over power line technology is shown in Figure1 [1].The Broadband over power line technology uses Power line communication to provide Internet access. The BPL signals are injected on low or medium voltage power line. A BPL signal will propagate along a power line for 1,000 to 3,000 feet before it becomes attenuated or distorted to be useful. To overcome the problems of attenuation and distortion, repeaters can be used. Repeaters will provide enough gain to signals and also remove the noise in order to provide clean signal. After the transfer of signal, Customer Premise Equipment (CPE) extracts the data signals from the lines for its connectivity to computers or any other IP enabled electronic devices. The user has to use the modem and connect it to the computer. In-House BPL uses indoor adapters to transmit the signals over existing interior electric wires and to connect the data signals to various appliances.

Figure1. Architecture of Broadband over Power line Technology
The BPL injector injects the IP data as an RF signal into the overhead or underground power lines using ferrite cores. The RF signal is typically injected at the medium voltage substation, bypasses low voltage transformers and is delivered to the end-users' electricity sockets in their premises. Figure 2 shows how the BPL injector converts the IP data traffic into an RF signal in a signal cable [2]. The signal is then injected into the Medium Voltage or Low Voltage cable by induction using ferrite cores. This is known as “inductive coupling” and can be done without switching off power. An alternative injection technique, known as “conductive coupling” connects the signal cable directly to the electricity cables but requires the power to be switched off during connection for safety reasons.
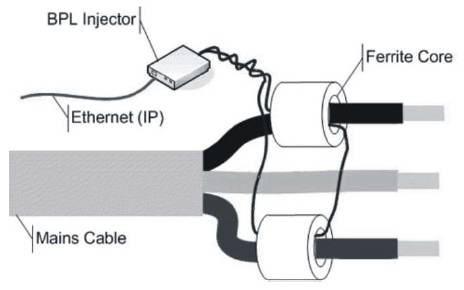
Figure 2. Inductive Coupling Injection Technique
The BPL modem converts the RF signal back into IP data and vice versa. The end-user connects the BPL modem into a computer, server, switch, or wireless access point. BPL modems use silicon chipsets which are specially designed to extract the data from power line. Using specially developed modulation techniques and adaptive algorithms, BPL modems are capable of handling power line noise on a wide spectrum. A BPL modem is plug and play and is approximately the size of a common power adapter. It plugs into a common wall socket, and an Ethernet cable running to the computer finishes the connection. Wireless versions are also possible. Figure 3 shows the BPL modem [3].
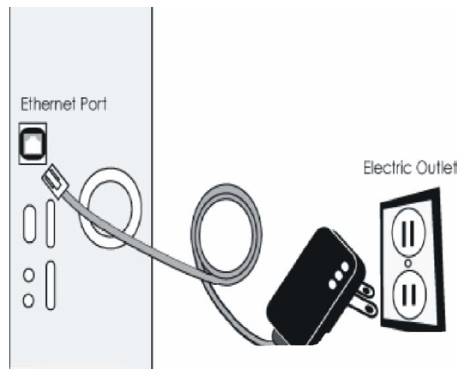
Figure 3. BPL Modem
In telecommunications and computer networks, multiplexing is a method by which multiple analog signals or digital data streams are combined into one signal over a shared channel. The multiplexing is used to share the expensive resourse. Figure 4 shows the Comparison of OFDM with Conventional multicarrier.
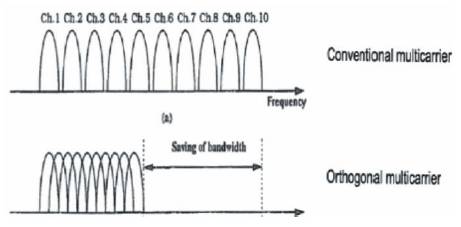
Figure 4. Comparison of OFDM with Conventional multicarrier
BPL technology can use Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) to distribute the BPL signal over a wide bandwidth using many narrowband sub-carriers. At the BPL injector, data from the Internet backbone is converted into the OFDM signal format and is then coupled onto one phase of the power line. In order to minimize contention for the channel, Carrier Sense Multiple Access (CSMA) is used with Collision Avoidance (CA) extensions. The BPL signal may be sufficiently tolerant of co-channel BPL interference to enable implementation of two or three of these systems independently on adjacent power lines. If one wishes to use Wi-Fi at home, the architecture extracts data signal with CPE and then converts it into an IEEE 802.11b Wi-Fi signal for a wireless interface in the home network [4].
This system uses different radio frequency bands to separate upstream and downstream BPL signals, and to minimize co-channel interference with other nearby access BPL devices.
Voice Over Internet Protocol (VOIP) can be set up using BPL. So, the home telephone system can run through Internet provided by BPL.
High speed and inexpensive Internet connections can be made available in remote areas using BPL.
With the use of BPL, world wide television services can be made available to remote user.
BPL combined with security cameras is one of the most contemporary and useful initiatives, in that it easily permits security and widespread access to visual security components.
BPL Technology is easy to deploy as there is need of additional infrastructure for deployment and installation.
The technology is economical compared to other technologies if the number of consumers per transformer is sufficiently large and contacts on power lines are thoroughly coupled.
The various opportunities provided by this technology are as follows:
The above opportunities will result into conservation of energy. Thus service providers will also be benefitted.
This technology is secured as its QoS (Quality of Services) mechanism offers different bandwidth latency and different traffic flows to different users. It is difficult to intrude the signal as the data is modulated using QAM or QPSK and multiplexed using OFDM. The signal value is dependent on Signal to Noise Ratio which changes dynamically in real time. This will make the communication more secured [4].
The quality of wiring is a huge problem in India as said by Mr. Subodh Vardhan, Director-Sales and Country Head for Government & Public Safety, Motorola India. The infrastructure is installed in much unorganized manner.
Power companies have readymade Infrastructure and that is why they will be most benefitted. So, there are some monetary issues between power companies and Internet service providers.
On the technology side, India have several residences which are served from a single Low Voltage (LV) cable line operating at 230–400V. This can cause problems such as radiated interference it is confined to the immediate vicinity of the BPL wire and is governed primarily by two parameters-signal power and electrical balance of system excitation. These factors are a cause for high concern in India due to the non-uniform and disorganized nature of the power supply network. Further, typical latency is below 3 ms. The latency is dependent on traffic load and number of users, so this number may increase if the network is highly loaded which may affect VoIP applications.
BPL system is expected to operate at the frequencies of 10 MHz – 30 MHz. The power line are unshielded, they will work as antennas. There will be an interference with short wave radio frequencies.
The design issues of repeaters, amplifiers and filters will be of major concern.
Broadband over power line can be considered as a technology to enhance the broadband penetration in India. It is a cost effective technology with ease of installation. It eliminates the requirement of separate infrastructure for different services. Quality of electrical grid supply is a major concern as far as the remote and rural areas are concerned. Once deployed, BPL will provide a cost effective solution for multiple services like electricity, Internet and VOIP services. Collaboration between Internet Service Providers and power companies are inevitable for the deployment of this technology. There are many challenges in the deployment like quality of cables, design issues, non uniform nature of electrical power supply network etc. So, initially it should be installed partially in selected areas. After successful deployment and execution, BPL should be deployed in other areas to enhance the quality and penetration of power line, Internet and telephony services. Broadband over Power line technology is already on the panorama with commercial products readily available. Green Energy technologies like Solar, Wind etc. may be used as Power Line solutions in remote areas.