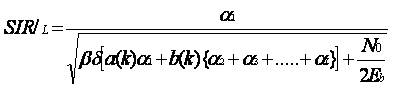
Continuation of an active call is one of the most important quality measures in cellular communication systems. Handoff process in the cellular system enables to provide such facility by transferring an active call from one cell to another cell. Signals transmitted over a multipath propagation channel can exhibits inter path interference and fading. To overcome the multipath effect, Rake receiver is used in CDMA technology. An important characteristic of a multipath channel is the time delay spread it causes to the received signal. This delay spread equals the time delay between the arrival of the first received signal component (LOS or multipath) and the last received signal component associated with a single transmitted pulse. Another characteristic of the multipath channel is its time-varying nature. Rake receiver is realized between the main path component and the local recovery carrier. In this paper the downlink performance parameters are estimated for a CDMA mobile system at the vertex of multiple adjacent cells. At the base station the received signal is coherently dispread and demodulated using a rake receiver. The effects of power control, error correction and rake receiver were also investigated and simulated based on the assumption that the received signals undergo Rayleigh fading.
In wireless communication systems, fading is one of the major problems that cause the signal fluctuation so it cause the signal degradation at the receiver. One of the wireless communication types that experiences fading is CDMA[1,2]. The per formance of the wireless communication is greatly affected by Multipath fading. It can be exploited by using Rake type of receiver. Path loss is caused by dissipation of the power radiated by the transmitter as well as effects of the propagation channel. Path loss models generally assume that path loss is the same at a given transmit-receive distance. The RAKE reception is a technique which uses several baseband correlators called fingers to individually process multi-path signal components
Another problem that CDMA suffers is signal interference from other users because all users in CDMA system use the same frequency. Interference usually refers to the interaction of waves that are correlated or coherent with each other, either because they come from the same source or because they have the same or nearly the same frequency. Diversity is the technic used to mitigate fading. Diversity can improve the quality of the received signal at the receiver. To combat other users' interference, power control is used to improve the CDMA system performance because power control can minimize the interference between users. In fading channel the Signal-to- Interference Ratio (SIR) varies according to the channel's response. The superposition of the multipath signals can be realized by the rake receiver which increase the output signal-to-noise ratio and also increase the power efficiency
The CDMA power control mechanism can be used to make the signal-to-interference ratio(SIR) nearly constant[3].The downlink performance of a CDMA system employs both open loop and closed loop power control. The open loop power control is performed at the mobile station based on the measurement of the downlink signals and it can compensate for the near far distance problem[5]. The closed loop power control is performed at the base station based on measurements of the SIR experienced at the base station and requires the information to be fed back from the base station to the
mobile station. Shadowing is caused by obstacles between the transmitter and receiver that attenuate signal power through absorption, reflection, scattering, and diffraction. When the attenuation is very strong, the signal is blocked. a radio signal transmitted from a fixed source will encounter multiple objects in the environment that produce reflected, diffracted, or scattered copies of the transmitted signa[4]. These additional copies of the transmitted signal, called multipath signal components, can be attenuated in power, delayed in transmitted signal are summed together at the receiver, which often produces distortion in the received signal relative to the transmitted signal.
CDMA is a method in which users occupy the same time and frequency allocations, and are channelized by unique assigned codes[11]. The signals are separated at the receiver by using a correlator that accepts only signal energy from the desired channel. Undesired signals contribute only to noise. The frequency of the transmitted signal is then made to vary according to a defined pattern (code), so it can be intercepted only by a receiver whose frequency response is programmed with the same code, so it follows exactly along with the transmitter frequency. CDMA networks use a scheme called soft handoff, which minimizes signal breakup as a handset passes from one cell to another. The combination of digital and spreadspectrum modes supports several times as many signals per unit bandwidth as analog modes.
In this paper, the section1 deals with the CDMA system and the problems associated with the system. Section 2 deals with the system model with power control and the probability of error in CDMA systems. The section 3 deals with the proposed method with Distributed balancing Algorithm. The section 4 deals with error control in t E system. The section 5 deals with the results and comparison of the system.
The quality of the radio reception is estimated at the junction of the multiple adjacent cells. If we consider many adjacent cells, for the first cell all the other cells are consider as interference to each other.
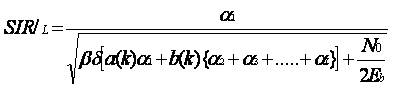
Figure1 shows the system with multiple adjacent cells with The SIR at the junction of L-adjacent cells is given by, Where a(k) represents the self-interference from the desired BS. This comprises of unwanted multipath components of the desired user's signal and the interference from signals intended for other users in the same cell. b(k) represents the interference from users in the other cells. 1/2No is the spectral density of the double sided additive white Gaussian noise (AWGN). Eb is the energy per bit. α1 is the signal strength received from BS I, is the signal strength received from BS II, etc. It is assumed that ,α2 α3 , ... L are each Rayleigh distributed, and the means of the Rayleigh distributions are assumed to be log-normally distributed. β is the voice activity factor. δ represents the interference reduction factor if power control is used.
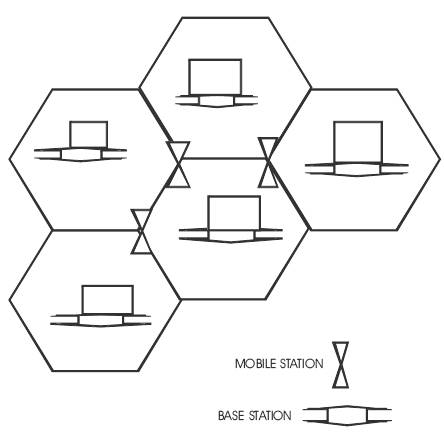
Figure 1. Multiple adjacent cells
Power control is an essential method in CDMA Communication systems. The quality of service for the mobile users are guaranteed with lowest optimum transmission powers[6,8]. The users benefit from minimum interference and good signal qualities. In this paper the closed loop power control used which is used to keep the received signal power at a specific threshold value.
In communication system, the BER may be affected by noise, interference, distortion, attenuation, multipath fading, etc[9].The momentary bit-error rate can be approximated as:
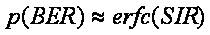
where the complementary error function erfc(x) is the probability that a normally distributed random variable will be x or more standard deviations from its mean. The expression for the momentary BER reduces to,
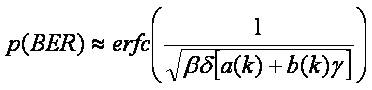
In order to determine the actual probability of error, the probability density function of γ; i.e., pdf(γ)must be determined using the Laplace transforms and then evaluating α1 terms using Mellin convolution. Thus, pdf of the signal strength received from BS A, i.e., pdf of α1 , is given by
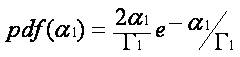
Where is the mean-square value of α1 , which again is assumed to be log-normally distributed. Often, the ratios of the mean-square values of the Rayleigh variables are preferred ie,
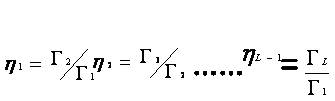 to study
to study
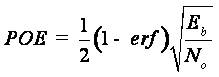
the relative signal strength variation as a consequence of adjacent cells influence. The mobile-to base station is viewed as separate subspace[7] expressed by,
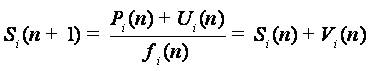
Where
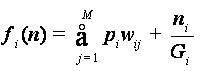 and
and is
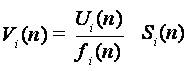 defined to be
defined to be
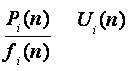 is the input to each subsystem. The aim is to make each Si(n)to track the threshold value. The Bit Error probability(BEP) at a receiver is monotonically decreasing function.
is the input to each subsystem. The aim is to make each Si(n)to track the threshold value. The Bit Error probability(BEP) at a receiver is monotonically decreasing function.
The BEP in an additive channel is given by,
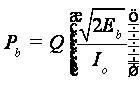
The Rake receiver can coherently combine L paths using Maximal Ratio Combining (MRC).
In the proposed method, the analysis of seven cells are considered in the CDMA system. Fading is one of the main problem which can cause signal degradation at the receiver. To reduce fading we can use the diversity technics. To evaluate the performance of a system we consider the parameters such as average bit error rate, service reliability, link availability, and power control. Bit error rate, power control, error control are used to reduce interference between users. Rake receiver is used to eliminate the fading effects in the system.
Service reliability is defined as the percentage of time the momentary BER is below a maximum desired BER[12]. If the BER is minimum then we can get the reliable service between the mobile station and the base station. Similarly link availability is defined as the percentage of locations that the average BER is below the maximum BER. It is the measure of available link from the number of mobile stations to the base station.
An effective power control scheme where a power increase command is sent to all users before a new high data rate packet is transmitted, could improve the quality of signal as well as the distribution of signals to mobile users within BS coverage[13]. A way to solve the near-far problems such that all the mobiles' transmitting powers are equally-received by the Base station. The power control is used to solve the near-far problem.
For the near-end mobile, it can be asked to transmit lower power
For the far-end mobile, it can be asked to increase transmit power
All mobiles are power controlled to the minimum power so as to maintain the link.
The power can be controlled by using many power control algorithms. An effective power control scheme where a power increase command is sent to all users before a new high data rate packet is transmitted could improve the quality of signal as well as the distribution of signals to mobile users within BS coverage.
When a mobile moves from one cell to another ,it can establish connection to the new cell before the connection to the old cell is terminated. In order to avoid having very small transmitted powers for mobiles close to the base, mobiles whose distance is less than a certain threshold value, the same transmitted power is allowed.
In the proposed method, Distributed Balancing Algorithm is proposed and simulated. Distributed Balancing Algorithm is a closed loop power control algorithm in which feedback from the mobile is used to adjust the transmitted power of the base station [14]. In this power control scheme, the base station updates its transmitted power for the mobile based on the average SIR received at the mobile, and the updates usually occur in multiple steps.
The mobile stations measure the observed value of the SIR over time and compare it with a pre-determined threshold value.
If the observed SIR is larger than the threshold, then the mobile sends a power down command to the base station. Otherwise, it sends a power up command.
The base station interprets the power control command from each of its mobile stations and updates the transmitted power accordingly.
The power control updates usually take place in Multiple size steps.
In effective power control scheme, a power increase command is send to all the users before a high data rate packet is transmitted.
BER is a performance measurement that specifies the number of bit corrupted or destroyed as they are transmitted from its source to its destination. Several factors that affect BER include bandwidth, SNR, transmission speed and transmission medium.
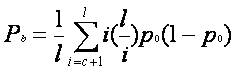
If the data is to be transmitted at a particular rate then as error correcting codes are added to the data the bandwidth occupied by the composite code increases[15]. If only a limited bandwidth is available for transmission, then the processing gain has to be reduced to compensate for the greater bandwidth of the baseband signal. SNR is defined as the ratio of a signal power to noise power and it is normally expressed in decibel (dB).
BER can also be defined in terms of the probability of error (POE) and is given by,
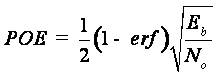
where erf is the error function, E is the energy in one bit and b No is the noise power spectral density. The term noise is the superimposed or added to the signal where it will limit the receiver ability to make correct symbol decisions and limit the rate of information.
The channel is randomly varying in time meaning each transmitted symbol gets multiplied by a randomly varying complex number the real and imaginary parts are Gaussian distributed having mean 0 and variance ½[16].
In AWGN, the probability of error for transmission of either +1 or -1 is computed by integrating the tail of the Gaussian probability density function for a given value of bit energy to noise ratio .The theoretical Bit error rate for BPSK modulation scheme over AWGN channel is given by,
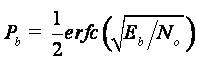
Where Eb is the energy per bit and No is the noise power spectral density.
One way to lower the spectral noise density is to reduce the bandwidth, but we are limited by the bandwidth required to transmit the desired bit rate
(Nyquist criteria) [10]. We can also increase the energy per bit by using higher power transmission, but interference with other systems can limit that option. A lower bit rate increases the energy per bit, but we lose capacity. Ultimately, optimizing Eb /No is a balancing act among these factor.
The Table 1 shows the simulation parameters used to simulate the CDMA system for better performance. The software used to simulate the CDMA system is Matlab7.6.
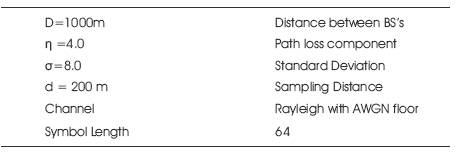
Table 1. Simulation Parameters
The power control for the system can be simulated for about 90 mobile users and the system consists of seven cells is considered. The power control is based on the Distributed Balancing Algorithm. The simulation result is plotted between the number of mobiles and outage probability of the mobiles. The outage probability is the probability of the mobiles that are out of the threshold value.
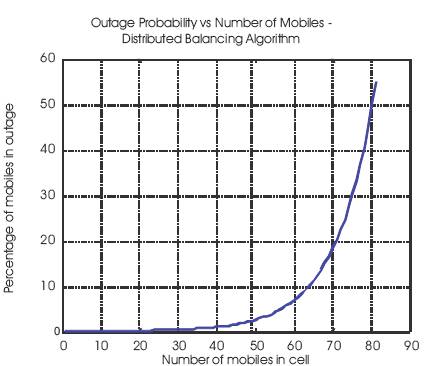
Figure 2. Distributed Balancing Algorithm
Figure 2 is the proposed plot for the Distributed Balancing Algorithm and it is plotted between the number of mobiles and the outage probability. For this the outage probability increases only from 20 to 30 mobiles. For this algorithm the number of mobiles in outage probability decreases and optimized power is given to all the users in the cell.
Similarly the probability of bit error is often the figure of merit for a error-control code. Figure 3 is the plot between BER and SNR.We want to keep BER number small, typically less than 10-4 . Bit error rate is a useful indicator of system performance on an independent error channel, but it has little meaning on bursty, or dependent error channels. If transmit power is fixed, the energy per bit can be increased by lowering the bit rate. Thus, the reason why lower bit rates are considered more robust.
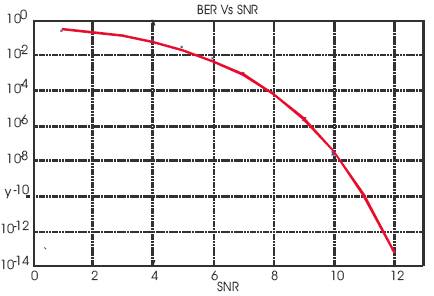
Figure 3. BER Vs SNR
The system model has been tested for BPSK modulation with an AWGN and Rayleigh fading channels. The simulation graph in figure4 shows that the AWGN channel gives better performance than the Rayleigh Channel for the transmission of signals. In AWGN channel BER of 0.001is achieved for 7db whereas in the Rayleigh channel BER of 0.01 is achieved for the same 7db. It is easy to understand that, in the analysis of the performance of a communication system, AWGN is always used to give an upper bound performance ,because the AWGN condition is the simplest case in wireless communication environment.
In this proposed method the Distributed balancing algorithm is simulated for 90 mobile nodes in the cell and the outage probability increases only from 20 to 30 mobiles. The probability of Bit Error Rate(BER) is effectively reduces by comparing the Signal-to-Noise Ratio(SNR) from multiple cells. The system with AWGN channel and Rayleigh channel is also compared. Thus, this system needs to be improved to simulate more number of users so that the performance of multiple access in CDMA can be studied more dynamically.
Based on the above analysis, the system can be implemented by using modified RAKE receiver. The downlink performance can be implemented for a CDMA mobile system at the vertex of multiple adjacent cells by increasing the number of cells. The performance of the above system can also be increased by the combined use of power control and error correction scheme.