Figure 1. Cloud computing
Cloud computing refers to a network that distributes processing power, applications, and large systems among many computers. Cloud computing seems to offer some incredible benefits for communicators: the availability of an incredible array of software applications, access to lightning-quick processing power, unlimited storage, and the ability to easily share and process information. All of this is available through the browser any time it can access the Internet. While this might all appear enticing, there remain issues of reliability, portability, privacy, and security, since the data transmission on the internet or over any networks are vulnerable to the hackers attack. The authors are in great need of encrypting the data. This paper combines the techniques of cloud data storage and content Distribution by dynamic broadcast encryption algorithm along with the Bit Torrent application which results in minimizing the difficulties of bulky data and aims in resulting efficient sharing of the secure storage services in cloud computing.
Cloud computing is a subscription-based service where one can obtain networked storage space and computer resources .Cloud computing is the long dreamed vision of computing as a utility, where data owners can remotely store their data in the cloud to enjoy on-demand highquality applications and services from a shared pool of configurable computing resources. Cloud computing is about moving services, computation and/or data—for cost and business advantage—off-site to an internal or external, location-transparent, centralized facility or contractor.
By making data available in the cloud, it can be more easily and ubiquitously accessed, often at much lower cost, increasing its value by enabling opportunities for enhanced collaboration, integration, and analysis on a shared common platform. Considering the installation of network infrastructure a cloud environment can be broadly categorized into three types- public cloud, private cloud and hybrid cloud. Though from operation and maintenance point-of-view cloud computing is a great cost-effective IT solution for business of any magnitude, it has at least two major concerns-technical developments, security and privacy. Since cloud computing is relatively a new technology in comparison to other existing computing solutions, it still has lots of scope of becoming a mature system as a reliable and cost-effective computing technology, where downloading a file provide content to other clients interested in the same file. Figure 1 of Cloud Computing.
The users require that their data remain secure and they need to have a strong assurance from the cloud servers to store their data correctly without tampering or partially deleting because the internal operation details of service providers may not be known to the cloud users. In this paper, an efficient and secure scheme for cloud data storage has to be in a position to ensure the data integrity and confidentiality. From the perspective of data security, which has always been an important aspect of quality of service, Cloud Computing inevitably poses new challengingsecurity threats for number of reasons.Considering various kinds of data for each user stored in the cloud and the demand of long term continuous assurance of their data safety, the problem of verifying correctness of data storage in the cloud becomes even more challenging.

Figure 1. Cloud computing
The main goal is to provide security and reduce the bulky data for the user data application in the cloud.
Cloud storage (Figure 2) is a model of networked enterprise storage where data is stored in virtualized pools of storage which are generally hosted by third parties. Hosting companies operate large data centers, and people who require their data to be hosted buy or lease storage capacity from them. The data center operators, in the background, virtualize the resources according to the requirements of the customer and expose them as storage pools, which the customers can themselves use to store files or data objects. Physically, the resource may span across multiple servers and multiple locations. The safety of the files depends upon the hosting companies, and on the applications that leverage the cloud storage.
Figure 2. Cloud Storage
A cloud provider provides two cloud-based services: storage and content delivery. A content provider utilizes these two services to store and distribute her content to multiple subscribers. The content provider and subscribers can access content via a cloud-based application service, which reads and manages the content stored in the storage service via cloud storage APIs. The application service is an application deployed in the cloud by the content provider or a third party. The content provider can use multiple cloud-based services from different cloud service providers to host her application service, content storage service, and content delivery service. The problem is identified in the systems with a Minimum distributed peer-to- peer systems. To achieve an MDT objective for a group of client requires judicious use of client uplink and downlink capacities, which are typically highly asymmetric as offered to their clients and download speeds that are significantly larger than upload speeds. In this paper we investigate the potential benefit from the on- demand deployment of cloud resources to upload capacity, we propose the use of Bit Torrent in receiving the entire content[6]. The major aspects of Content distribution are,
A BitTorrent client is a computer program that manages downloads and uploads using the Bit Torrent protocol. Bit Torrent is for distributing large amounts of data over the Internet. Bit Torrent is one of the most common protocols for transferring large files and it has been estimated that networks collectively have accounted for roughly 43% to 70% of all Internet Traffic[2]. The Bit Torrent protocol can be used to reduce the server and network impact of distributing large files. Rather than downloading a file from a single source server, the Bit Torrent protocol allows users to join a file of hosts to download and upload from each other simultaneously.
Broadcast Encryption (BE) schemes enable the sender of a message to specify a subset of the registered (the target set or privileged set), who will be able to decrypt the ciphertext sent to all users via a broadcast channel. The complement of the target set (in the set of the registered users) is called the revoked set[3]. To accomplish user revocation when sending a message, a BE generally generates three parts: the ID Header, that is a bit-string that unambiguously identifies the target set/revoked set; the Key Header, that encapsulates a session key for the privileged users; and the Message Body, that contains the payload encrypted under the session key.
Broadcast encryption is the cryptographic problem of delivering encrypted content (e.g. TV programs or data on DVDs) over a broadcast channel in such a way that only qualified users can decrypt the content. The challenge arises from the requirement that the set of qualified users can change in each broadcast emission, and therefore revocation of individual users or user groups should be possible using broadcast transmissions, only, and without affecting any remaining users. 26
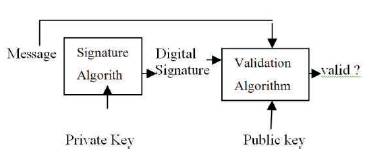
Figure 3. Digital Signature
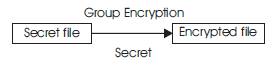
Figure 4. Group Signature
A Group Signature scheme GS = (GKg, GSig, GVf, Open) consists of four polynomial-time algorithms:
The overarching goal of this setting is to get minimizing the maximum time of bulk synchronous content distribution where it takes any client in a set to download content of the required file. In the paper, the authors have developed a formulation of Bit Torrent to split the content over the file, through the cloud resources. In future work the authors would use another content distribution algorithm by implementing RSA algorithm along with dynamic broadcast encryption algorithm to provide security in the cloud.