Figure 1. INP File Format
Water is a basic necessity for every human being and is used for various purposes like drinking, cleaning, sanitation, etc. This shows the fact that how important it is to make water available for residential locales, industries and other such commercial establishments. Designing is an important part in the construction of any major infrastructure. Supplying and availability of water is an integral part of construction now-a-days. With the advent of technology, the authors have now designed, analysed, studied and modified various types of pipes and pipe networks for complex and sophisticated conditions. EPANET is one such software which allows to carry out all such operations. The process gives us to explore a wide variety of choices quickly and in a short span of time. If any new buildings are constructed in future, the pipe lines are easily designed by using EPANET on trial and error process. The present analysis explains about the functioning and working of EPANET. The solution is robust, simple, and it proved to be useful and practical for the modeling as it is illustrated on the hydraulic models of DIET campus.
Water is a prime natural resource, a basic human need and a precious national asset. Water is necessary not only to the mankind, but also to the animal and plant world. Much of the ill health in the underdeveloped countries is largely due to lack of safe drinking water. There can be no state of positive community health and well bearing without safe water supply. Safe provision of safe community water supply is one of the most effective and permanent health technologies for improving the health of people. Universal access to drinking water is the right of every citizen. Water intended for human consumption should be not only be safe, but also wholesome. Safe water is the one that cannot harm the consumer, even when ingested over prolonged periods. Water may be safe, but it has an unpleasant taste or appearance, it derives the consumer to other less safe sources.
Safe and wholesome water is defined as water that is free from pathogenic agents, harmful chemical substances, pleasant and useful for domestic purposes. Water is an essential factor in the economic, social and cultural development of a community. Elimination of water borne diseases promotes the rural development and improves the quality of life.
Water distribution systems are designed to satisfy the water requirements for the following demands [8-11].
Generally in practice, there are four different systems of distribution. Depending upon their layout and direction of supply, they are classified as follows [8-11].
According to Zong Woo Geem’s study, there is a cost minimization model for the design of water distribution networks. The model uses a recently developed harmony search optimization algorithm for satisfying all the design constraints. The harmony search algorithm mimics a jazz improvisation process to find better design solutions, in this case pipe diameters a water distribution network. The model also interfaces a popular hydraulic simulator, EPANET to check the hydraulic constraints. If the design solution vector violates the hydraulic constraints, the amount of violation in the cost function is considered as a penalty. The model applied to five water distribution networks gives the designs that were either the same or cost of 0.28 - 10.26% which is less than those of the competitive meta-heuristic algorithms, such as the genetic algorithm, simulated annealing and tabu search under similar or less favorable conditions.
EPANET is a computer program that aids to model the water distribution piping systems. It is used for the installation of valves, tanks and pumps. It not only study the chlorine behavior, but also helps in the establishment of the secondary chlorination plants.
The EPA network performs external period simulation of the water motility and quality behavior within the network that is pressurized. The pipe network includes valves, pumps, nodes, reservoirs and pipes. EPANET detects the flow of the water in a pipe and also can calculate the pressure at each node. Further, it is used to know the height of the water in a reservoir and the concentration of chemicals in the water. It can also trace the chemical consumption of the water and the age of the water along with its source.
EPANET is designed as a research tool to know the constituents of the drinking water and with which the safety conformation is assured. Additionally, EPANET is used to assess the alternative management strategies to improve the quality of the water.
The EPANET software program runs on windows 95/98 operating system. The user friendly program facilitates, a conducible environment to edit data in the computer. EPANET is a binary file format, where the data can be imported and exported. These include color-coded network maps, data tables, contour plots and time series graphs.
Accurate hydraulic modeling plays a significant role for effective water quality modeling.
EPANET comprises the following capabilities [1, 3- 6].
Firstly, it is needed to describe the system operation and running analysis of the pipe network. Secondly, the properties of the objects that makeup the system to be edited. Network representation of the distribution system is to be drawn [1].
To analyze the network of the pipe line, the following input data is mandatory [1].
Pipes are the links that allows the water to flow from one point to other in the allowed network. EPANET assumes that the pipes are full at all times. The flow direction is from the end of the higher hydraulic head to lower head. The hydraulic input variable for pipes include roughness coefficient [1].
After the analysis, the output results of the pipe are,
These are the points in the network, where the links join together and at which, the water enters and leaves the network. The input data required for the junctions are [1],
After the analysis, the output results of the junctions are
The nodes where the volume of stored water that vary with time during a simulation is tank data. The primary input properties for tanks include [1].
The result obtained after computing is,
Tanks are required to be operated at their minimum and maximum levels. EPANET blocks the outflow of a tank at its minimum levels and also prevents the inflow at its maximum level.
The input file is given in the INP file format as shown in the Figure 1. Editing Junction properties is shown in Figure 2.
The hydraulic and water quantity activities can be analyzed after the detailed network description. For the analysis, specification of options is necessary like – how to run the analysis and trouble shoot the problems that occur during the analysis [7].
The hydraulic and water quantity analysis is possible by editing the junction property index box. Further, the node details are to be edited. Additionally, the pipe details like pipe diameter, co-efficient of roughness value of pipe, pipe length is required [1,2].
After editing the tank properties index box, it gives the following data and is shown in Figure 3.
After editing the pipe properties, the index box and the pipe details like roughness value, diameter of pipe, status of the pipe is known whether it is opened or closed, are changed Editing Pipe properties is shown in Figure 4.
If problems are encountered while running the hydraulic and water quality analysis, then the EPANET displays error and warning messages. The most common problems are [1,2].
EPANET displays, the 'network is disconnected' message, if there is no path for water provision to all the nodes that have demand. The situation takes place when there is no path between a junction with demand and a junction with negative demand. If the problem is occurred by a closed link, then the EPANET will still compute a hydraulic solution and detects to identify the problem link that doesn't exist, then the EPANET will display an error 110 message after the analysis. During external period simulation, the possibility of disconnection of nodes takes place as the links changes its status after certain time or prolonged periods.
This is a warning message displayed by EPANET, when it encounters negative pressures at the junctions that has positive demands. It indicates the design or operational problem. Negative pressure is possible whose portions of the network can only receive water that has been shut off.
At this junction, an additional warning message 'network disconnected' will also be issued by EPANET.
After the analysis, the results of the junctions and pipes are to be documented as shown in Table 1. The Junction output and Pipe output results are shown in Figures 5 and 6.


The input file is given as FINAL.NET. The output results are shown in Table 2.
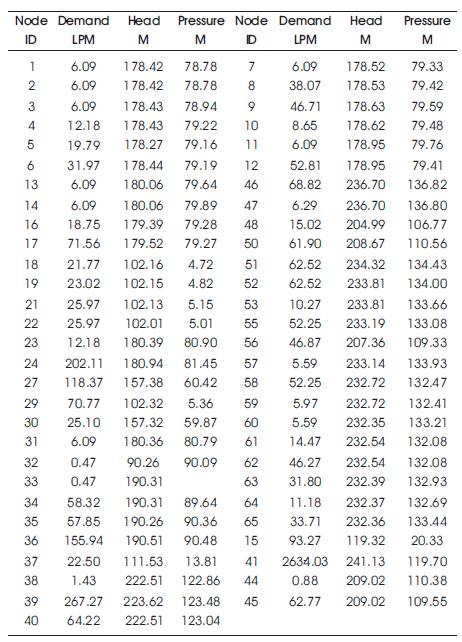
Table 1. Node Results
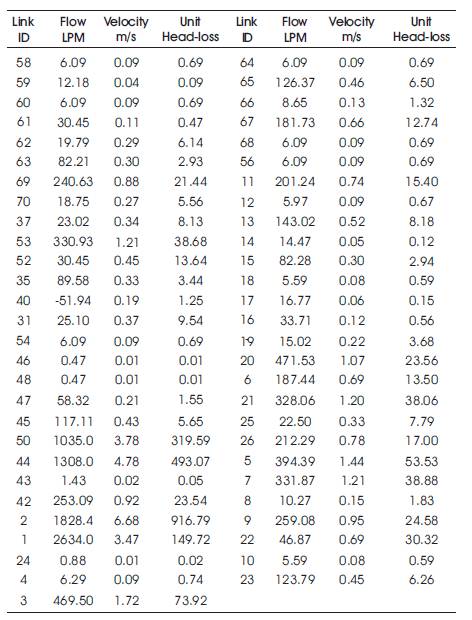
Table 2. Link Results
Proper supply of water is an important need during the construction of DIET, which is a wide campus imparting education to many students. The solution for modeling intermittent water supply is based on EPANET toolkit for hydraulic modeling. The solution is robust and simple and is proved to be useful and practical for the modeling as it is illustrated on the hydraulic model of DIET campus. Further, while constructing the new building in the future, pipelines can be designed by using EPANET. With this, the quantity of water supply can be designed in less time compared to manual designing. Thus, with the usage of innovate software like EPANET, and WASP, an improved and accurate designing of water distribution network can be modelled to meet the requirements.