Figure 1. Satellite Image of STP Based on Bio-Tower Technology In Kodra and Ponghat Plants
The Wastewater Treatment plants are designed and constructed with an aim to control wastewater so that it helps to reduce the quantity of pollutants, nutrients, biological organism, bacteria, etc. The study is based on continuous monitoring and collection of data for six months (July 2015 to December 2015) of two plants, Kodra and Ponghat plants in Allahabad city. Both the plants are based on Bio-Tower Technology, which is an improved or modified version of trickling filters. The research work presents the results of the evaluation carried out for the efficiency analysis of STP based on Improved Bio-Tower Technology located in Allahabad city for handling and treating the municipal wastewater.
Every community produces both solid and liquid wastes. The liquid portion is essentially the water supply of the community, which has been fouled after variety of uses. From the standpoint of sources of generation, wastewater may be defined as a combination of the liquid or water carried wastes removed from residences, institutions, commercial and industrial establishments together with such groundwater, surface water and storm water as may be present. If untreated wastewater is allowed to accumulate, the decomposition of the organic materials it contains can lead to the production of large quantities of malodorous gases. In addition, untreated wastewater usually contains numerous pathogenic, or disease causing microorganisms that dwell in the human intestinal tract or that may be present in certain industrial waste. Wastewater also contains toxic compounds. For these reasons, the immediate and nuisance-free removal of wastewater from its sources of generation, followed by treatment and disposal, is not only desirable but also necessary in an industrialized society. There are several methods of treating the domestic/municipal/industrial wastewater. Certain parameters, which are on a high side in raw wastewater needs to be reduced according to the pollution control board's norms by giving specific treatment. One of them is to supply the oxygen for removal of BOD (i.e.) Bio-chemical Oxygen Demand. This is achieved by different methods of Aeration like, surface aeration or diffused aeration, etc., that requires external power to drive the aeration mechanism. Natural air draught is a method used in Bio-Towers, where aeration is achieved without using an external power. The Trickling Filter with incorporation of plastic media now called as 'Bio- Tower' is now getting popular day-by-day as the same is extremely efficient, while it occupies lesser plot area, and requires a much less power. The principle of the Bio-Tower is very simple and logical. The Bio-Tower pertains to the attached growth type of treatment. On the Bio-Tower, the waste is fed from the top, the microorganisms within the wastewater gradually develops a colony over the surface of the plastic media, which provides stability and a high surface area. In this process, temperature within the Bio-Tower goes above the ambient temperature and the hot air within the Bio-Tower is released through the top (because it is light). Obviously to substantiate the air loss within Bio- Tower, fresh air rushes from the bottom of Bio-Tower and therefore, a cycle of air movement is formed, which satisfies air requirement of the Bio-Tower to a greater extent.
Thus, as stated above, there are several methods for removing BOD in respective units of the particular technology adopted for treating the wastewater, However, The detailed study / survey of the Bio-Tower with Forced Aeration for the removal of BOD in attached and the growth technology of the Bio-Tower/s with natural draft or forced aeration from bottom may be available but Bio-Tower with powerless forced aerators installed on top of tower is a new concept, which we have developed. By adopting Forced Aeration in the Bio-Tower Technology, limitations due to natural air draft will be removed and the plant will operate at a better performance without spending any amount on power for aeration within the Bio-tower. According to this invention, a Forced Aeration technique in the Bio-Tower Technology is introduced by providing a non-conventional and eco-friendly wind-operated air exhaust mechanism at the top of the Bio-Tower. Because of the normal wind speed, wind-operated air exhaust mechanism rotates and removes the air inside the Bio-Tower, allowing fresh air to enter from the bottom of the Bio-Tower. Thus, by introducing a wind operated air exhaust mechanism at the top, a forced aeration is achieved and oxygen from the fresh air supplied is used to remove the BOD. The above process is achieved by providing Cover and Forced Aeration through the wind operated air exhaust mechanism on the top of conventional Bio-Tower, which is operated by wind speed, thereby increasing the circulation of air and also resulting in improving the quality of effluents, which is better than the conventional Bio-Tower. No additional power is required for the movement of the air, as this is achieved by a wind operated air exhaust mechanism at the top.
The FAC Bio-Tower Technology is a modification of Trickling Filter Technology, which is used for the treatment of Industrial, Domestic / Municipal Wastes. The influent is fed on the top of the tower and with the help of media placed within the tower, microbiological growth is obtained, which helps in treating wastewater to an acceptable level of pollution. It improves the performance without significant increase in its cost and eliminates all the drawbacks of the system (Bhat Hemant Nagesh, 2004).
The main advantages of the Bio-Tower technology are as follows:-
The objective of this literature review is to examine the traditional works done in the field of the trickling filters, as we know that Bio-Tower is simply the high rate bio-trickling filter with a height of 10 to 12 m.
Constructed wetlands are specially designed systems, that use different types of plants, soils and microbes to treat wastewater, but the main drawback is that they require a large space (Vymazal, 2010). (Vucinic et al., 2012) compared the municipal sewage treatment in the constructed wetlands and trickling filters. The efficiency of the purification process was monitored over a period of three years and recommended implementation of the trickling filter for high contaminants removal rates.
In activated sludge process, a microbial is used for the removal of pollutants, but this system is only efficient in biological nitrogen and phosphorus removal (Gernaey et al., 2004). Anaerobic digestion system is a new technology for wastewater treatment. Although it is highly efficient in wastewater clarification, the main drawback is that they are expensive because a specially designed system would be required for it (Rajeshwari et al., 2000). Among these different biological treatment technologies, the attached growth process such as, TBF is assumed to be quite effective in the poorly developing areas of the world due to their low energy, space, maintenance requirements, ease of operation, resistance to toxins and shock loads. Moreover, due to their simple and reliable processing, effluents of high quality would be produced, if properly designed (Defilippi and Lewandowski, 1998).
Trickling filters are aerobic attached growth biological reactor used in the wastewater treatment (Van Rijn, et al., 2006, Skjolstrup et al., 1998). Trickling Bio- Filter is an emerging man-made Eco technology that gains popularity, since the early 1982s (Chunrong et al., 2005). It is recognized as a reliable technology, if properly designed for the treatment of wastewater from different sources, industrial, agricultural and swine wastewater and acid marine drainage, etc. (Szogi et al., 1997; Evangelho et al., 2000; Tanaka, 2002; Dermou et al., 2005; Wang et al., 2006).
The study area covers Sewage Treatment Plant (STP) based on the improved Bio-Tower Technology, situated on the north bank and the other on the right bank of river Ganga in North–west in Allahabad city. The Satellite image indicating the location of both the Plants is shown in Figure 1 and the Process Flow Diagram of Sewage Treatment Plant with improved Bio-Tower Technology installed at Kodra and Ponghat is given in Figure 2. The STP capacity of Ponghat and Kodra is 10 MLD and 25 MLD respectively. The plant was constructed by HNB Engineers Pvt. Ltd for U.P. Jal Board under Ganga pollution control unit and was commissioned before Kumbh Mela in the Year 2013. This research work evaluated the performance of the STP based on the improved Bio-Tower Technology in terms of wastewater characterization to derive a comparative account between the pollution load before and after the treatment processes, besides, discerning their efficiency.
The study carries out the parameters such as PH, BOD, COD and TSS of both the plants followed by the overall efficiencies and the results of Kodra and Ponghat plant are shown in Table 1 and Table 2 respectively.

Table 1. Performance Monitoring Data of Kodra Plant
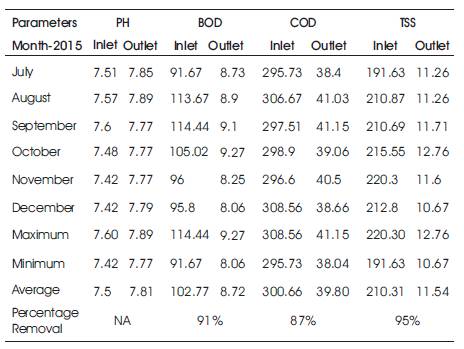
Table 2. Performance Monitoring Data of Ponghat Plant
The conclusions drawn from the study are as follows:
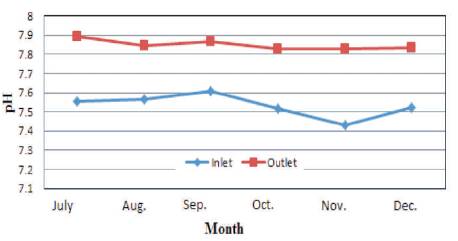
Figure 3. Variation of pH in Kodra Plant
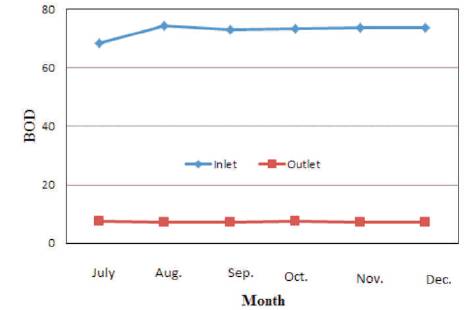
Figure 4. Variation of BOD in Kodra Plant
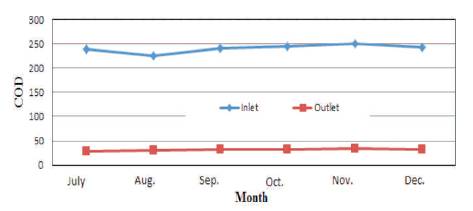
Figure 5. Variation of COD in Kodra Plant
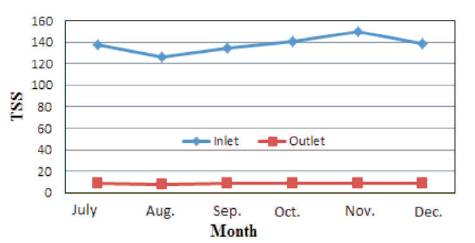
Figure 6. Variation of TSS in Kodra Plant
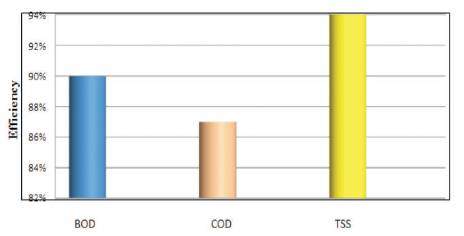
Figure 7. Overall Efficiency in Kodra Plant
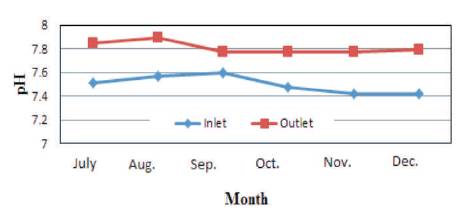
Figure 8. Variation of pH in Ponghat Plant

Figure 9. Variation of BOD in Ponghat Plant
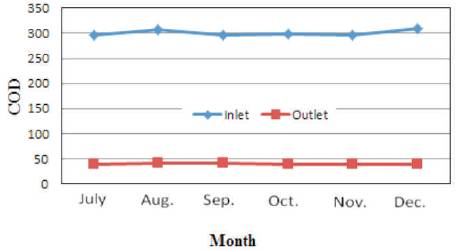
Figure 10. Variation of COD in Ponghat Plant
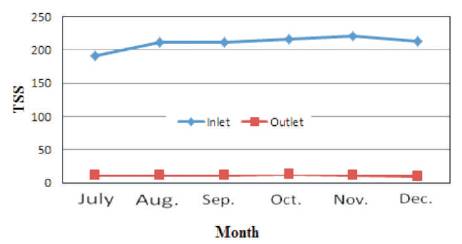
Figure 11. Variation of TSS in Ponghat Plant
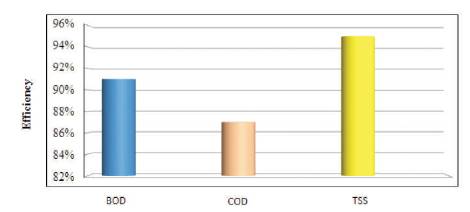
Figure 12. Overall Efficiency in Ponghat Plant