E-Governance with Cloud Computing
Abstract
Cloud computing offers services to the end users, or the consumers, in a convenient and on-demand fashion. This computing model has several other features which increase its dependency to an incomparable degree, such as resource pooling, pay-per-use (economic), scalability, rapid elasticity, security, and availability. This model allows big or small organizations to get started with the work and to focus primarily on the business modules without worrying about the underlying infrastructure setup costs, i.e., the cost of powerful servers, expensive network devices, etc. Cloud computing finds a very important utility in e-Governance, which allows government applications to offer uninterrupted services to its citizens. Cost-effective, scalable, and secure e-services are possible with the integration of cloud computing. This paper shows the importance of cloud computing in e-Governance.
Keywords :
- Cloud Computing,
- IaaS,
- PaaS,
- SaaS,
- e-Governance,
- Public Cloud,
- Private Cloud,
- Hybrid Cloud.
Introduction
Cloud computing is the computing service that offers services to its end users, or consumers, over the internet and treats every service as a resource from the user's perspective. Figure 1 shows the basic diagram of cloud computing. This revolutionary technology is currently utilized in several sectors of the industry, such as manufacturing industries, healthcare industries, entertainment industries, finance and banking industries, education industries, transportation industries, and many more Alouffi et al., 2021). Cloud computing enables new startups or organizations that cannot afford to set up personal data centers or infrastructure to run smoothly while focusing on the core of the businesses and outsourcing infrastructure and other overheads to the cloud service provider. This technology is also surrounded by various security threats and risks from the outside environment. Gartner's Seven cloud computing security risks can be summarized as follows,
- Privileged User Access: Consumers must have knowledge about the individuals who manage and handle the data.
- Regulatory Compliance and Audit: It is almost impossible to audit client data transparently as there is no consumer-side auditing facility available. Also, there is no trusted third-party auditory available.
- Data Location: This refers to data jurisdiction, as the location of the data centers of the cloud providers is not known to the consumer, whether they are in their own country data center or some other country data centers, as each country has different data regulatory policies.
- Data Segregation: Data at rest and data in motion both need to be encrypted due to security concerns. Encryption proves to be the only solution for this, but it itself is a complex process, and its effectiveness and the degree of security that it provides need to be proven to the consumer.
- Recovery: It states how much time is needed to recover the data in case of any emergency situation that may occur at the data centers (Recovery Time Objective). In addition, what percentage of data is recoverable in case of failure, i.e., the maximum data loss (Recovery Point Objective)?
- Investigative Support: As the data is completely under the control of service providers, there is no user data control.
- Long-Term Viability: What is the provision for the consumer to switch to a different service provider in case the consumer is not satisfied with the current provider? In cloud computing, there is vendor lock-in, making it difficult for consumers to switch providers.
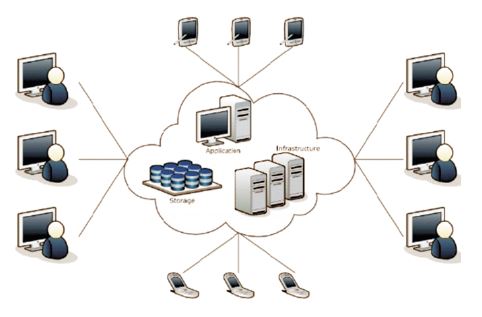
Figure 1. Basic Diagram for Cloud Computing
1. Essential Characteristics of Cloud Computing
Apart from characteristics such as virtualization, resilience, reduced cost offerings, and advanced security features, there also exist some essential characteristics that are briefly described as follows (Abdulsalam & Hedabou, 2022; Alouffi et al., 2021).
- On-demand Self-ser vice: A consumer can unilaterally provision computing capabilities, such as server time, storage, etc., as required automatically without human interaction by the service provider.
- Broad Network Access: Support is available over the network for accessing the offered services by the service providers using various types of thin or thick client platforms, for example, desktops, mobile devices, laptops, and tablets.
- Resource Pooling: Multiple consumers are served concurrently by the service provider via sharing the computing resources among the consumers, with different resources being dynamically assigned and reassigned according to consumer requirements.
- Measured Service: Utilization of the resources is monitored and controlled in order to provide transparency to both the consumer and the provider. The automatic optimization and control over resource use at some level of abstraction appropriate to the type of service, for example, processing, storage, and bandwidth are also taken care of by the cloud systems.
- Rapid Elasticity: Automatic scaling of the provisioned services and releasing them in case of nonuse with demand is also provided by the cloud computing paradigm, which appears as the unlimited availability of the services at any time from the user's perspective.
2. Cloud Computing Service Models
- infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): The capability provided to provision storage, networks, processing, and other fundamental computing resources to the end users. Examples of Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) are Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure, International Business Machines Corporation (IBM) SmartCloud, Google Compute Engine, Rackspace Open Cloud, etc. (George & Pramila, 2021).
- Platform as a Service (PaaS): The capability to deploy the applications that are built or created using services, programming languages, libraries as well as tools supported by the cloud service provider onto the cloud infrastructure. The end user does not have control over the underlying cloud infrastructure, such as servers, operating systems, networks, and storage, but has control over the deployed applications. Examples of Platform as a Service (PaaS) are Microsoft Azure, Amazon Web Services (AWS) Lambda, Heroku, Google App Engine, Salesforce Lightning, IBM Cloud Foundry, etc.
- Software as a Service (SaaS): The provision to consume the provider's applications running on a cloud infrastructure over the internet is termed "Software as a Service" (SaaS). The applications can be accessed via several client devices (Attaran & Woods, 2018;George & Pramila, 2021). End users do not have any control over the deployed application or the underlying cloud infrastructure, such as servers, storage, operating systems, networks, etc. Examples of SaaS are Zoom, Salesforce, Gmail, Slack, G Suite, HubSpot, Shopify, Netflix, etc. Figure 2 shows the shared responsibilities of IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS.
3. Cloud Deployment Models
- Public Cloud: General public is offered and is allowed to use the Public Cloud infrastructure. Business organizations, government organizations, or some combination of both of them are allowed to use or share this type of deployment model. The public cloud has potentially large computing as well as storage resources, which can be accessed over the public internet. Examples include Google App Engine, Microsoft Windows Azure, IBM Smart Cloud, Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2), etc.
- Private Cloud: The private cloud services or the infrastructure are provisioned for exclusive use by a single organization. This type of cloud deployment model is managed, owned, and operated by the concerned private organization and may exist on or off premises. Examples of private clouds include Eucalyptus, Ubuntu Enterprise Cloud (UEC), Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (VPC), Virtual Machine (VM) ware Cloud Infrastructure Suite, and Microsoft Einstein Conversations Insights (ECI) data centers.
- Community Cloud: Community Cloud infrastructure is provisioned for exclusive use by a specific community of consumers from organizations that have shared concerns, for example, mission, security requirements, policy, and compliance considerations. It may be owned, managed, and operated by one or more of the organizations in the community, a third party, or some combination of them, and it may exist on or off premises. Examples of community clouds include Google Apps for Government and Microsoft Government Community Cloud (Attaran & Woods, 2018; Dwivedi et al., 2019).
- Hybrid Cloud: The cloud infrastructure is a composition of two or more distinct cloud infrastructures (private, community, or public) that remain unique entities but are bound together by standardized or proprietary technology that enables data and application portability. Examples of hybrid clouds include Windows Azure (capable of hybrid clouds) and Virtual Machine (VM)ware vCloud.
4. e-Governance
The only way to provide efficient, transparent, and responsive government services to end users is via e- Governance. Almost all the applications of the government can be automated and reformed as applications that can be consumed over the internet, and higher productivity can be achieved. This can be made more productive as well as secure by adopting the cloud computing model for e-Governance applications. Applications such as income taxes, administration, pension services, logistics, road transportation services, insurance, banking, etc. are utilized as an e-Governance applications (Al-Rashedi, 2014). The three basic elements that comprise e-Governance are government, citizens, and investors. Increasing the number of applications for the government enhances the productivity of the government.
4.1 Types of e-Governance
Figure 3 shows the four different types of e-Governance models that exist as follows (Al-Rashedi, 2014; Belwal & Sharma, 2017).
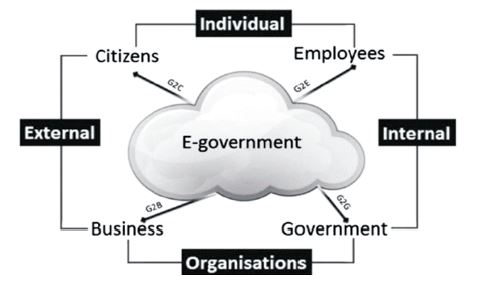
Figure 3. e-Governance Types
- Government to Government (G2G): The Government to Government (G2G) model involves the interaction, coordination, and collaboration of various government organizations. The organizations involved shared the same infrastructure, database, and other resources in order to fulfill the requirements. This also provides a smooth connection between global and domestic governments. This includes policy formation, administration services, etc.
- Government-to-Business (G2B): The interaction between business firms and the government is primarily addressed by the government-to-business e-Governance model. The B2B model allows access to critical information required to conduct business. All the business sectors require guidance from the government, such as the enforcement of new business laws and regulations, tenders for new government projects, submission of business deeds, new taxation policies, etc., for producing more productive businesses, which is only possible with the Government-to-Business (G2B) model.
- Government-to-Employee (G2E): The primar y objective of the Government-to-Employee (G2E) model is to unite the employees with the government. Services such as reviewing salary records, income tax, holiday counting, applying for a pension, applying for leave, etc. are offered to the employees through this model.
- Government-to-Citizen (G2C): Government-to- Citizen (G2C) includes the services offered by the government for the citizens of the country that can be availed by the citizens from anywhere and at any time. Information such as land records, birth certificates, payment of house tax, and enrollment for the voter card are provisioned by the Government-to- Citizen (G2C) model.
5. Cloud and e-Governance
Three service models supported by the cloud computing paradigm play an important role in the contribution to e- Governance (Tomson, 2016).
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): IaaS is responsible for provisioning the storage, networks, processing, and other fundamental computing resources to the end users. e-Governance applications demand 24x7 infrastructure availability in order to minimize and reduce service lag or delay, and thus they require unlimited utilization of the processing unit, bandwidth, and storage, which is only possible with the integration of the application with the IaaS model of cloud technology.
- Platform as a Service (PaaS): Cloud technology provides the support of various development platforms and frameworks for the development of required applications without the overhead of purchasing the licensed software versions or the frameworks. e-Governance application developers can just focus on the requirements of the application development by pooling the PaaS cloud resources (Belwal & Sharma, 2017; Tomson, 2016).
- Software as a Service (SaaS): The SaaS cloud model allows end users to consume the cloud-deployed application as a resource over the internet. Some of the SaaS-based e-Governance applications are e- Aadhar, e-FIR (First Information Report), e-Court, House Tax Payment System, Municipal Tax System, e- Compliant register portal, etc. (Tomson, 2016).
6. Challenges with e-Governance resolved by Cloud Computing
- Disaster Recovery: e-Governance with cloud computing eliminates the destruction of computing resources caused by the occurrence of natural disasters such as earthquakes, floods, etc.
- Auditing and Logging: Provision for auditing and logging are highly and periodically required in government-based applications, which can be applied in a secure as well as transparent way via the integration of cloud technology with the application.
- Data Scaling: The ability to scale with the increase in data is only possible with cloud technology. As the data is increasing exponentially the storage, as well as the processing of such volumetric data, is achieved by cloud technology.
- Enhanced Performance: The demands of the applications can be met by the resource pooling ability of cloud computing, such as vertical or horizontal scaling in cases of higher demand, so as to improve the overall performance.
- Green Technology: e-Governance with the cloud reduces the biohazards caused by electronic waste, air conditioners, and paper losses.
- New Technology Migration: The migration towards the new framework or technology is only possible with e-Governance in the cloud and without much overhead or application downtime.
Conclusion
This computing model has several features which increase its dependency to an incomparable degree, such as resource pooling, pay-per-use (economic), scalability, rapid elasticity, security, and availability. This model allows big or small organizations to get started with the work and to focus primarily on the business modules without worrying about the underlying infrastructure setup costs, i.e., the cost of powerful servers, expensive network devices, etc. The government must realize this importance and promote the continued development of e-Governance applications that can interconnect the government and its citizens by providing uninterrupted cloud-based services.
References
[1]. Abdulsalam, Y. S., & Hedabou, M. (2022). Security and privacy in cloud computing: technical review. Future Internet, 14(1), 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi14010011
[2]. Alouffi, B., Hasnain, M., Alharbi, A., Alosaimi, W., Alyami, H., & Ayaz, M. (2021). A systematic literature review on cloud computing security: Threats and mitigation strategies. IEEE Access, 9, 57792-57807. https://doi.org/ 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3073203
[3]. Al-Rashedi, A. A. (2014). E-government based on cloud computing and service-oriented architecture. International Journal of Computer and Electrical Engineering, 6(3), 201-206. https://doi.org/10.7763/IJCEE.2014.V6.822
[4]. Attaran, M., & Woods, J. (2018). Cloud computing technology: Improving small business performance using the Internet. Journal of Small Business & Entrepreneurship, 13(2), 94-106. http://doi.org/10.1080/08276331.2018.1466850
[5]. Belwal, H., & Sharma, A. (2017). Cloud computing for e-governance: Indian perspective. International Journal on Emerging Technologies (Special Issue NCETST-2017), 8(1), 619-622.
[6]. Dwivedi, R. K., Saran, M., & Kumar, R. (2019). A survey on security over sensor-cloud. In 2019 9th International Conference on Cloud Computing, Data Science & Engineering (Confluence) (pp. 31-37). IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/CONFLUENCE.2019.8776897
[7]. George, S. S., & Pramila, R. S. (2021). A review of different techniques in cloud computing. Materials Today: Proceedings, 46, 8002-8008. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2021.02.748
[8]. Tomson, N. K. (2016). Cloud computing for e-governance. International Journal of Engineering Research & Technology, 4(27), 1-11.


