Figure 1. V3 of Big Data
The volume of data usage is growing drastically day by day. Hence, it is not easy to maintain the data. In Big Data, huge amount of structured, semi-structured and unstructured data, produced daily by resources all over the world are stored in the computer. Mapreducing, a programming model, is used for implementing such large data sets. MapReduce program is used to collect data as per the request. To process the large volume of data, proper scheduling is used in order to achieve greater performance. Task scheduling plays a major role in Big Data cloud. Task scheduling contains a lot of rules to solve the problems of users and provides the quality of services to achieve the goal of that task to improve the resource utilization and turnaround time. Capacity and Delay Scheduling are used to improve the performance of the Big Data. This paper presents an overview of the Map-Reduce technique for shuffling and reducing the data and also the Capacity Scheduling and Delay Scheduling, for improving the reliability of the data.
Everyday 2.5 quintillion bytes of data are generated. Big Data generates value from the storage and processes very large quantities of digital information that cannot be analyzed with traditional computing techniques. The data comes from everywhere, i.e., from informationsensing mobile, aerial (remote sensing), software logs, cameras, microphones, Radio-Frequency Identification (RFID) readers, and networks mobiles, systems, sensors, etc [4] to gather the information about posts to social media sites, digital pictures and videos, purchase transaction records, and cell phone GPS (Global Positioning System) signals to name a few. This data is Big Data.
In Big Data, there is a large volume of data. For easy access of data, the Map Reduce technique and scheduling algorithms are used. Then map reducing is used to split, map, shuffle and reduce the data. The scheduling algorithms are used to access the data faster.
The Big Data is a collection of multiple heterogeneous mixes of structured, semi-structured and unstructured data. Big Data describes data sets. The data is very large, moves very fast, or doesn't fit the structures of database architecture [1] [8]. Fast- changing massive data is too difficult for conventional technologies, skills and infrastructure to address efficiently [2]. Besides, it is large and difficult, so that they are impractical to manage with traditional software tools. Specifically, Big Data relates to data creation, search, transfer, visualization and storage. It needs to store, process and analyze, and involves large amount of data retrieval and analysis that is remarkable in terms of volume, velocity, and variety.
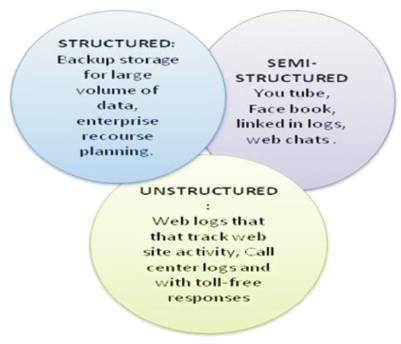
Big Data is not just a buzzword. It manages large volumes with 51% of structured data, 21% of unstructured data, 21% of semi-structured as shown in Figure 1. Big Data storage ranges from several tera bytes to peta bytes.

Figure 1. V3 of Big Data
Big Data is an important part of the $64 billion data base and data analytics [3]. Big Data is not a process for storing the data. It solves problems in better way; it takes decisions and performs actions at the right time.
Nowadays, technologies like Hadoop gives flexible storage of data [5]. Big Data being larger, requires different approaches – techniques, tools, and architectures. Big Data generates the storage and processing of very large quantities of digital and analog information that cannot be analyzed.
Big Data definition is categorized as follows:
Big Data: that mass of data that is everything in the universe which accumulates daily and is many bytes of data.
Dark Data: that data which is relevant to your company and business, but difficult to get to.
Black Data: this is combined dark data that provides actionable business relevant insights.
The Big Data has five main characteristics. They are as follows.
Volume describes the amount of data generated by organizations or individuals. Big Data is usually associated with this characteristic. Enterprises of all industries will need to find ways to handle the ever-increasing data volume that's being created every day.
Velocity describes the frequency at which data is generated, captured and shared. Recent developments suggest that not only consumers but also businesses generate more data in much shorter cycles. Due to the speed, enterprises can only capitalize on this data if it is captured and shared in real-time.
Big Data means much more than rows and columns. It means unstructured text, video, audio that can have important impacts on company decisions – if it's analyzed properly in time.
Variability describes the changes in structure or format of Big Data. It is the process of handling and managing the data effectively. Change in structure from the source data may not even be feasible with the horizontal scaling typically associated with Big Data architectures.
Veracity describes the truthfulness, accuracy, authentication, fidelity, faithfulness and realism of the data. Veracity is a challenge in combination with other Big Data characteristics, but is essential to the value associated with or developed from the data for a specific problem / application.
The Big Data sources include Social network profiles, Social influencers, Activity generated data, SaaS and cloud apps, Public web information, Map-Reduce results, Data warehouse appliances, NoSQL Databases, Network and in stream monitoring technologies and Legacy documents.
MapReduce [1] is a programming model, which simplifies the large program into small means and reduces the given problem. MapReduce is the new way of thinking. MapReduce programs are written in a particular style influenced by functional programming constructs, especially idioms for processing list of data [6]. MapReduce model supports parallel processing on distributed data using cluster of computers [8] [7]. It recovers from any failure. It is a mode and is like a machine, because it takes input, and the machine converts the input into related output efficiently and gives desired output.
MapReduce contains several sections, and each section performs set of operations to get the desired output by the Big Data [9]. The operation of MapReduce starts with the user request and runs until the results are back to the HDFS[R].
The MapReduce has two functions: Map ( ) and Reduce ( ) An example of MapReduce is shown in Figure 2.
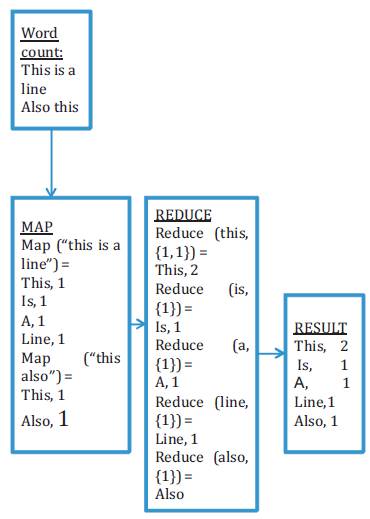
Figure 2. MapReduce Example
Map (): map is a function and that identifies the number of files, and splits them into intermediate files.
Reduce (): reduce is a function and that shuffles and filters or transforms the desired result.
Reduce has 3 phases namely: Shuffle, Sort, and Reduce
Task Scheduling plays a vital role in Map Reduce technique for improving the performance, reliability and scalability [16] [8]. The key technique is to run a large number of reduce tasks, splitting the map output into many more partitions than reduce machines in order to produce smaller tasks [15]. By assigning these tasks to the reduce machines, Task Scheduling reduces the work. Thus many small tasks can be easily run. Generally, the tasks are scheduled by user requirements. The tasks are completed within a given time using the resources and it satisfies the user requirement. In Big Data, resources are of many types i.e. cups, firewall etc [15]. The resources are dynamically allocated according to the sequence of problems, sub tasks and tasks as shown in Figure 3. There are many tasks to execute, after that the tasks share the time simultaneously. The scheduling of tasks in cloud means allocating the suitable resource for executing the tasks in such a way that the execution time is as minimized as possible.
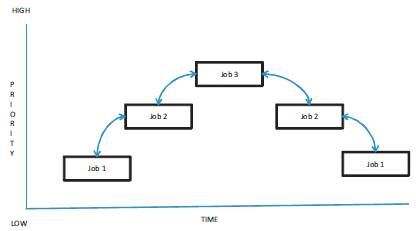
Figure 3. Task Priority
There are many task scheduling algorithms in Big Data of cloud. These algorithms are chosen by their requirement. In task scheduling algorithms, list of tasks are arranged by giving priority to each and every task. The users select the task scheduling algorithm according to their priority.
For example, in Figure 3, job1 is preempted by higherpriority task job2, which in turn is preempted by job3. When job3 completes, job2 continues executing. When job2 completes execution, job1 continues executing.
There are several types of task scheduling algorithms. They are
The Scheduling problems are raised by users and solved by data centers. The data centers typically consist of many physical machines and millions of tasks. These tasks are received by many users. The salvation of user scheduling problems is assigned to the physical machine[8]. The physical machine schedules the problems of users in data centers.
The Static Scheduling performs pre-fetching and pipelining of data for much different execution of tasks. Static scheduling imposes less runtime overhead, in case of dynamic scheduling information of the task and execution time is not known and the allocation of task [8] is not known before the execution.
In Static Scheduling the tasks are scheduled in known environment i.e. it already has the information about complete structure of tasks and mapping of resources before execution and then the execution/running time is estimated.
Dynamic Scheduling must depend not only on the tasks submitted to cloud environment but also on the current states of systems to make scheduling decision.
This method is also called approximation method. The optimization problems can be solved by enumeration method, heuristic method or approximation method. Optimal solutions are selected by enumeration method and all possible solutions are enumerated and compared one after the other. Enumeration process is usually fast. In this method, approximation algorithms are used for finding the optimized solutions from approximate solutions.
This method increases the throughput and minimizes the average response time of the problem in Big Data.
Initially, MapReduce used FIFO Scheduling but because of its low resource usage, Capacity Scheduling is preferred.
The Capacity Scheduler allows sharing the resources in a simpler manner as shown in Figure 4. The users share the clusters equally and performs fair sharing between all jobs [12] [11]. When an organization raises the number of Map-Reduce jobs continuously in the clusters then the best Scheduling method i.e. Capacity Scheduling is chosen [10]. The Capacity Scheduler is designed to share the clusters among the organization [12]. This provides elasticity for the organization in a cost effective manner. Queues are allocated as a fraction of capacity. The capacity of the resources will be distributed. Capacity Scheduler [10] contains a number of queues. Each and every queue allots map and reduce slots [8]. Each queue contains various jobs and it allots capacity to that queue. Every queue shares the capacity with other queues for a higher priority job [12]. It also provides security. There are safe-guards to ensure that users cannot view and/or modify jobs from other users if they so desire.
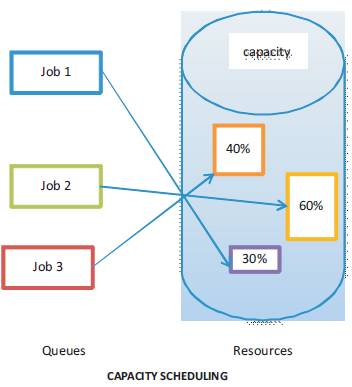
Figure 4. Capacity Scheduling
D-Scheduling means Delay Scheduling. In this, the data is stored in different locations. A task runs to access each data from multiple locations by searching, and if it is not found, then scheduler skips that task and searches for next job [3] [15]. In this method, two locality problems are identified. They are: head-of-line scheduling and sticky slots [14]. To overcome these problems, the Delay scheduling provides a solution by asking the job to wait temporarily for Scheduling opportunity on a node with local data, to improve the velocity of the Big Data. When a node requests a task and if the head-of-line job cannot launch a local task, then it is skipped and looks for other jobs to process, thus avoiding Starvation [3] [13].
Starvation: Starvation is a resource management problem where, a process does not get the resources it needs, for a long time, because the resources are being allocated to other processes.
The Big Data is the high volume of data base with velocity and veracity of data. In this paper, the authors have explained about the MapReduce technique for shuffling and reducing the data and also the Capacity Scheduling and Delay scheduling for improving the reliability of the data.