
Markov chain is a powerful technique employed to forecast the variations in the sharemarket, customer behaviour, marketing, customers' brand loyalty, weather, game of golf, weather report, gold rate, conversion of currency rate, etc. This study focuses on research discrete-time Markov chain. Some significant properties of Markov chains are evoked and then the research and knowledge gained on Markov chains is applied to predict Eid al-Fitr day for the succeeding years and also in the long run. The Eid al-Fitr day for each year depends only on the previous year Eid al-Fitr day and not on its previous years' Eid al-Fitr days. The authors have also justified is study that the application of Markov chain is an appropriate process in predicting Eid al-Fitr day in Oman.
A major Muslim festival in Oman is Eid al-Fitr, which is also known as Meethi Eid. It is a festival of breaking the fast and is celebrated across Oman on the first day of tenth month 'Shawwal' of the Islamic calendar (Drikpanchang).
The festivities of Ramzan began in the holy city of Medina after the migration of Mohammed Prophet from Mecca. He established that two holiest days for indulging in festivities have already been marked in the Quran by Almighty or Allah called Eid al-Adha and Edi al-Fitr, thus the tradition of celebrating Eid came into existence (Drikpanchang).
Ramzan largely signifies the breaking of fast and beginning the new month on a sweet note. During Ramzan, Muslims abstain from all kind of wordly pleasure and strictly follow teaching of Allah sanctifying their souls of vices and other impurities. Many Muslims read the Quran during the month of Ramzan and strive to establish a connection with Allah, thus Eid al-Fitr quintessentially a day of revelry and merriment after strict observance and abstinence. Muslims embrace their fellow humans that symbolizes accepting and loving everyone of whatever social strata and class one belongs to (Drikpanchang).
Oman's diversity will be on full display this Eid al-Fitr, as people across the Sultanate celebrate the biggest day of the year in their own traditional style. From prayer to special dishes and traditional dances, Eid in Oman differs from place to place, making every celebration unique.
In this study, the authors have implemented the technique of Markov chain. The Markov chain paradigm states that future behaviour depends only on the present state and not on the past. This method is used to predict future behavior movements from those of the recent past. They predict the Eid al-Fitr day for the succeeding years from 2019 and also in the long run by applying the technique of Markov chain.
In this section, the fundamental concepts involved in Markov chain are recalled, comparing with analysis or indicators regarding prediction of share market price by other methods.
A stochastic model describing a sequence of possible events in which the probability of each event depends only on the state attained in the previous event.
One of the interesting models of a random process is the Markov process (Markov model), where the value of the process depends only upon the most recent previous value and is independent of all values in the more distant past. Such a model is called a Markov model or Markov process.
Comparing to other methods, Markov process is an effective and powerful tool for prediction of share market since this process assumes probability values, which yields better predicted values.
Other indicators or analysis used to predict the future movements are as follows,
A random process is a collection of random variables {x(s, t)} that are functions of a real variable, namely time 't', where sϵS (sample space) and tϵT (Parameter set or index set) (Wang & Leu, 1996).
The set of possible values of any individual member of the random process is called state space (Wang & Leu, 1996).
1.2.1 Remark
As the dependence of a random process on 's' is obvious, 's' will be omitted in the notation of a random process. If the parameter set 'T' is discrete, the random process will be denoted by {X(n)} or {Xn}. If the parameter set 'T' is continuous, the process will be denoted by {X(t)}.
The Markov process is a random process in which the value of the process depends only on the most recent previous value and not on the more distant past values. Therefore, in a Markov process, the future value does not depend on the past values, but only on the present value.
A random process {X(t)} is said to be Markovian if

where t0≤t1≤t2≤....tn≤tn+1.
Here x0, x1, x2, ..., xn, xn+1 are called the states of the process. If the random process at time tn is in the state xn, the future state of the random process xn+1 at tn+1 depends only on the present state xn and not on the past states (Wang & Leu, 1996), Xn-1, xn-2, ..., x0
1.3.1 Example
The probability of raining today depends only on previous weather conditions existed for the last two days and not on past weather conditions is a Markovian process.
1.3.2 Example
A first order difference equation is Markovian.
1.3.3 Example
If Airplane departed now is of certain airline, then there is less probability of having next airplane from same airline. That means if we know the airplane departed then we can predict the probability of airplane from certain airline.
1.4 Definition
Let {X(t)} be a Markov process that possess Markov property and which takes only discrete values whether it is discrete or continuous. Then {X(t)} is called as Markov chain.
Mathematically, we define the Markov chain as follows:
If

for all n, then the process {Xn}; n=0,1,2,... is called as Markov chain. Here a0, a1, a2,..., an are called the states of the Markov chain (Wang & Leu, 1996).
The conditional probability P{Xn =aj | Xn-1 =ai} is called the one-step transition probability from state ai to state aj at the nth step (trial) and is denoted by (Wang & Leu, 1996), pij (n-1, n).
If pij (n-1, n) = pij (m-1, m), then the Markov chain is called the homogenous Markov chain or the chain is said to have stationary transition probabilities (Wang & Leu, 1996).
When the Markov chain is homogenous, the one-step transition probability is denoted by P. The matrix P={Pij} is called (one-step) Transition Probability Matrix (TPM) (Wang & Leu, 1996).
The conditional probability that the process is in state a at step n given that it was in state a at step 0. That is, P{Xn =aj|X0 =ai} is called the n-step transition probability and is denoted by (Wang & Leu, 1996), P = [Pijn].
1.8.1 Theorem (Chapman-Kolmogorov)
If P is the transition probability matrix of a homogenous Markov chain, then the n-step transition probability matrix P(n) is equal to Pn. That is (Wang & Leu, 1996), [Pij(n)] = [pijn] .
A stochastic matrix P is said to be a regular matrix, if all the entries of Pm (for some positive integer m) are positive. A homogenous Markov chain is said to be regular if its transition probability matrix is regular (Wang & Leu, 1996).
1.9.1 Theorem
If P = {Pij} is the state probability distribution of the process at an arbitrary time, then after one step is P . P, where P is the transition probability matrix of the chain and after that n steps is (Wang & Leu, 1996), P . Pn.
1.9.2 Theorem
If a homogenous Markov chain is regular, then every sequence of state probability distribution approaches a unique fixed probability distribution called the stationary (state) distribution or steady-state distribution of the Markov chain.
Moreover, if P is the transition probability matrix of the regular chain, then πP = π, where π is a row matrix. Using this property of π, the steady-state probability distribution can be found out (Wang & Leu, 1996).
In this study, the authors have collected the days of Eid al-Fitr for the years from 1970 to 2019 from the website (Drikpanchang). Using this data, by employing Markov chain technique, the Eid al-Fitr day for the succeeding years 2020 and 2021 are predicted. We can also extend this idea to predict Eid al-Fitr day in succeeding years after 2021.
They also compute the initial probability distribution, construct transition probability matrix, and predict the steady state probability value of the Eid al-Fitr day. Since there are seven days in a week, each day is considered as a state. The states are denoted by x1, x2, x3, x4, x5, x6, x7.
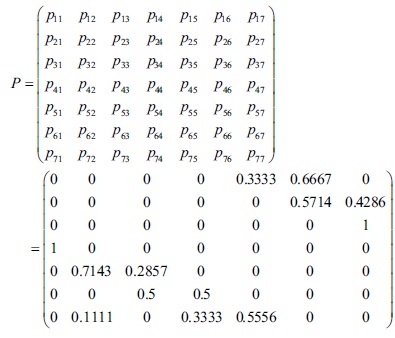
In the sequel, transition probability matrix has been constructed related to the raw data in Table 1.
In Table 1, there are Eid al-Fitr days of the last 50 years from 1970 to 2019, where Sunday x1= 6, Monday x2= 7, Tuesday x3 = 6, Wednesday x4= 7, Thursday x5 = 7, Friday x6 = 8, and Saturday x7 = 9 are the states of the Markov chain. Hence the probability of each state is calculated as follows:
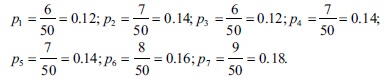
The probability P(0) = (0.12, 0.14, 0.12, 0.14, 0.14, 0.16, 0.18) is called initial probability distribution.
Since the number of state from Sunday to Sunday is 0, and the number of Eid al-Fitr festivals fall on Sundays before 2019 is 6 times, the corresponding transition probability is p1 1 = 0/6 =0. Similarly, we can obtain
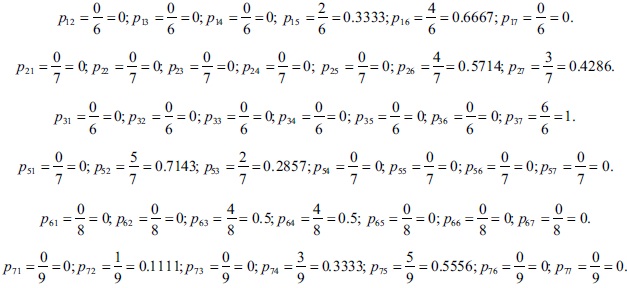
Since Eid al-Fitr falls on Wednesday on the last year of the data, the total number should be should be taken for Wednesday as 7-1=6. The transition probabilities for the state Wednesday are:
These state transition probability values are given in Table 2.
Table 2. The Transition Probability Matrix showing the Changes in Eid al-Fitr Days for the Years from 1970 to 2019
The following matrix is the transition probability matrix for predicting Eid al-Fitr day:
As per Table 1, Eid al-Fitr day for 2019 is Wednesday, it is regarded as the initial probability distribution as P(0) = (0 0 0 1 0 0 0). In lieu of the initial probability distribution and transition probability matrix, the probability of various closing date in the future can be predicted. The state probability of Eid al-Fitr for 2020 is calculated as:
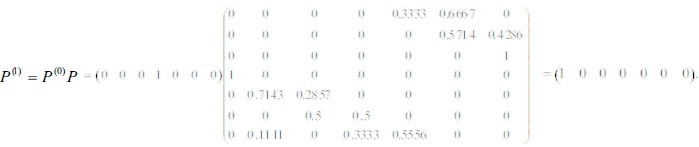
The above calculation implies that Eid al-Fitr day may fall on Sunday in 2020. Similarly, the state probability of Eid al-Fitr for 2021 can be computed as:
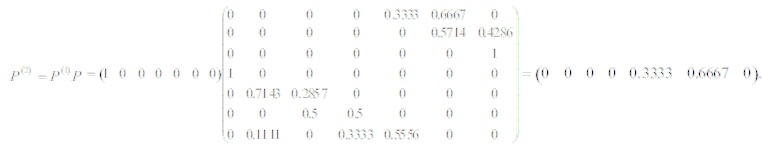
From the above computation, it can be concluded that Eid al-Fitr day may fall on Thursday (with probability 0.3333) or Friday (with probability 0.6667) in the year 2021. It means that probability that Eid al-Fitr falling on Friday is more when compared with Thursday. Now, let us consider p = (y1 y2 y3 y4 y5 y6 y7) be the steady state probability distribution such that y1 +y2 +...+y7 = 1. Then using the property πP = π, we have

which on further simplification yields y1 =0.1390; y2 =0.1214; y3 =0.1218; y4=0.1390; y5 =0.1429; y6 =0.1620; y7 =0.1739. From the above estimations, the authors predict that more chance for Eid al-Fitr festival to fall on Saturday in the long run.
Markov chain is one of the best effective methods for forecasting in many fields. The prediction of future behavior like stock market rate, currency rate, gold price, weather report, etc., could be achieved by the application of Markov Chain. This is the first attempt that the authors have employed Markov chain to predict Eid al-Fitr day in Oman. They have also checked the data of Eid al-Fitr days for the years from 1970 to 2018 to predict for the year 2019. The Eid al-Fitr day was obtained as exactly th on 5 June, 2019. In the similar way, they have accomplished the prediction of Eid al-Fitr days in the recent future for the years 2020 and 2021 and also in the long run (after so many years), considering the Eid al-Fitr day for the years from 1970 to 2019. From this study, it is concluded that in the long run, Eid al-Fitr day may fall on Saturday with more probability when compared with the probability of other days.