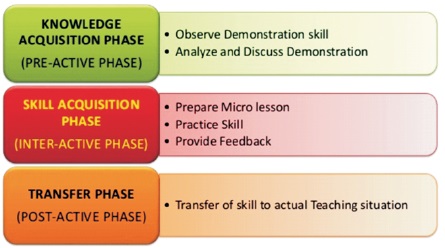
Figure 1. Phases of Microteaching (Vijayalakshmi, 2016)
Microteaching, as defined by Allen in 1969, in his book “Micro-Teaching-A Description” is a scaled down teaching approach in which a teacher teaches a small group of approximately 5 pupils for a small period of 5 to 20 minutes. This is helpful for an experienced or inexperienced teacher to acquire new teaching skills and to refine old ones. Ever since its introduction in 1961, it was practiced in classrooms. In the present era of the pandemic, when physical distancing and isolation is inevitable, how would it aid in improving teaching skills and the knowledge of the use of technology among novice or experienced teachers, and what skills of micro teaching must be focused on with prime importance, and what new skills, in addition to the existing ones, must be included to augment teaching skills and make it more effective? Would a simulated environment of teaching aid in the skills to be acquired and mastered by the student teachers, especially when it is conducted online. Now that societal and governmental norms are in practice with regard to the pandemic, a combination of microteaching and simulated teaching, rather a micro teaching in a simulated environment will have to be adopted for the mastery of skills and modification of teacher behavior for the student teachers. This article discusses about the possible skills that can be introduced, and the probable effects and consequences of micro teaching in a simulated environment online.
Teacher Training is mandatory for those seeking teaching as their career. In the course of attaining the Bachelor of Education Degree, a necessary training is that of microteaching. Microteaching by definition is a scaled down teaching approach in which a student teacher teaches a small group of students for a very short period of time and gets the feedback for the class based on which the class is re-taught making the necessary corrections and thereby mastering that particular skill which is aimed at (Allen, 1969). For the modification of teacher behavior, yet another technique called simulated teaching is accepted, both in India and abroad. It is a method adopted whereby skills to be acquired are practiced through role play.
Microteaching is what shapes a teacher trainee's behaviour and etiquettes and helps the individual to become a professional in the long run. It is a step by step approach taken by teacher training institutes whereby each teaching skill is focused at a time and perfection is attained. The complexity of a teaching situation can be overpowering, and to deal effectively with it is even a much more complex task. Teachers must not only possess a good knowledge of their respective subject, but also communication skills such as ability to observe, supervise, lead a discussion and pose questions in addition to various other skills like black board writing, voice modulation or stimulus variation, demonstration, reinforcement and so on. Besides, a teacher should be aware of how students observe him or her. This observation of a student is often quite different from the teacher's self-image. It is difficult to self-assess one's own abilities, rather we benefit from colleagues' feedback to recognize our strength and identify with the help of microteaching and discover areas for possible improvement. As a student teacher is observed by a small group of his/ her own classmates in a protected classroom, free from any serious reprimands by students, the student teacher feels more comfortable and can take the suggestions put forward by the small group of people around more positively rather than having their morale degraded when they receive the students' feedback in a real classroom situation. The student teachers are hence emotionally and psychologically protected in this respect. At the same time, observing another person keenly can aid in bringing selfimprovement.
There are various assumptions, according to Alan and Ryan (1969) based on which microteaching is practiced and executed for training the pre-service and in-service teachers.
Microteaching components include:
A combined action of all these components enable an effective shaping of a student teacher and expertise in the skills required for teaching.
Microteaching is structured in three phases (Figure 1) (Maheshwari, 2011).
It is also known as modeling phase. Student-teacher observes model teacher who presents the teaching behavior to be learned.
It is also known as practicing phase. Student-teachers are given opportunity in real classroom situations, but scaled down, to practice the same behavior or skill.
It is also known as feedback phase. Student-teachers are reinforced for those instances of desired behavior they have acquired and have provision for feed-back for developing the desired behavior or skill up to the mark.
After this, based on the comments the student teacher prepares the lesson once again with the necessary modifications suggested and re-presents the lesson for the next set of feedback. This cycle continues until perfection of a target skill is achieved Figure 2.

Figure 1. Phases of Microteaching (Vijayalakshmi, 2016)
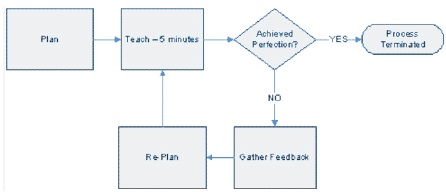
Figure 2. Microteaching Process (Maheshwari, 2011)
Simulated teaching is a teacher training technique which was developed by Cruickshank in 1968. It is denoted by several terms such as Role Playing, Artificial Teaching, Pilot Training, Laboratory method, Clinical method and inductive scientific method. Simulations build in the cooperative aspect of real-life teaching situations are how the teacher sets up his or her own well defined teaching situation and carries it through (Raser, 1969). When a teacher decides on a plan for a reading lesson, he or she is also making decisions that affect the tone of the lesson, the cognitive processes the students will engage in, the degree of active participation and involvement of the students, and in general, the manner in which he or she will teach the lesson. The teacher knowingly chooses a way or a combination of ways of teaching a lesson (Hyman, 1970).
The organization of simulated teaching involves 5 to 7 student-teachers who are to practice the required skill. One who teaches is called an Actor, two students assume the role of observers and the trainees who play the role of students are called Foils whose number varies from 2 to4.
Flanders(1970) recommends the following steps.
As per definition, Micro simulation (from micro analytic simulation) is a category of computerized analytical tools that perform highly detailed analysis of activities such as highway traffic flowing through an intersection, financial transactions, or pathogens spreading disease through a population. (Micro teaching, n.d., para 1). Micro simulation is used to estimate how demographic, behavioral, and policy changes might affect individual outcomes, and to better understand the effects of current policies. It is usually used in social sciences. It mimics the operation of various programs (governmental or demographic) on a micro level population then outcomes are extrapolated using computer program to assess the outcomes on large scale. Microsimulation can be of two types namely – static and dynamic. Dynamic micro simulation models can "age" the population measured by a survey many decades into the future by applying demographic and economic processes like births, deaths, marriage, divorces, employment, retirement, and so on-year by year, person by person; and can then run simulations on an aged population. Static models focus on the present, past, and near future; their strength lies in detailed simulations of government programs and their interactions.
Micro simulation has been used in various arenas of life like – medicine, traffic control and study (traffic micro simulation, pedestrian or crowd micro simulation), spatial micro simulation to study impacts of changes in environmental, economic, or policy conditions on a given population of individuals.
In education, as this paper focuses on, micro simulation, a combined technique of microteaching and simulated teaching may be used in mastering specific skills required for teaching. While microteaching aims at mastering specific skills required for teaching, creating a simulated environment for micro teaching can lead to bringing reality into the scene thereby providing a chance to practice and expertise in various skills. Now that physical presence of even a small group in a classroom is risky, the so called small group can gather in an online environment, view an online class by a prospective student-teacher, and the other members in the group can post their comments along with the teacher-educator. Various new skills also need to be introduced in such a situation which will be discussed further on in this paper.
In the present scenario where delivering instruction and getting education has become an online affair worldwide, approaches, techniques and methodologies like micro simulation must come into play to train the prospective student teachers. As usual a small 5 minute class might be prepared by a student teacher, and then delivered online realtime (synchronous mode) or in asynchronous mode. The other fellow class mates and teacher educator may view this and post their comments to the prospective student teacher and the necessary rectifications may be carried out. However, the difference lies in the types of skills that student teachers need to expertise. Traditionally, the various skills included (Vijayalakshmi, 2016).
These skills now with the introduction of micro simulation need to be restated. The following are a few skills that need to be focused.
The teacher also needs to learn how to look professional whatever be the setting the teacher is in (either at home or in a school classroom). Camera settings need to be mastered by the student teacher.
Eye contact of the teacher must be towards the camera such that the students feel that they are being observed.
Harassment of teachers may be expected in an online class. Teachers must be made ready to face by training, the harassment boldly in a composed and matured manner that might not degrade their demeanor or the institution they are associated with.
Students also might take this as a chance to play around with teachers, especially with the ones who are technically weak. Teachers must hence beware of that and take the necessary precautions.
Skill of time management and technological literacy- This includes the following points.
Skill of smooth flow of class – There can be many background issues (noise, people moving around, etc.) while a class is either being taken synchronously (real time) or being recorded in an asynchronous mode. The student - teacher must learn to deal with such issues and expertise in maintaining the continuity of the class by putting in fillers during the interruption.
When these skills are to be focused, some of the traditional skills like skill of black board writing, skill of questioning (if it's an asynchronous class), skill of reinforcement (in an asynchronous class), skill of stimulus variation may be forgone or replaced appropriately by some of the above mentioned skills.
As teaching learning process is taking a turn worldwide and moving to online mode, it becomes mandatory that teacher trainees should be prepared to face the technological challenges and learn to prepare online lessons and get equipped with technological literacy. By micro simulation, it is possible that teacher trainees attain the skills required for online teaching. The existing traditional skills of microteaching need to be redefined and new ones added and a few old ones forgone while preparing the teacher trainees for real life online teaching. By simulating the environment the prospective teachers get to learn the hidden issues (specially the technical errors and the problems associated with it).
The feedback from fellow students and the teacher educator helps student teachers recognize their weak points and may focus on improving that. Moreover neither the syllabus, nor schools and students suffer due to inexperience of a teacher. In addition, the student teachers notice their weaknesses in handling an online class and try to improve that (Sharma, 2015).
SimSchools, simulated classroom environment created with the help of computerized technology, are softwares that are available online and can be purchased by any individual or institution for using technology based simulation for teacher training. There is also simulation video technique that may be used to train student teachers. Special software concerning class simulation is designed entirely for the institution. By using such softwares, a student teacher gets the benefit to work with a wide diversity of virtual students, including special needs children. Hence it gives them a more understanding of the individual differences. Different strategies of teaching and learning may also be explored by the teacher trainees with the use of such softwares.
In a research conducted at the University Terbuka, Indonesia, online micro teaching program a questionnaire was administered in the Smart Teacher Portal with the aim of seeking teachers' opinions on the performance of micro teaching. Small scale, but in-depth, interviews were conducted to elucidate the in-service teachers' beliefs about the virtues of online micro teaching. The result showed that 82.68% of survey respondents agreed that online micro teaching improved their professional teaching. Most respondents interviewed admitted that they were more confident in their teaching after their involvement in the online micro teaching program. It was generally admitted that online micro teaching had strengthened their ability to develop more extensive critical thinking and reflective actions while practicing quality teaching (Kusmawan, 2017).
A knowledgeable teacher varies his or her ways of teaching to provide pupils with many ways of learning. If this is the case, microsimulation provides the inexperienced teacher with the opportunity of experiencing many ways of teaching and learning (Ruddell,1974).
In yet another study conducted by Casteel and Gregory (1975) an investigation was conducted to determine: (a) if pre-service teachers who have acquired and practiced complex teaching skills through micro simulation employ these skills when placed in a micro teaching situation, and (b) if these acquired skills are used functionally. Results of the investigation indicate that those subjects who participated in this study employed four moves they practiced in a micro simulation setting in a micro teaching situation. The practice moves include the following: (a) structuring moves, which provide a context within which discussion is to be focused; (b) conditional moves, involving a given premise and a following consequence; ( c ) wait-time moves, involving teacher utilization of silence; and (d) indicative moves. The results also indicated that teachers may acquire, practice, and learn to use a cluster of technical teaching skills functionally through micro simulations of teaching.
Weschke and Barclay (2011), investigated the impact of teachers who graduated from a fully online master's degree program with training in pedagogy and a contentspecialization in elementary reading and literacy (oERL) on reading achievement in a large urban public school system in the northwestern United States. Their research results support the view that a fully online program aimed at training teachers can provide opportunities for those teachers to obtain the pedagogical content knowledge that can positively influence instructional effectiveness.
In the study conducted by Frazer et al., (2017), online education programs in nursing were studied and it was observed that such mode of education was increasing rapidly. Faculty need to be competent in their role and possess the skills necessary to positively impact student outcomes. Teaching effectiveness, indicators of quality, and student success were three categories that emerged from the analysis of data. What materialized from the analysis was an over arching concept of a dance, a process that best describes the fluid nature of what constitutes good teaching practices in an online environment. Effective online teachers facilitate, connect, lead, and work in synchrony with students to obtain indicators of quality such as student success, student improvement over time, and student application of knowledge to the professional role. This study adds to the body of evidence supporting best teaching practices for online instruction.
These research results themselves lead us to the supposition that micro simulation is a possible method that may be adopted for a better training to be provided for the pre-service and in-service teachers to enhance their capabilities especially in the pandemic striken era where all are forcefully confined to their homes for safety.
Even though micro simulation by theory might seem beneficial to train prospective teachers, there are some detriments to it. The primary one being the focus of training might switch to technical and specializing in those aspects, rather than giving importance to the content being taught. The teaching learning process hence tends to become more technical than content oriented.
Various skills that a teacher needs to focus on, specially the skill of blackboard writing, skill of reinforcement and the skill classroom management, which is very essential for a teacher to practice will go unnoticed, unpracticed and might in the long run prove to be an inefficiency of the teacher.
The modern classes which ought to be activity oriented will lose its significance in the case of online sessions as most often students might not get a chance to have hands on experience in physics or chemistry classes to have a real experience of the experiments and activities being discussed. More of a demonstration lesson will be what they receive from the teacher's end.
Realtime (synchronous) teaching might not always be possible and affordable to all. Double the amount of time is required for the preparation and uploading of the lessons thus increasing the workload of the teacher educators as well as the student teachers.
With all these arguments in light, the effectiveness of a real classroom situation can possibly in no way match the effectiveness an online micro simulation class provides for practicing various microteaching skills. For online sessions to be effective, learners must be intrinsically motivated, disciplined, self-directed, and be good at time management. However, in situation such as these like the pandemic or any other such unforeseeable and abrupt situations that may crop up and disrupt the routine that once existed and that the people at the providing and receiving end of education are used to, micro simulation will come to aid and perhaps enable effective and smooth flow of the course. Effectiveness of any system depends on how the users take advantage of the available resources and make it effective for their own personal development. We are yet to reach a conclusion about that. However, modifications as suggested may be brought in the micro teaching skills and optimistically in the long run be effective for influencing teachers. We can conclude that simulation activity is a valuable teaching experience for the simulation teacher (Mayes, 1976). In addition, it provides the other pre-service or in service teachers in the group the opportunity to critique the teaching they have experienced in the student role. By giving teachers the opportunity to discuss their first hand experiences as teachers and students, the group leader builds an awareness of the concomitants of a variety of teaching patterns experience awareness, and book knowledge are linked together in the teaching program based on micro simulation.
The number of online education programs will possibly continue to grow and expand in the near future. To put up with this expansion and growth, there will be a need for instructors who demonstrate teaching effectiveness in an online environment. A few recommendations to enhance instructor knowledge of teaching effectiveness are receiving guidance by faculty mentors, feedback from student and peer evaluations, sharing of best practices among faculty in established e-college (online) communities or forums, and orientation programs for instructors transitioning into an online role.